全站搜索
Pesquisar em todo o sítio Web
Pesquisar em todo o sítio Web
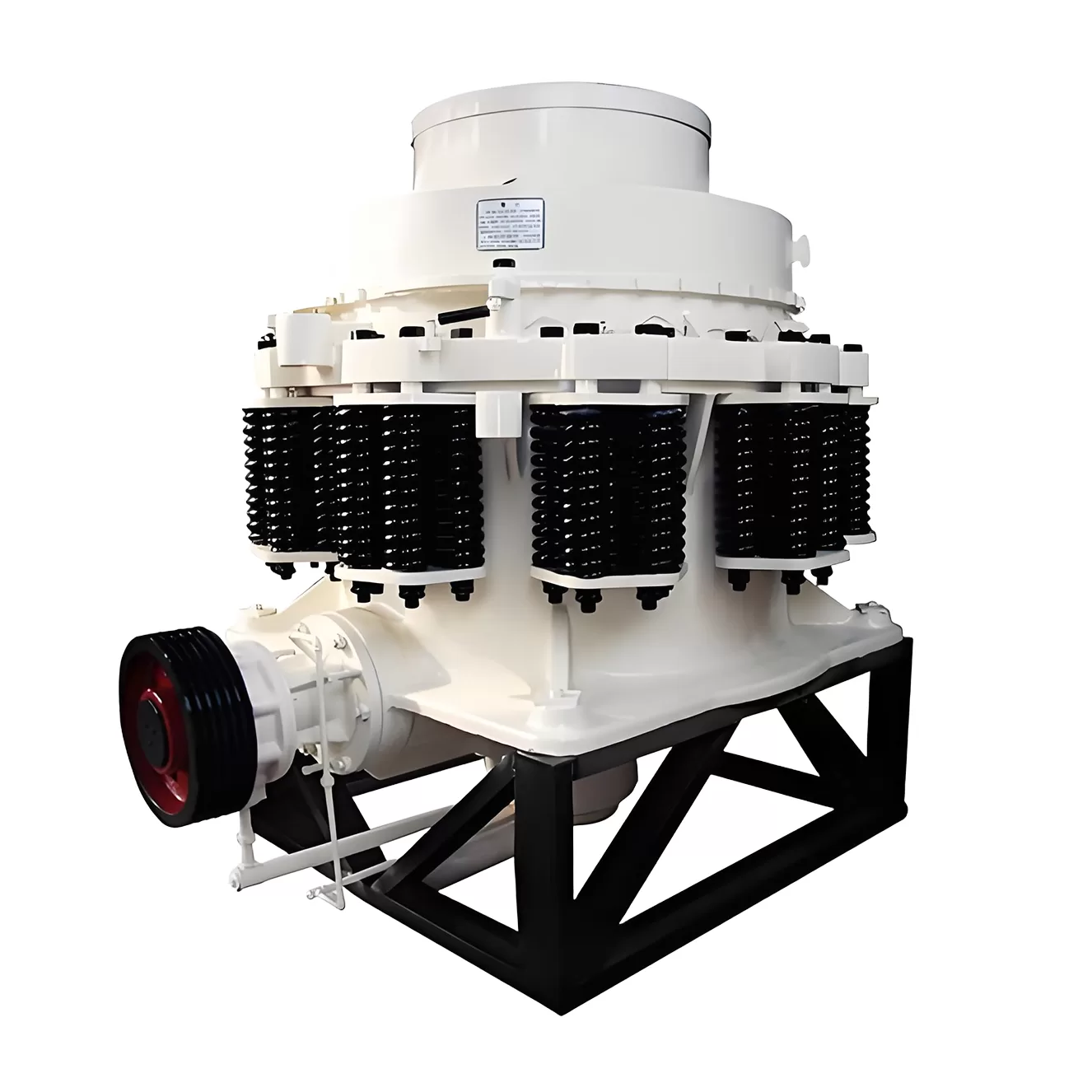
A medium and fine crushing equipment. The spring is the insurance device that can also influence crushing force.
Spring cone crusher is a medium and fine crushing equipment, the spring is not only a safety device but also affects the crushing force. The crushing chamber type is determined by the ore use: the standard type is suitable for medium crushing, the medium type is suitable for fine crushing, and the short head type is suitable for ultrafine crushing. Spring cone crusher is suitable for crushing hard and medium hard ores and rocks, such as iron ore, copper ore, limestone, quartz, granite, basalt, diabase, etc., widely used in metallurgy, construction, road construction, chemistry and phosphate and other industries.

