全站搜索
ابحث في الموقع الإلكتروني بالكامل
ابحث في الموقع الإلكتروني بالكامل
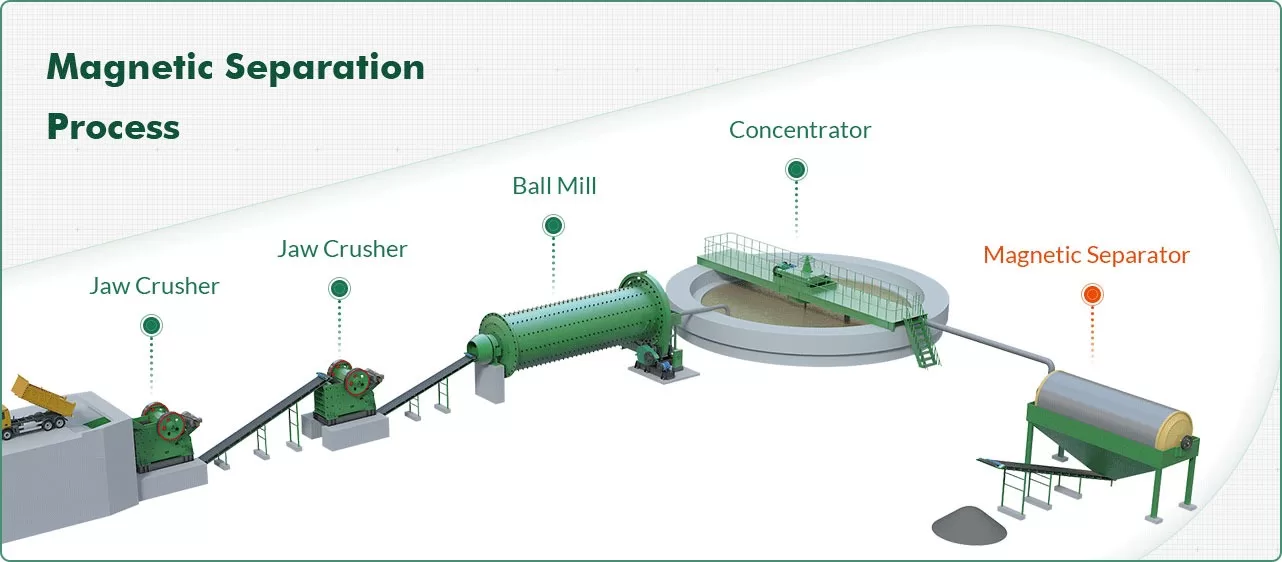
Magnetic separators are key equipment in the mineral processing and recycling industry and are widely used to separate magnetic minerals from non-magnetic minerals.
In mineral processing, a magnetic drum separator, also known as a drum magnet, separates non-magnetic material from magnetic material by using magnetic differences.
