全站搜索
Buscar en todo el sitio web
Buscar en todo el sitio web
The vibration feeder can evenly feed materials for the crushing equipment in the sand production line, and screen materials roughly. It can also serve materials for belt conveyors, bucket elevator, screening equipment, crushing equipment and grinding machines.
Vibrating feeder, also known as vibration feeder, is a kind of feeding equipment with advanced economic and technical indexes. The vibratory feeder can uniformly, regularly and continuously convey lumpy and granular materials from silo to receiving device, which is the ideal equipment for continuously and uniformly feeding materials for stone crushing machinery in sand and gravel production line, and linear vibratory feeder can roughly screen the materials.
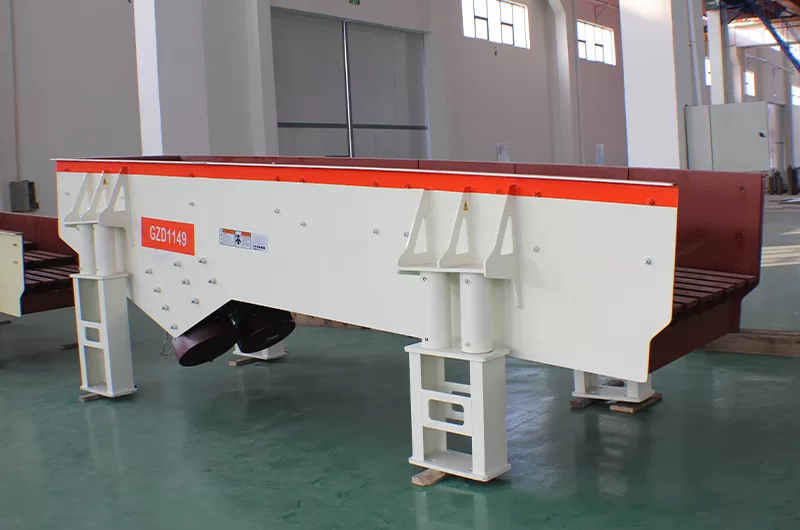
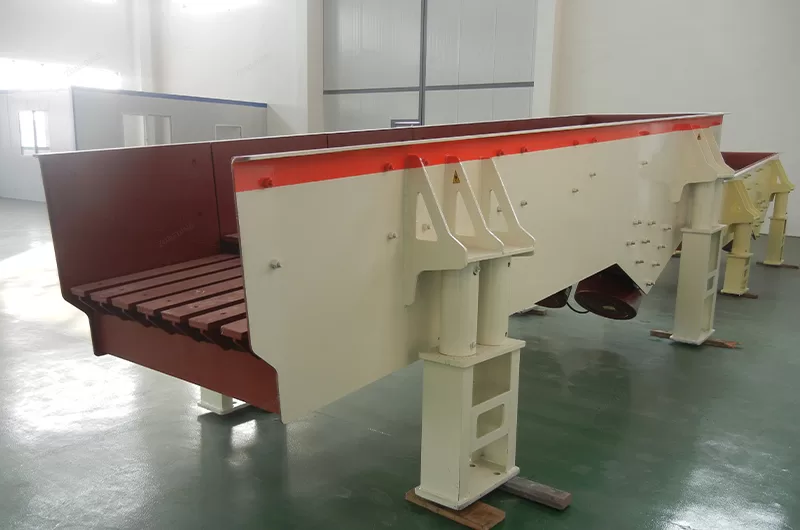



Mining vibrating feeder has a very wide range of use, mainly used in mining, metallurgy, coal, building materials, chemical industry, electric power and other industries.
• In the mining industry, the linear vibrating feeder is used to convey raw ore from the excavation site to the crusher or screening equipment. Its efficient vibration mechanism can effectively separate and convey ores of various particle sizes and improve production efficiency.
• In the metallurgical industry, the vibrating screen feeder is used to feed lumpy, granular and powdery materials uniformly, continuously or quantitatively from storage silos or other storage equipment to the receiving equipment, in order to meet the needs of automatic batching, quantitative packaging and automatic control.
• In the coal industry, vibratory table feeder can be used to evenly transport coal from the silo to the crusher or screening equipment to improve the efficiency of coal processing.