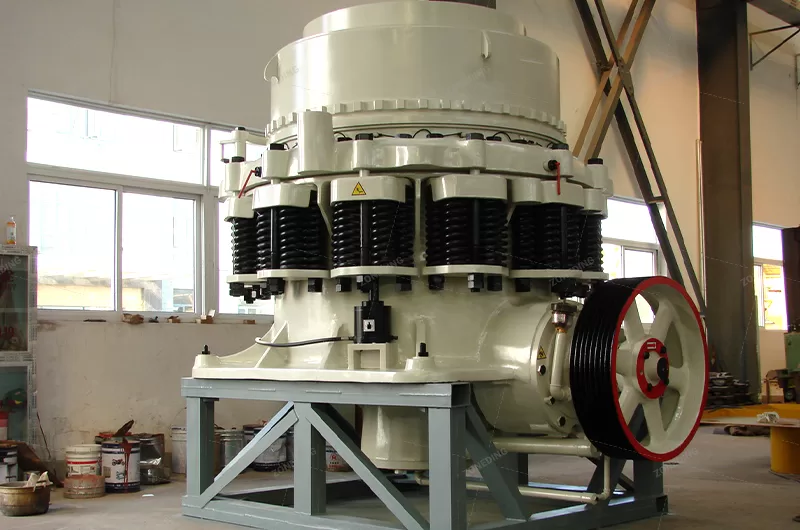
CS Spring Cone Crusher utilizes the lamination crushing principle, combining a high swing frequency, optimized cavity type, and rational stroke. This type of classic cone crusher is ideal for crushing hard materials such as granite, basalt, and river stones.CS Spring Cone Crusher utilizes the lamination crushing principle, combining a high swing frequency, optimized cavity type, and rational stroke. This type of classic cone crusher is ideal for crushing hard materials such as granite, basalt, and river stones.
Aplicação: iron ore, granite, limestone, quartzite, sandstone, cobblestone and etc. CS Symons cone crusher is applied to cement mills, mining, building construction, road & bridge construction, railway construction and metallurgy, and some other industries. Materials like iron ore, granite, limestone, quartzite, sandstone, cobblestone, and some others are easily crushed by cone crusher.

A cone crusher is one of the most widely used mining equipment. Symons cone crusher as a medium or fine crusher used in the site where not require a high granularity standard. Since the Simmons cone crusher controls the product size by reducing the size of the discharge opening, it is not suitable for use for superfine crushing and sand-making operations.
Features
1. Easy maintenance and easy operation. The lamination crushing process makes the final material have a good particle shape.
2. The hydraulic overload protection device helps to remove iron and reduce downtime. The thin oil lubrication station is equipped with a cooling system for better cooling performance.
3. The standard or short head crushing chamber can be replaced by different sleeves and bowl liners to better meet the needs of users.
4. Heavy-duty design and use of high-quality components with optimized wear parts reduce operating costs.

The structure of spring cone crusher is mainly composed of frame, fixed cone, moving cone assembly, spring mechanism, bowl shaft frame and transmission.
