全站搜索
Buscar en todo el sitio web
Buscar en todo el sitio web
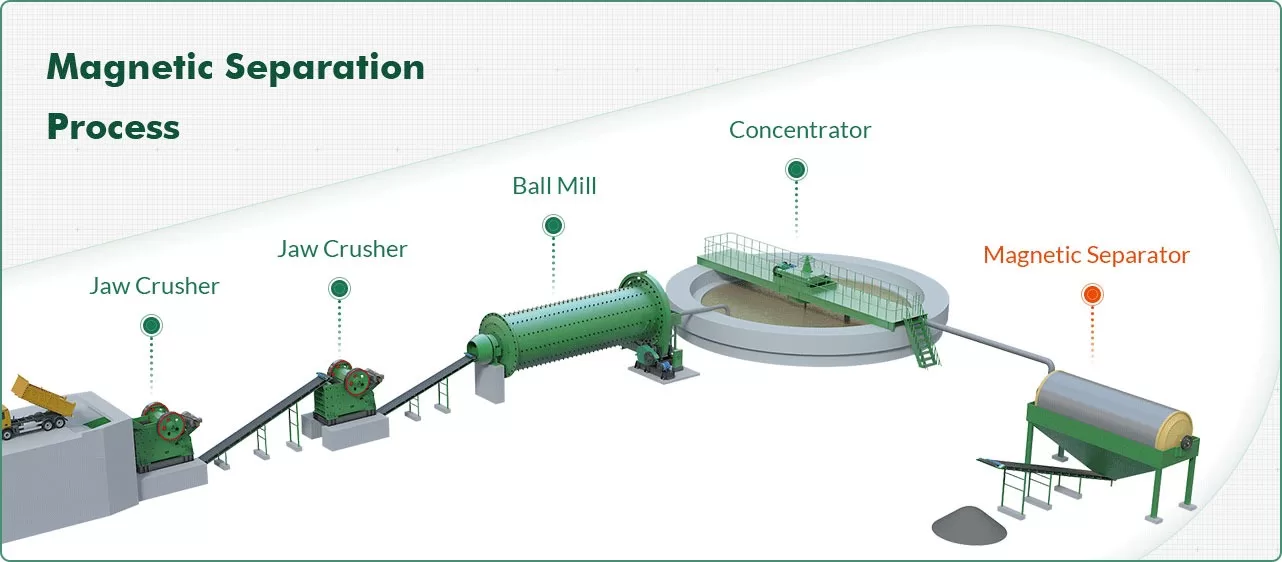
Magnetic separators are key equipment in the mineral processing and recycling industry and are widely used to separate magnetic minerals from non-magnetic minerals.
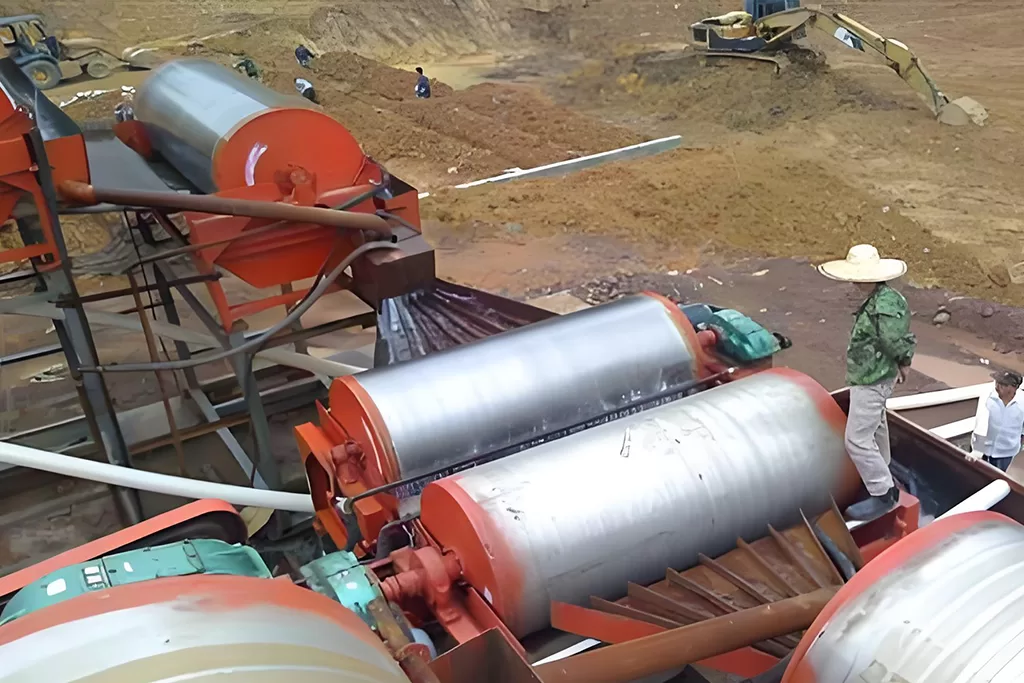