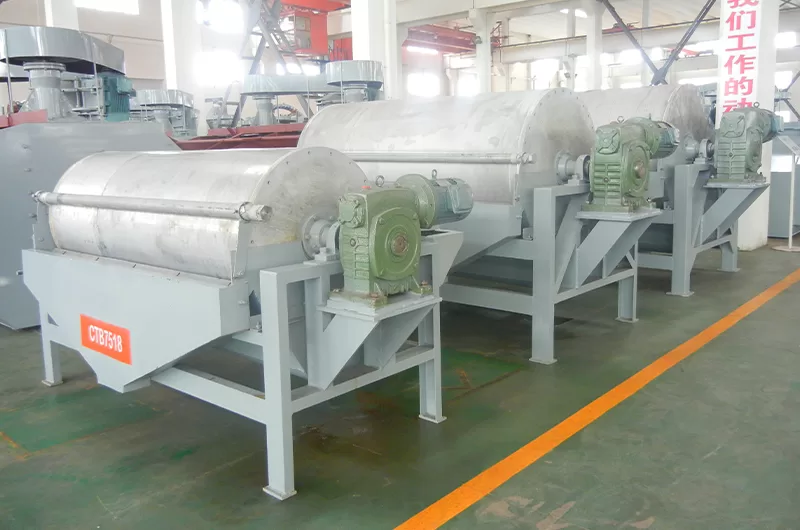
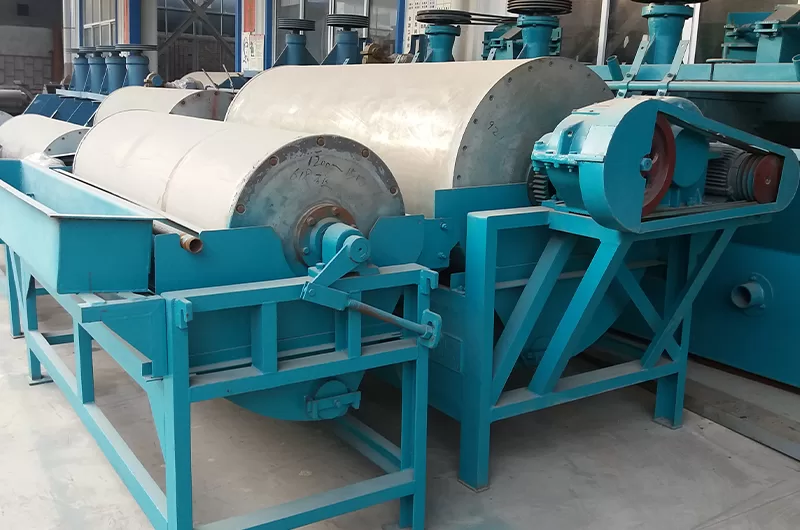


Magnetic separators are divided into dry magnetic separators and wet magnetic separators.
A dry magnetic separator, as the name suggests, operates without the use of water or a liquid medium.
The dry feed with a particle size less than 3mm is fed onto the rotating drum, where magnetic particles adhere to the drum’s surface. Non-magnetic particles are unaffected by the magnetic field and fall off the drum due to gravity or other forces. The separated magnetic particles are carried to a discharge point and released or brushed off the drum.
Dry magnetic drum separators use magnetic field strength, gradient, gravity, and other forces to separate and transport particles without the need for water or a liquid medium.
A model of dry drum magnetic separator includes a rare earth roll (RE Roll), which is a high-intensity magnet capable of separating strong and weak magnetic materials from non-magnetic material in a dry state.
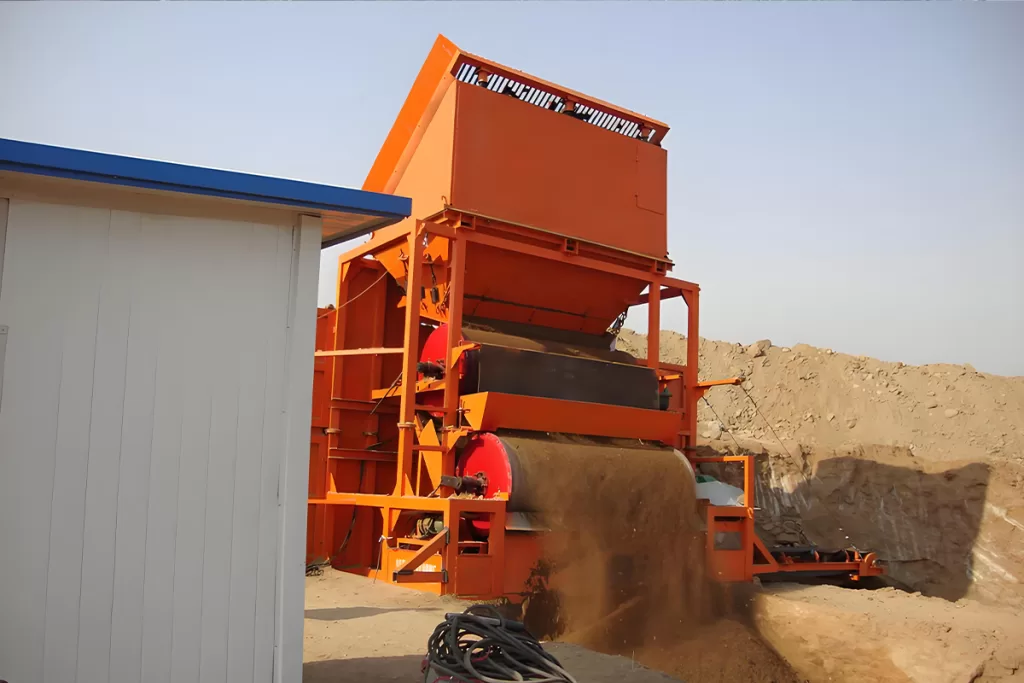

Advantages of the dry magnetic separators