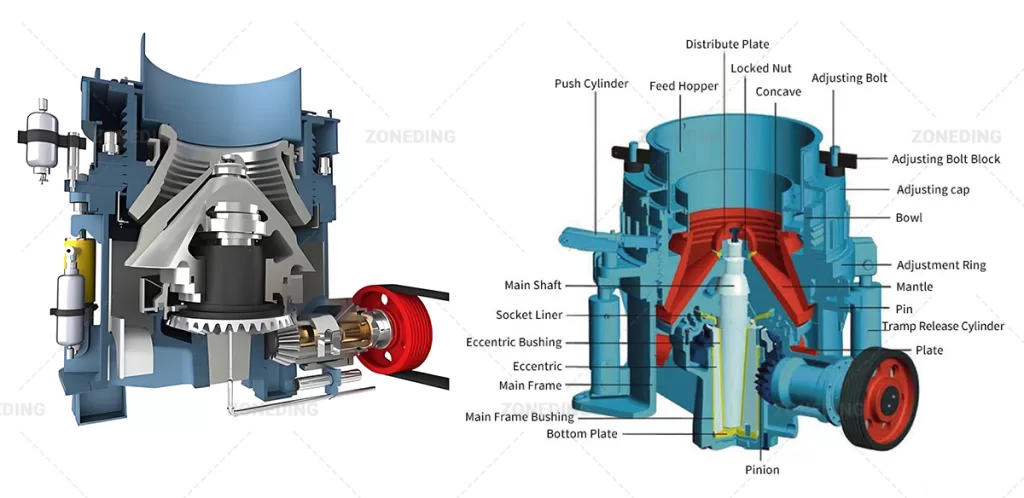
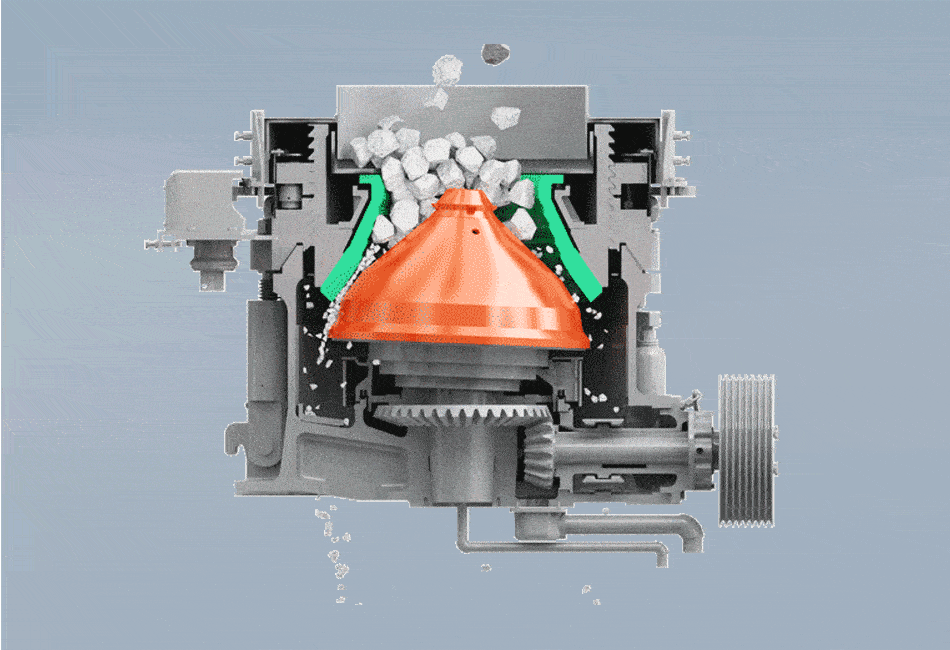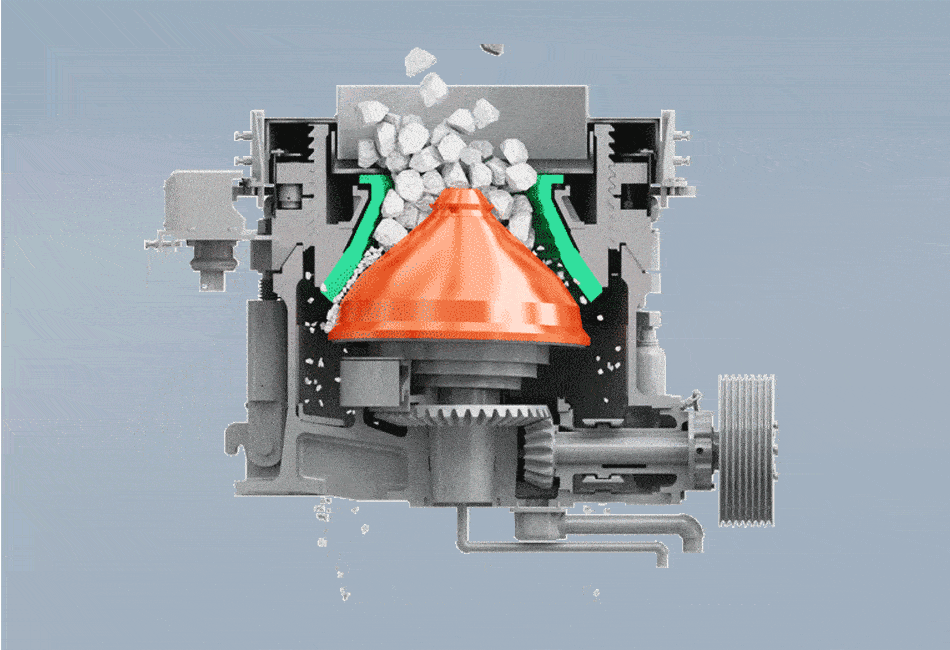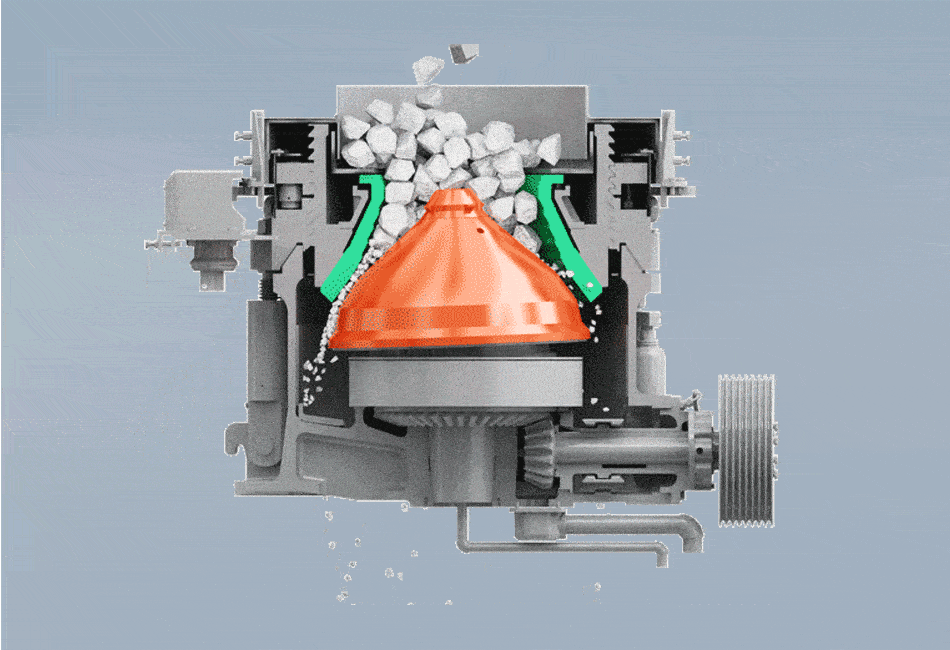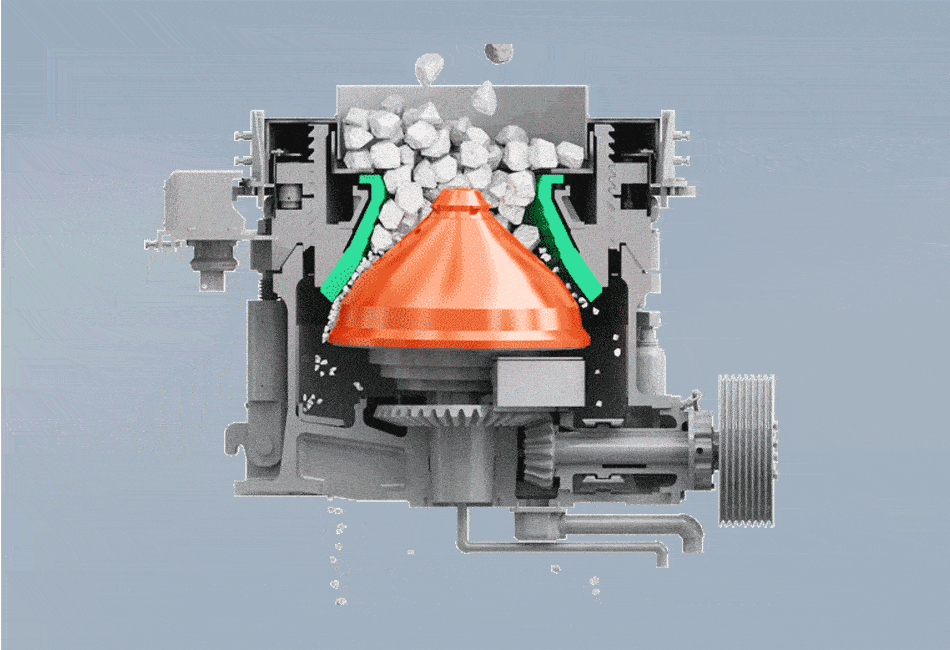
The working principle of the spring cone crusher commences when the electric motor is powered. This motor drives an intricate linkage of gears.The core action stems from the transmission gear driving the eccentric sleeve. This rotation forces the moving cone (mantle) to execute a gyratory or eccentric pendulum-like motion , relative to the fixed cone (bowl liner). As the moving cone gyrates, the gap between it and the fixed cone constantly closes on one side while opening on the opposite. Material entering the crushing cavity is caught in this closing gap, where it undergoes intense compression, impacting, and crushing forces. As the gap widens on the other side, the crushed material falls lower into the chamber for further size reduction or discharge.