• Mining vibrating feeder is also widely used in building materials, chemical industry, electric power and other industries for conveying and processing various materials.

The working principle of the vibrating feeder is mainly to use the eccentric block in the vibrator to rotate to produce centrifugal force, so that the movable parts of the screen compartment and vibrator make a forced and continuous circular or nearly circular motion. This movement is transmitted to the conveying trough connected to the vibrating motor, so that the material is subjected to vibration force in the trough, thus generating sliding and dislodging, and realizing the uniform and continuous conveying of materials.
Specifically, when the vibrating feeder works, the motor drives the main shaft through the triangle belt, and then drives the follower shaft to rotate through the meshing of gears. The rotation of the main shaft and the driven shaft causes the eccentric block to generate centrifugal force that varies periodically, and this centrifugal force acts on the screen compartments and the vibrator, making them do continuous circular or nearly circular vibration. This vibration is transmitted to the conveying trough, so that the material in the trough is subject to the action of the vibration force and jumping and sliding, along the direction of the conveying trough, and ultimately realize the uniformity of the material, continuous or quantitative conveying.
In addition, the mining vibrating feeder can also be adjusted by adjusting the phase and weight of the eccentric block to change the size and direction of the excitation force, so as to adapt to the changes in different materials and process requirements. This kind of adjustment is flexible and convenient, and can realize precise feeding control.
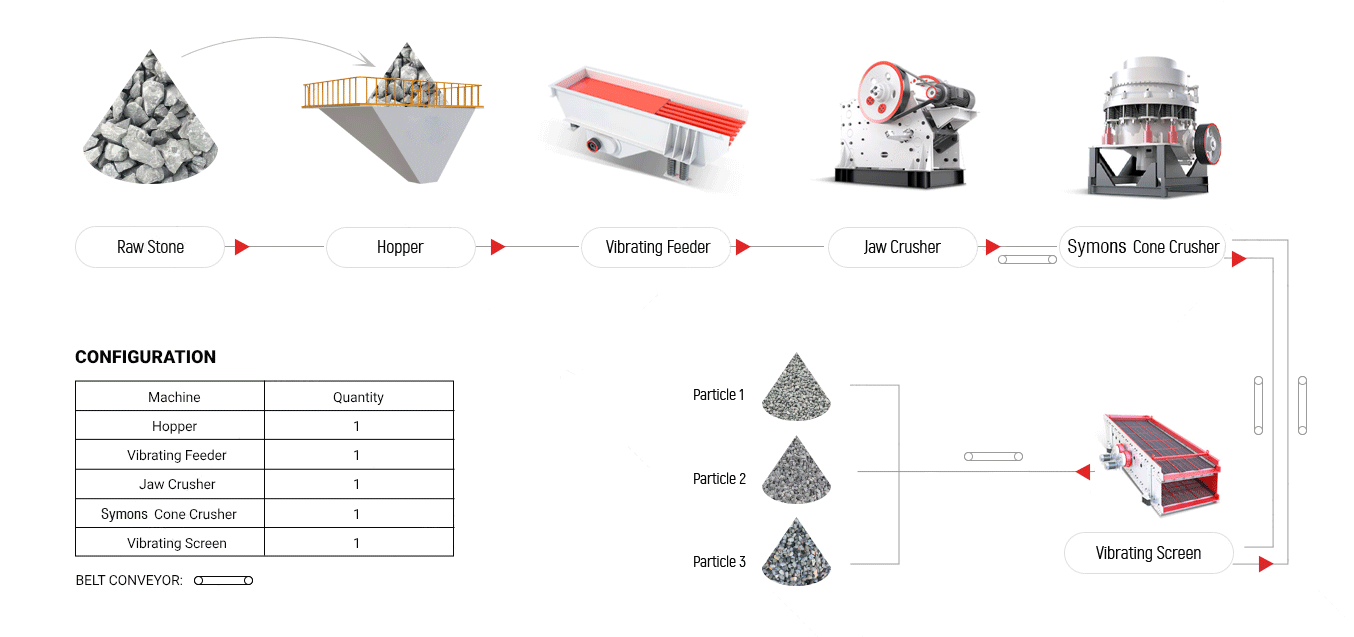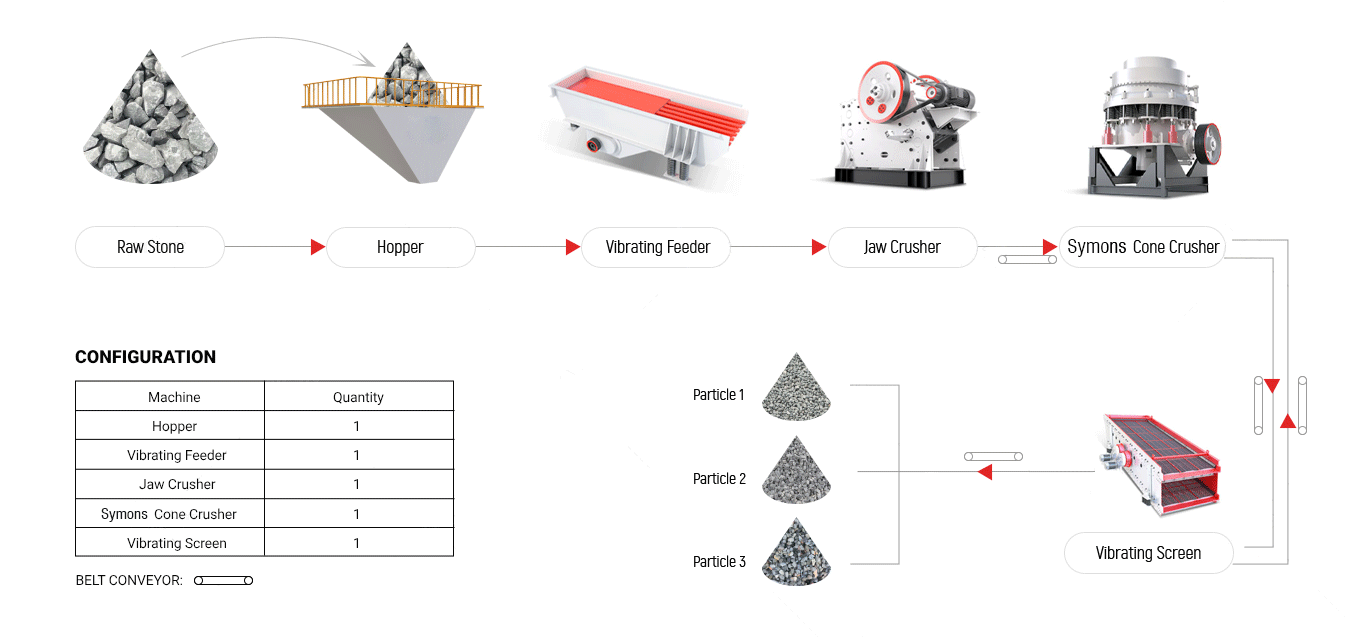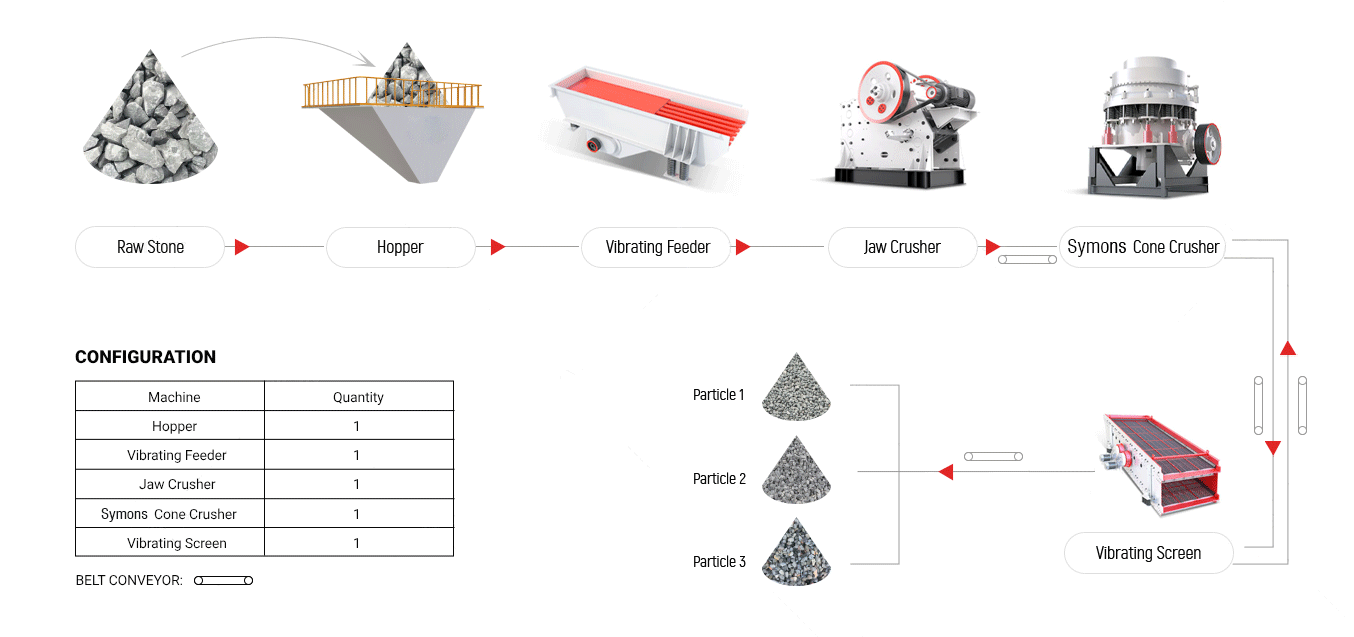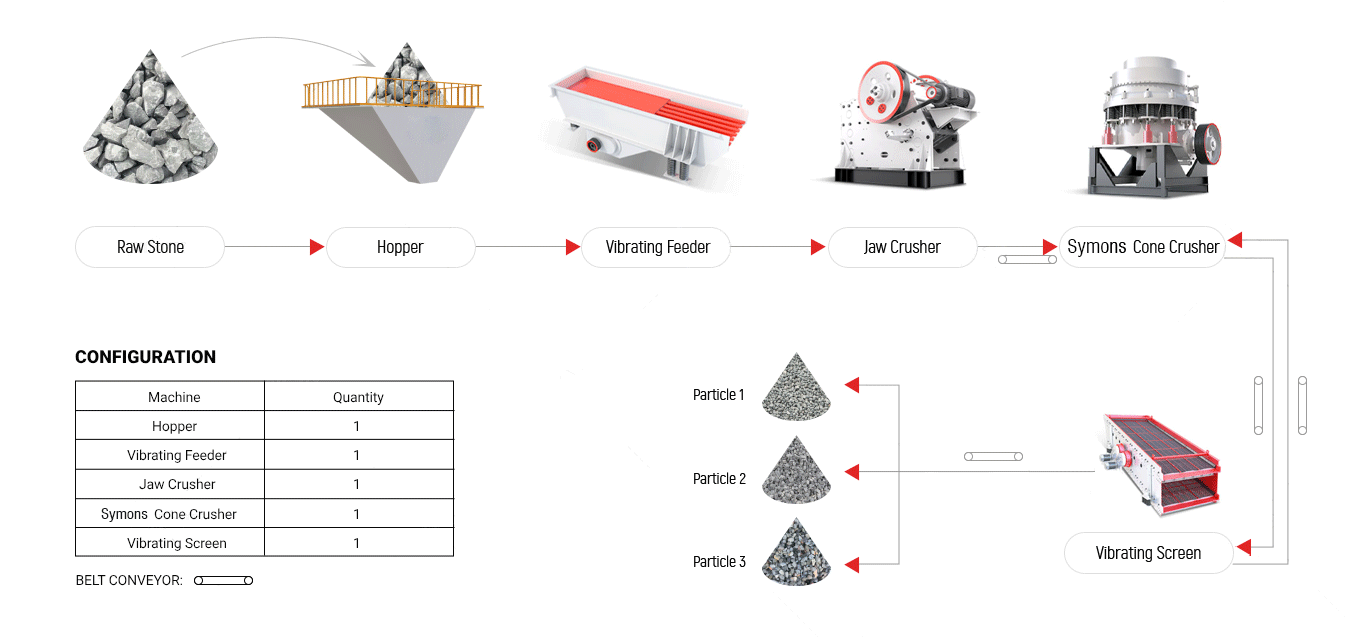
| Modelo | Max.Feeding Size(mm) | Processing Capacity(t/h) | MotorPower(kw) | Obliquityof materialtrough(°) | Troughsize(mm) | Dimensions(mm) |
| GZD-650×2300 | 300 | 80-100 | 1.2×2 | 10-20 | 650×2300 | 2300×1360×780 |
| GZD-750×2500 | 350 | 100-130 | 1.5×2 | 10-20 | 750×2500 | 2500×1460×780 |
| GZD-850×3000 | 400 | 120-150 | 3×2 | 10-20 | 850×3000 | 3110×1800×1600 |
| GZD-1000×3600 | 500 | 150-200 | 3.7×2 | 10-20 | 1000×3600 | 3850×1950×1630 |
| GZD-1100×3600 | 580 | 240-300 | 3.7×2 | 10-20 | 1100×3600 | 3600×2050×1660 |
| GZD-1300×3600 | 650 | 450-600 | 7.5×2 | 10-20 | 1300×3600 | 3900×2350×1750 |