1.No water requirement: Dry magnetic drum separators operate without a liquid medium, making them convenient and cost-effective. They are particularly advantageous in situations with limited water availability or a focus on water conservation.
2.Versatility: By adjusting magnetic field strength, drum speed, and other parameters, dry magnetic separators can process various minerals including iron ore, chromite, garnet, tantalite, and other magnetic minerals.
3.Easy maintenance: Dry high intensity magnetic separators generally have simpler designs and fewer components compared to wet separators, resulting in easier maintenance and lower maintenance costs.
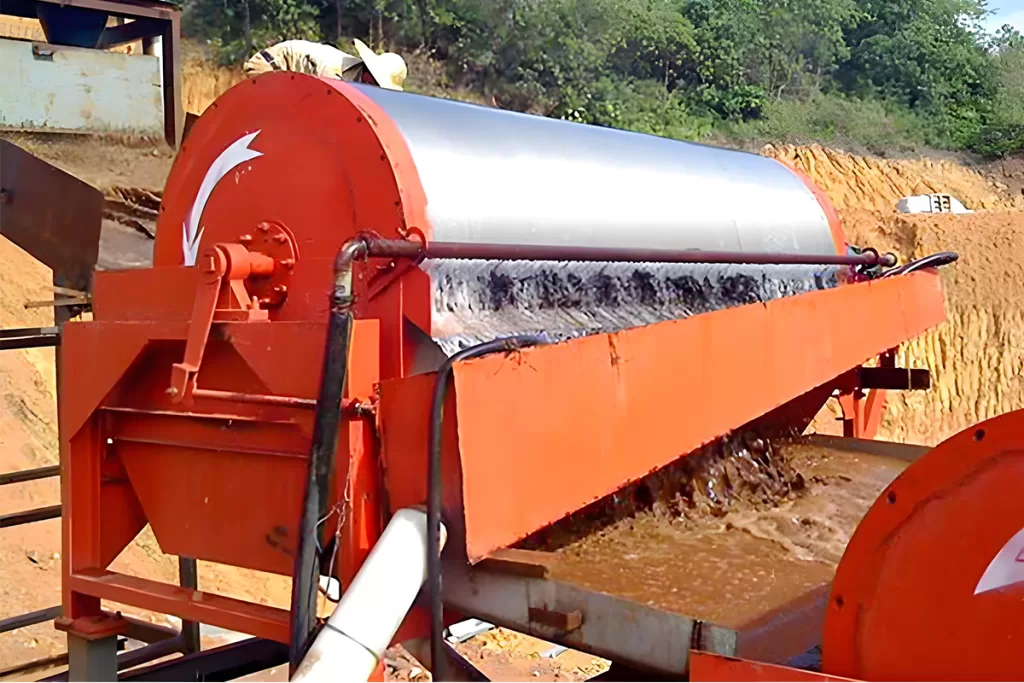

A wet magnetic separator operates in the presence of water or a liquid medium.
he feed material is mixed with water and fed onto the rotating drum. Magnetic particles stick to the drum’s surface as it rotates, while non-magnetic particles fall off due to gravity or other forces. Magnetic particles are eventually released or flushed off at the discharge point.