In mineral processing, a magnetic drum separator, also known as a drum magnet, separates non-magnetic material from magnetic material by using magnetic differences.
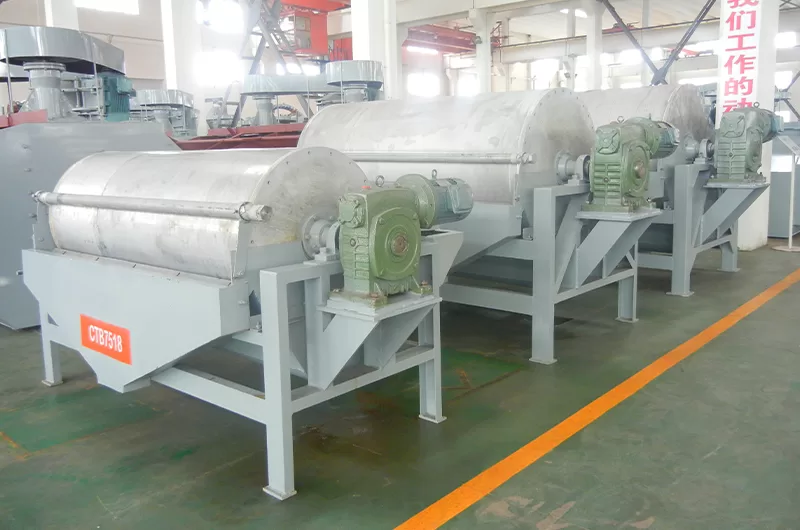
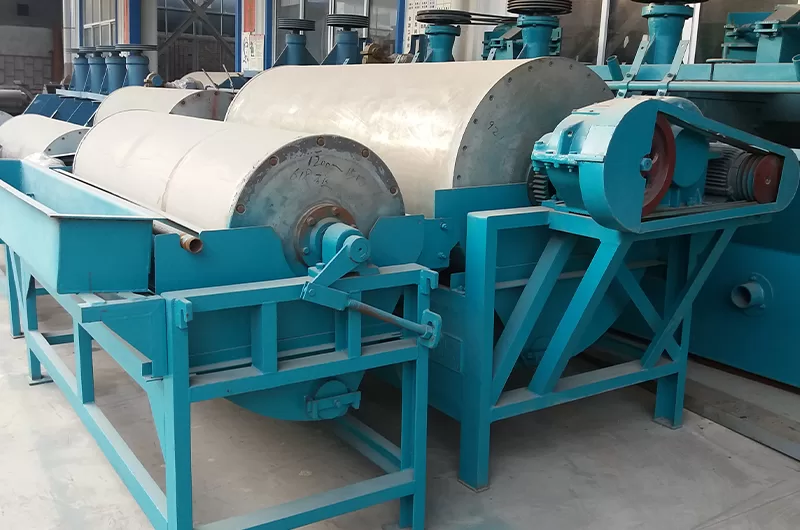


Magnetic separators are divided into dry magnetic separators and wet magnetic separators.