| Modelo | Moveable Cone Dia. (mm) | Cavity Type | Feeder Opening Size | Adjusting Range of Discharge Opening(mm) | Main Shaft Speed (r/min) | Motor Power (kw) | Capacity(t/h) | Overall Dimension L*W*H (mm) | |
| Shutting Size(mm) | Opening Size(mm) | ||||||||
| CS75B | 900 | Fine | 83 | 102 | 9-22 | 580 | 75 | 45-91 | 2821×1880×2164 |
| Coarse | 159 | 175 | 13-38 | 59-163 | |||||
| CS110B | 1200 | Fine | 127 | 131 | 9-31 | 485 | 110 | 63-188 | 2821×1974×2651 |
| Medium | 156 | 156 | 13-38 | 100-200 | |||||
| Coarse | 178 | 191 | 19-51 | 141-308 | |||||
| CS160B | 1295 | Fine | 109 | 137 | 13-31 | 485 | 160 | 109-181 | 2800×2342×2668 |
| Medium | 188 | 210 | 16-38 | 132-253 | |||||
| Coarse | 216 | 241 | 19-51 | 172-349 | |||||
| CS220B | 1650 | Fine | 188 | 209 | 16-38 | 485 | 220 | 181-327 | 3911×2870×3771 |
| Medium | 213 | 241 | 22-51 | 258-417 | |||||
| Coarse | 241 | 268 | 25-64 | 299-635 | |||||
| CS315B | 2134 | Fine | 253 | 278 | 19-38 | 435 | 315 | 381-726 | 4613×3251×4732 |
| Medium | 303 | 334 | 25-51 | 608-998 | |||||
| Coarse | 334 | 369 | 31-64 | 789-1270 | |||||



Resposta: Os principais factores que influenciam a separação incluem o movimento da mesa (curso e frequência), o volume e a inclinação da água, a taxa de alimentação e a concentração, bem como o tamanho e a forma das partículas do material de alimentação. O ajuste correto destes factores é fundamental para uma separação eficiente. As inclinações longitudinais e transversais da mesa devem ser controladas com precisão. A concentração de alimentação também deve ser adequada, normalmente 20-30% para minerais grosseiros e 15-25% para minerais finos.
Resposta: A operação envolve a observação da superfície da mesa e o ajuste da inclinação, do fluxo de água e da taxa de alimentação. A manutenção regular inclui a verificação de peças soltas, a lubrificação dos componentes móveis, a inspeção do desgaste e a limpeza da superfície da mesa. A manutenção preventiva deve ser efectuada regularmente, com intervalos que variam entre cada mês e uma vez por ano.
Resposta: Os problemas mais comuns podem incluir a vibração da mesa ou cortes irregulares, distribuição desigual do material ou separação deficiente. A resolução de problemas pode envolver a verificação de parafusos soltos, molas danificadas ou desalinhamento, o ajuste da tensão da correia, a inspeção dos componentes eléctricos e a garantia de uma lubrificação adequada. Se houver um ruído invulgar, identifique a fonte e elimine o problema.
Resposta:
Vantagens: As mesas vibratórias oferecem elevadas taxas de enriquecimento, são relativamente simples de operar e produzem zonas de separação visíveis, permitindo um fácil ajuste e monitorização. São adequadas para uma vasta gama de tamanhos e densidades de partículas.
Desvantagens: Normalmente, têm uma capacidade de produção inferior à de outros métodos, como os jigues ou as espirais. Também requerem uma área relativamente grande e consomem uma quantidade significativa de água.
Resposta: A seleção depende do material a ser processado, do rendimento desejado e da gama de tamanhos de partículas. Os factores a considerar incluem a área da plataforma, o comprimento do curso e o design do riffle. Recomenda-se a consulta de um fabricante ou especialista para determinar a configuração ideal.