The presence of water or liquid medium in the wet magnetic drum separator facilitates the movement and separation of the magnetic and non-magnetic particles. It also aids in the transportation of the separated magnetic particles to the discharge point.
The permanent magnetic drum wet separator is suitable for the ores like magnetic pyrite, roasted ore, ilmenite, and other materials with a particle size of less than 3mm.

Magnetic Separators typically consist of a magnetic drum, transmission system, tank, feeding device, and discharge device. The magnetic drum, a crucial component, is equipped with high-performance permanent magnets or electromagnets that generate a powerful magnetic field. The tank holds the pulp, while the feeding device evenly distributes the pulp into the magnetic separator. The discharge device is responsible for removing the separated minerals.
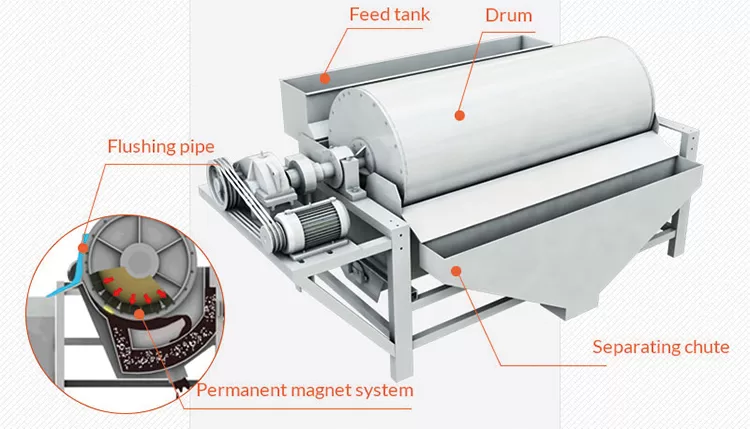
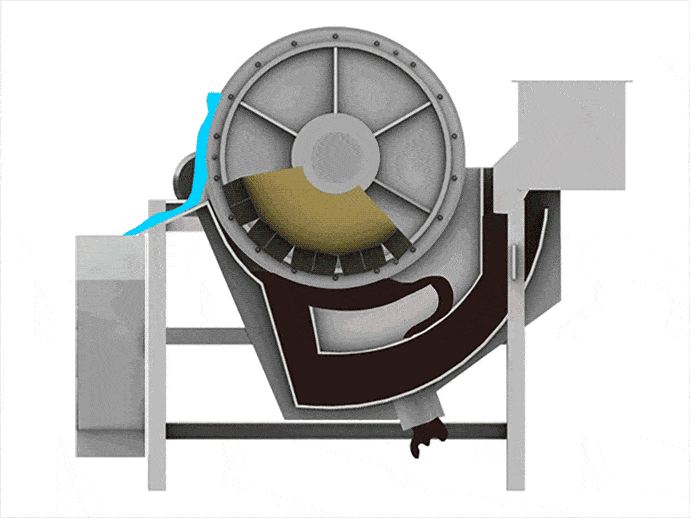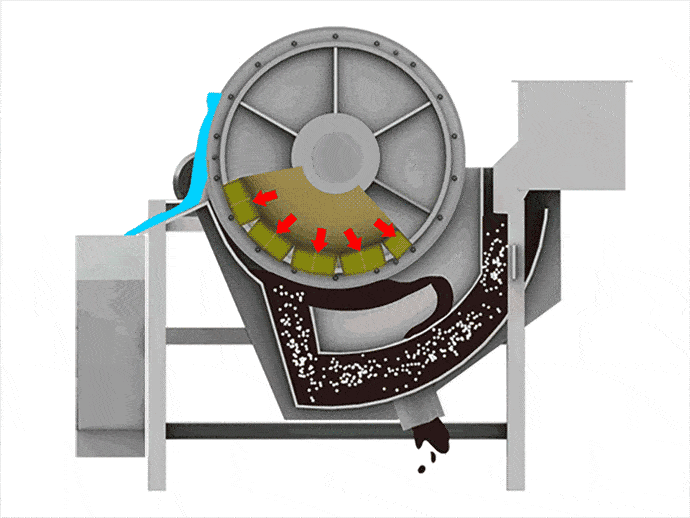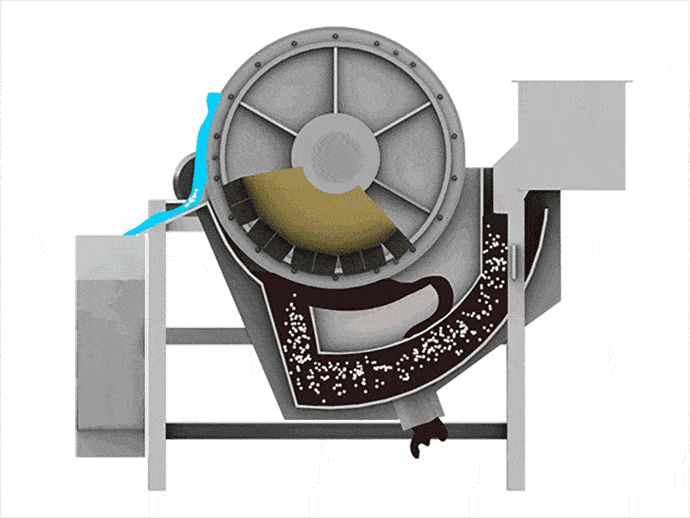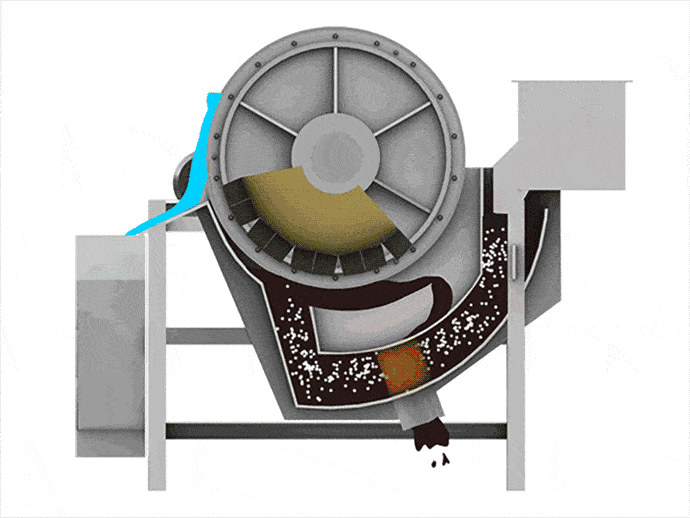
When materials go through the permanent magnetic drum, the magnetic particles are absorbed to the drum surface and discharged through the magnetic product area. Meanwhile, the non-magnetic particles are ejected from the drum surface under the influence of the centrifugal force and gravitation and discharged through the non-magnetic product area.
1. Magnetic drum separator adopts the multi-magnetic pole arrangement with short distances between poles in the internal magnetic system, which can increase the stirring of the magnetic particles and remove the gangues from minerals.
2. 180° broad-angle magnetic system can effectively prolong the separation area, and improve the recovery of iron ores.