| GZD-1500×3600 | 1050 | 450-1000 | 7.5×2 | 10-20 | 1500×3600 | 3900×2000×1750 |
| GZD-2000×3600 | 1200 | 550-1000 | 10×2 | 10-20 | 2000×3600 | 3600×2000×1750 |
| GZD-2500×5000 | 1500 | 650-1500 | 18×2 | 10-20 | 2500×5000 | 5000×2500×1800 |
| ZSW-380×95 | 500 | 100-180 | 11 | 0-10 | 3800×960 | 3920×1640×1320 |
| ZSW-490×110 | 630 | 150-400 | 15 | 0-10 | 4900×1100 | 4980×1830×1320 |
| ZSW-490×130 | 750 | 400-700 | 22 | 0-10 | 4900×1300 | 4980×2580×2083 |
| ZSW-600×130 | 750 | 400-700 | 22 | 0-10 | 6000×1300 | 6082×2580×2083 |
| ZSW-600×150 | 800 | 500-900 | 30 | 0-10 | 6000×1300 | 6086×2662×1912 |
| ZSW-600×180 | 900 | 700-1300 | 45 | 0-10 | 6000×1500 | 6310×3262×2230 |
| ZSW-600×200 | 1200 | 800-1500 | 55 | 0-10 | 6000×2000 | 6310×3462×2230 |



La selección depende de las características del material (tamaño máximo de alimentación, dureza, abrasividad), el rendimiento requerido (tph), el tamaño de salida deseado (CSS), la potencia del motor disponible y el presupuesto. Un análisis minucioso garantiza un rendimiento óptimo y rentable.
Una instalación correcta requiere una base sólida y nivelada y una alineación precisa. Un funcionamiento correcto implica comprobaciones previas minuciosas, una puesta en marcha en vacío, una alimentación uniforme controlada, evitar la sobrecarga/ahogo y seguir la secuencia de parada adecuada.
Las comprobaciones diarias incluyen la fijación, la lubricación y la inspección visual de las piezas de desgaste. El mantenimiento regular implica inspecciones más profundas y la revisión de los componentes. Prolongue considerablemente la vida útil de las placas de las mandíbulas mediante una selección adecuada del material, una alimentación uniforme, un cribado previo y una rotación o volteo estratégicos de las placas.
Entre las averías más comunes se encuentran las paradas repentinas (ahogamiento), la reducción del rendimiento, los problemas con las placas de mordazas, el sobrecalentamiento de los cojinetes, las vibraciones excesivas y la rotura de las placas basculantes. La localización de averías implica identificar sistemáticamente causas como bloqueos, desgaste, piezas sueltas o ajustes incorrectos.
Las trituradoras de mandíbulas destacan en la trituración primaria de materiales grandes y duros gracias a su robustez. Trituradoras de cono son más adecuadas para la trituración secundaria/terciaria de roca dura, ya que ofrecen una mayor reducción y una mejor forma. Trituradoras de impacto producen un excelente producto cúbico pero se desgastan mucho más rápido en roca dura y abrasiva.