A dry magnetic separator, as the name suggests, operates without the use of water or a liquid medium.
The dry feed with a particle size less than 3mm is fed onto the rotating drum, where magnetic particles adhere to the drum’s surface. Non-magnetic particles are unaffected by the magnetic field and fall off the drum due to gravity or other forces. The separated magnetic particles are carried to a discharge point and released or brushed off the drum.
Dry magnetic drum separators use magnetic field strength, gradient, gravity, and other forces to separate and transport particles without the need for water or a liquid medium.
A model of dry drum magnetic separator includes a rare earth roll (RE Roll), which is a high-intensity magnet capable of separating strong and weak magnetic materials from non-magnetic material in a dry state.
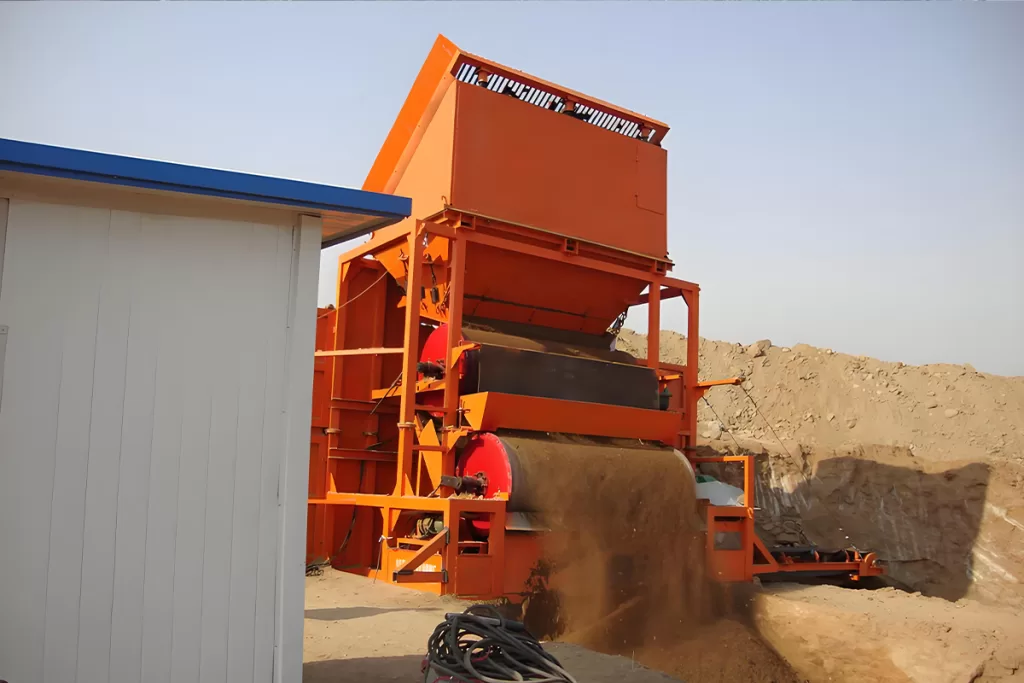

Advantages of the dry magnetic separators
1.No water requirement: Dry magnetic drum separators operate without a liquid medium, making them convenient and cost-effective. They are particularly advantageous in situations with limited water availability or a focus on water conservation.
2.Versatility: By adjusting magnetic field strength, drum speed, and other parameters, dry magnetic separators can process various minerals including iron ore, chromite, garnet, tantalite, and other magnetic minerals.
3.Easy maintenance: Dry high intensity magnetic separators generally have simpler designs and fewer components compared to wet separators, resulting in easier maintenance and lower maintenance costs.