3. Wear-resistant ceramics are stuck on the drum surface, the hardness HRA is ≥85, maximum HRA92 over
4. Simple material distribution device, which can conveniently control the grade of the concentrate and the tailing.
| الطراز | Shell diameter (mm) | Shell lenght (mm) | Shell rotation speed(r/min) | Feeding size (mm) | Processing capacoty (t/h) | Power(kw) |
| CTB6012 | 600 | 1200 | 2-0 | 10-20 | 1.5 | |
| CTB6018 | 600 | 1800 | 2-0 | 15-30 | 2.2 | |
| CTB7518 | 750 | 1800 | 2-0 | 20-45 | 2.2 | |
| CTB9018 | 900 | 1800 | 3-0 | 40-60 | 3 | |
| CTB9021 | 900 | 2100 | 3-0 | 45-60 | 3 | |
| CTB9024 | 900 | 2400 | 3-0 | 45-70 | 4 | |
| CTB1018 | 1050 | 1800 | 3-0 | 50-75 | 5.5 | |
| CTB1021 | 1050 | 2100 | 3-0 | 50-100 | 5.5 | |
| CTB1024 | 1050 | 2400 | 3-0 | 60-120 | 5.5 | |
| CTB1218 | 1200 | 1800 | 3-0 | 80-140 | 5.5 | |
| CTB1224 | 1200 | 2400 | 3-0 | 85-180 | 7.5 | |
| CTB1230 | 1200 | 3000 | 3-0 | 100-180 | 7.5 | |
| CTB1530 | 1500 | 3000 | 3-0 | 170-280 | 11 |



الإجابة: تشمل العوامل الرئيسية التي تؤثر على الفصل حركة الطاولة (الشوط والتردد)، وحجم الماء وانحداره، ومعدل التغذية وتركيزها، وحجم جسيمات مادة التغذية وشكلها. الضبط المناسب لهذه العوامل أمر بالغ الأهمية للفصل الفعال. يجب التحكم في المنحدرات الطولية والعرضية للطاولة بدقة. يجب أن يكون تركيز التغذية مناسبًا أيضًا، عادةً 20-30% للمعادن الخشنة و15-25% للمعادن الدقيقة.
الإجابة: يتضمن التشغيل مراقبة سطح السرير وضبط المنحدر وتدفق المياه ومعدل التغذية. تتضمن الصيانة الدورية فحص الأجزاء المفكوكة، وتشحيم المكونات المتحركة، وفحص التآكل، وتنظيف سطح الطاولة. يجب إجراء الصيانة الوقائية بانتظام، على فترات تتراوح من كل شهر إلى مرة واحدة في السنة.
الإجابة: يمكن أن تشمل المشكلات الشائعة اهتزاز الطاولة أو القطع المتقطع، أو التوزيع غير المتساوي للمواد، أو سوء الفصل. قد يتضمن استكشاف الأعطال وإصلاحها التحقق من وجود براغي مفكوكة، أو نوابض تالفة، أو اختلال المحاذاة، وضبط شد السير، وفحص المكونات الكهربائية، والتأكد من التشحيم المناسب. إذا كان هناك ضوضاء غير عادية، فحدد المصدر وقم بإزالة المشكلة.
الإجابة:
المزايا: توفر طاولات الاهتزاز نسب تخصيب عالية، وهي سهلة التشغيل نسبيًا، وتنتج مناطق فصل مرئية، مما يسمح بسهولة التعديل والمراقبة. وهي مناسبة لمجموعة واسعة من أحجام الجسيمات وكثافاتها.
العيوب: وعادةً ما تكون قدرتها الإنتاجية أقل مقارنةً ببعض الطرق الأخرى مثل الرقصات أو الحلزونات. كما أنها تتطلب مساحة كبيرة نسبيًا وتستهلك كمية كبيرة من المياه.
الإجابة: يعتمد الاختيار على المواد التي تتم معالجتها، والإنتاجية المطلوبة، ونطاق حجم الجسيمات. وتشمل العوامل التي يجب مراعاتها مساحة السطح، وطول الشوط، وتصميم المنحدر. يوصى بالتشاور مع الشركة المصنعة أو الخبير لتحديد التكوين الأمثل.