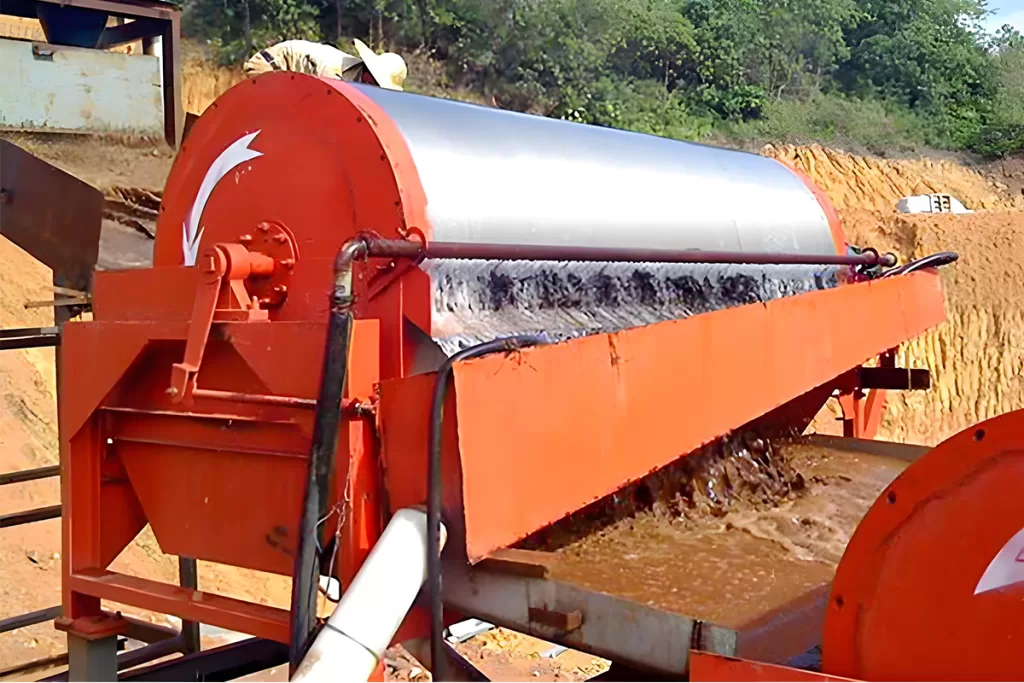

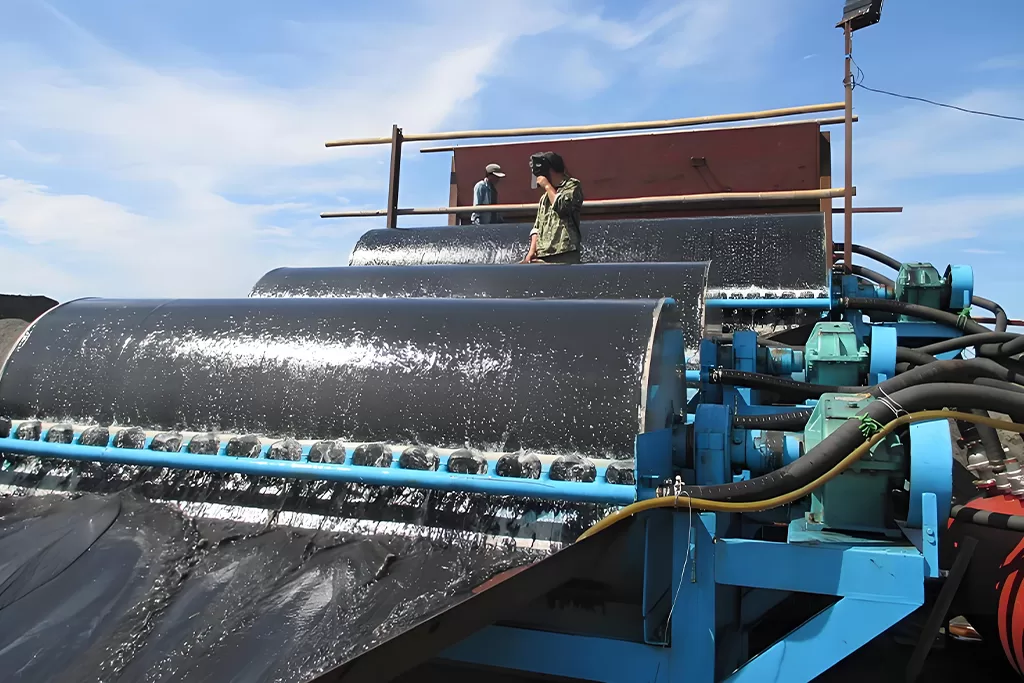
A wet magnetic separator operates in the presence of water or a liquid medium.
he feed material is mixed with water and fed onto the rotating drum. Magnetic particles stick to the drum’s surface as it rotates, while non-magnetic particles fall off due to gravity or other forces. Magnetic particles are eventually released or flushed off at the discharge point.
The presence of water or liquid medium in the wet magnetic drum separator facilitates the movement and separation of the magnetic and non-magnetic particles. It also aids in the transportation of the separated magnetic particles to the discharge point.
The permanent magnetic drum wet separator is suitable for the ores like magnetic pyrite, roasted ore, ilmenite, and other materials with a particle size of less than 3mm.

Magnetic Separators typically consist of a magnetic drum, transmission system, tank, feeding device, and discharge device. The magnetic drum, a crucial component, is equipped with high-performance permanent magnets or electromagnets that generate a powerful magnetic field. The tank holds the pulp, while the feeding device evenly distributes the pulp into the magnetic separator. The discharge device is responsible for removing the separated minerals.
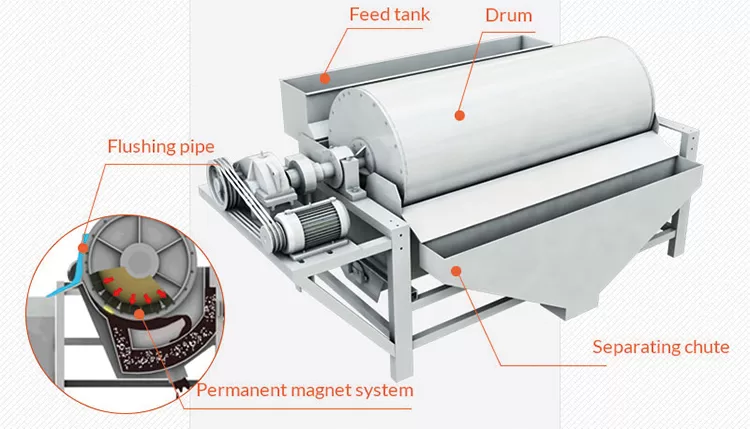
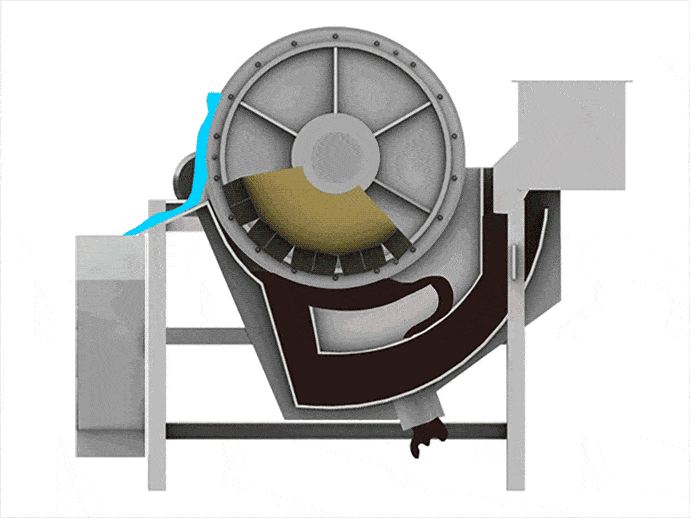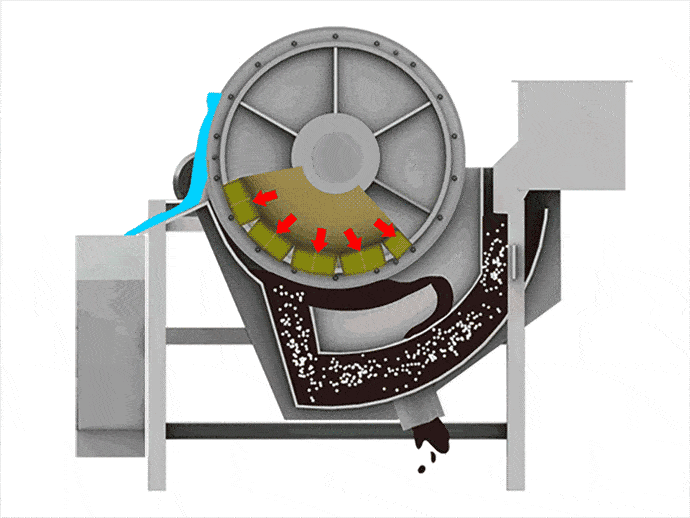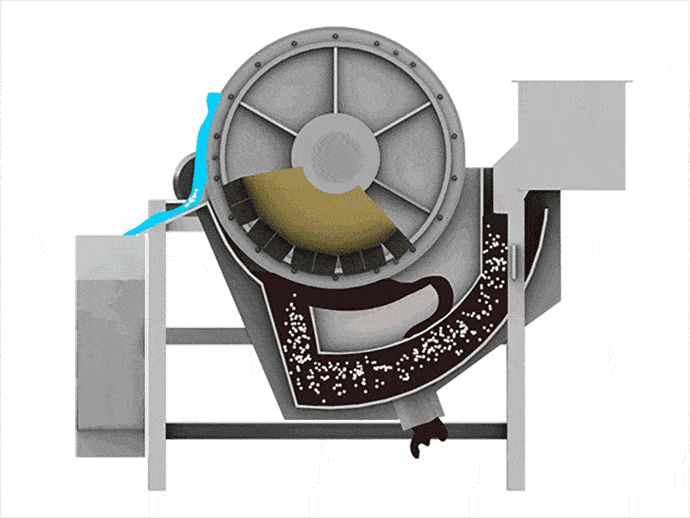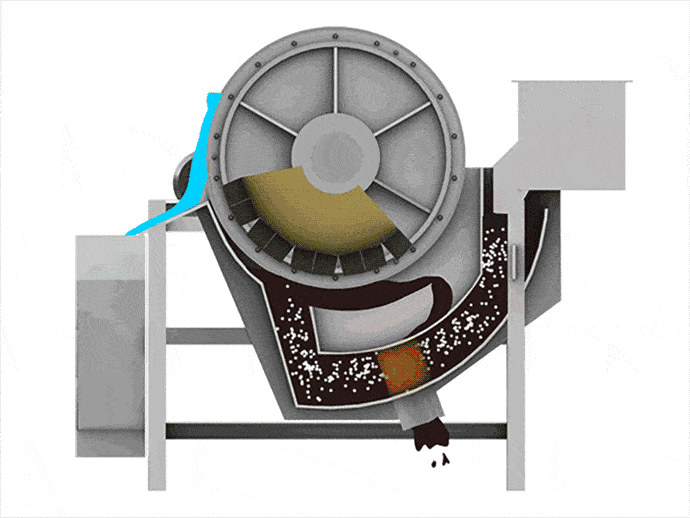
When materials go through the permanent magnetic drum, the magnetic particles are absorbed to the drum surface and discharged through the magnetic product area. Meanwhile, the non-magnetic particles are ejected from the drum surface under the influence of the centrifugal force and gravitation and discharged through the non-magnetic product area.
1. Magnetic drum separator adopts the multi-magnetic pole arrangement with short distances between poles in the internal magnetic system, which can increase the stirring of the magnetic particles and remove the gangues from minerals.
2. 180° broad-angle magnetic system can effectively prolong the separation area, and improve the recovery of iron ores.
3. Wear-resistant ceramics are stuck on the drum surface, the hardness HRA is ≥85, maximum HRA92 over
4. Simple material distribution device, which can conveniently control the grade of the concentrate and the tailing.
| Modelo | Shell diameter (mm) | Shell lenght (mm) | Shell rotation speed(r/min) | Feeding size (mm) | Processing capacoty (t/h) | Power(kw) |
| CTB6012 | 600 | 1200 | 2-0 | 10-20 | 1.5 | |
| CTB6018 | 600 | 1800 | 2-0 | 15-30 | 2.2 | |
| CTB7518 | 750 | 1800 | 2-0 | 20-45 | 2.2 | |
| CTB9018 | 900 | 1800 | 3-0 | 40-60 | 3 | |
| CTB9021 | 900 | 2100 | 3-0 | 45-60 | 3 | |
| CTB9024 | 900 | 2400 | 3-0 | 45-70 | 4 | |
| CTB1018 | 1050 | 1800 | 3-0 | 50-75 | 5.5 | |
| CTB1021 | 1050 | 2100 | 3-0 | 50-100 | 5.5 | |
| CTB1024 | 1050 | 2400 | 3-0 | 60-120 | 5.5 | |
| CTB1218 | 1200 | 1800 | 3-0 | 80-140 | 5.5 | |
| CTB1224 | 1200 | 2400 | 3-0 | 85-180 | 7.5 | |
| CTB1230 | 1200 | 3000 | 3-0 | 100-180 | 7.5 | |
| CTB1530 | 1500 | 3000 | 3-0 | 170-280 | 11 |



Contesta: Los factores clave que influyen en la separación son el movimiento de la mesa (carrera y frecuencia), el volumen y la pendiente del agua, la velocidad y la concentración de la alimentación y el tamaño y la forma de las partículas del material alimentado. El ajuste adecuado de estos factores es fundamental para una separación eficaz. Las pendientes longitudinal y transversal de la mesa deben controlarse con precisión. La concentración de la alimentación también debe ser la adecuada, normalmente 20-30% para minerales gruesos y 15-25% para minerales finos.
Contesta: El funcionamiento implica observar la superficie de la mesa y ajustar la pendiente, el caudal de agua y la velocidad de avance. El mantenimiento regular incluye la comprobación de piezas sueltas, la lubricación de los componentes móviles, la inspección del desgaste y la limpieza de la superficie de la mesa. El mantenimiento preventivo debe realizarse con regularidad, con intervalos que oscilan entre cada mes y una vez al año.
Contesta: Los problemas más comunes pueden incluir sacudidas de la mesa o cortes entrecortados, distribución desigual del material o separación deficiente. La solución de problemas puede incluir la comprobación de pernos sueltos, muelles dañados o desalineación, el ajuste de la tensión de la correa, la inspección de los componentes eléctricos y la lubricación adecuada. Si hay ruidos extraños, identifique la fuente y elimine el problema.
Contesta:
Ventajas: Las mesas de agitación ofrecen altos índices de enriquecimiento, son relativamente sencillas de manejar y producen zonas de separación visibles, lo que permite ajustarlas y controlarlas fácilmente. Son adecuadas para una amplia gama de tamaños y densidades de partículas.
Desventajas: Suelen tener menor capacidad de producción que otros métodos, como las plantillas o las espirales. También requieren un espacio relativamente grande y consumen una cantidad significativa de agua.
Contesta: La selección depende del material que se procese, del caudal deseado y de la gama de tamaños de las partículas. Los factores a tener en cuenta son la superficie de la plataforma, la longitud de la carrera y el diseño de la canaleta. Se recomienda consultar a un fabricante o experto para determinar la configuración óptima.
