全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
Tungsten is a vital metal. Its unique properties make it indispensable. It displays extreme hardness. It boasts a remarkably high melting point. Many industries rely on tungsten. These include aerospace, electronics, and tool manufacturing. Extracting tungsten from its raw ore is a complex process. It requires several stages of beneficiation. This guide details each essential step. Miners use it from raw ore to high-grade concentrate.
Tungsten ore processing aims to separate tungsten minerals. These minerals are wolframite and scheelite. They are separated from barren rock. The process also removes other undesirable impurities. Efficient processing maximizes tungsten mineral recovery. It also ensures the purity needed for industrial applications. Understanding these methods helps optimize plant operations. This also ensures sustainable resource utilization.
Tungsten ore represents the raw material. It contains tungsten minerals. Miners extract this ore from the earth. These minerals typically occur as compounds. They are not pure tungsten metal. Tungsten ore processing begins after mining. This process extracts the valuable tungsten. The aim is to achieve high-grade tungsten concentrate.


Two primary minerals contain tungsten. These are wolframite and scheelite. They account for most mined tungsten. These minerals reside within various rock types. Their composition and occurrence vary widely. Understanding them is crucial for effective beneficiation. Each mineral presents unique processing challenges.
Wolframite is an iron-manganese tungstate mineral. Its chemical formula is (Fe,Mn)WO₄. This formula signifies a solid solution. It ranges from ferberite (FeWO₄) to huebnerite (MnWO₄). Wolframite typically appears dark brown to black. It possesses a submetallic luster. Wolframite has high density. It also shows a magnetic property. This magnetism is a key for its separation.
Wolframite often forms in granite pegmatites. It occurs in hydrothermal veins. Its distinct properties allow specific recovery methods. Magnetic separation proves highly effective for wolframite.
Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral. Its chemical formula is CaWO₄. Scheelite usually presents as white, yellow, or reddish-brown crystals. It boasts a vitreous to greasy luster. Scheelite is non-magnetic. It fluoresces blue under shortwave ultraviolet light. This property aids in its identification.
Scheelite commonly occurs in contact metamorphic deposits. It is found in high-temperature skarns. Its non-magnetic nature necessitates different beneficiation. Flotation and gravity methods suit scheelite processing well. ZONEDING designs mineral recovery plants. These plants efficiently handle both wolframite and scheelite ores.
Tungsten ore transforms into a versatile metal. Its end applications are diverse. They span many industrial sectors. The unique properties of tungsten drive this demand. Tungsten material applications contribute to technological advancement. High-grade tungsten concentrate is the starting point for these products.
Tungsten carbides are a major application. They create hard materials. These materials include cutting tools and drilling bits. These tools machine other metals. They are essential for manufacturing. Aerospace industries use tungsten alloys. They require high-temperature resistance. Tungsten forms filaments in light bulbs. It makes X-ray tubes. Military applications also utilize tungsten.
Tungsten carbide possesses extreme hardness. It is second only to diamonds. This property makes it ideal for wear-resistant parts. Drills, milling cutters, and dies use tungsten carbide. Mining bits often incorporate this material. It withstands abrasive conditions well.
Tungsten has the highest melting point of all metals. This makes it crucial for high-temperature applications. Filaments for incandescent light bulbs use tungsten. Electrical contacts also use it. Its high density finds use in counterweights. It features in radiation shielding. Kinetic energy penetrators also use its density.
Tungsten exhibits good electrical conductivity. It offers excellent corrosion resistance. This makes it suitable for electrodes. It also features in certain chemical equipment. These properties ensure tungsten’s lasting industrial importance. Efficient tungsten extraction methods support these diverse applications.
Tungsten ore properties directly influence processing choices. Understanding these characteristics is fundamental. It allows for optimized tungsten beneficiation strategies. Mineral properties dictate effective separation techniques.


Tungsten minerals are generally dense. Wolframite exhibits magnetism. Scheelite is non-magnetic. Both are relatively hard. These physical properties are crucial. They guide the selection of appropriate mining equipment and processing methods.
| Property | Wolframite | Scheelite | Impact on Processing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Gravity | 7.0-7.5 g/cm³ | 5.9-6.1 g/cm³ | Both suitable for gravity separation |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 4-4.5 | 4.5-5 | Requires robust crushing and grinding equipment |
| Luster | Sub-metallic | Vitreous to greasy | – |
| Color | Dark brown to black | White, yellow, brownish | – |
| Magnetic Behavior | Paramagnetic (responsive to magnets) | Non-magnetic | Magnetic separation for wolframite; flotation for scheelite |
| Fluorescence | None | Blue (under UV light) | Aids identification and sorting in some operations |
Tungsten minerals also have brittle characteristics. This property aids in grinding. However, it can lead to over-grinding. Over-grinding creates fine particles. These fines can be difficult to recover. Efficient tungsten ore upgrading must account for these properties.
Tungsten minerals are chemically stable. They do not readily dissolve. This stability necessitates specific chemical treatments for refining. Cyanide is not used for tungsten. Strong acids or alkalis are used instead. This happens after physical concentration. Processing methods select based on these chemical behaviors.
For scheelite processing, collectors are needed for flotation. Fatty acids are typical. They make the scheelite surface hydrophobic. This allows it to attach to air bubbles. Wolframite processing predominantly relies on physical differences. Its magnetism offers a key advantage. These properties dictate the entire tungsten extraction methods.
Tungsten ore processing presents several unique challenges. Operators must address them for efficient and profitable operations. These challenges stem from the ore’s characteristics. They also relate to desired product purity. Implementing effective solutions ensures successful tungsten beneficiation.
Common issues include fine particle loss. Complex mineralogy also poses difficulties. Impurity removal is critical. Hardness of the ore is another factor. Environmental compliance adds further complexity.
Liberated tungsten minerals often occur as very fine particles. These fines are prone to losses. They escape in tailings during gravity separation. This significantly reduces overall tungsten mineral recovery.
Solution: Advanced fine particle recovery techniques solve this. These include spiraling. Shaking tables for fines are also used. Flotation becomes crucial for very fine scheelite. Careful control of grinding minimizes over-grinding. This reduces fines generation. ZONEDING’s finely tuned equipment helps manage these issues.
Tungsten ores often contain associated minerals. These include sulfides, silicates, and other oxides. These impurities must be removed. They reduce the high-grade tungsten concentrate quality. Some minerals have similar densities to tungsten, making separation difficult.
Solution: A multi-stage processing approach is vital. This combines different separation technologies. Gravity, flotation, magnetic, and electrostatic separation are used sequentially. Each stage targets specific impurities. ZONEDING offers customized flowsheets. These maximize impurity rejection. They ensure the final tungsten ore upgrading.
Tungsten ores are typically hard and abrasive. This causes significant wear on processing equipment. Frequent maintenance becomes necessary. Equipment wear increases operational costs. It also leads to downtime.
Solution: Using robust, wear-resistant equipment is essential. ZONEDING manufactures heavy-duty crushers and grinding mills. These machines feature durable components. They are designed for continuous, demanding operation. Regular maintenance schedules also reduce unexpected breakdowns. This approach ensures sustainable tungsten production.
Tungsten mining and processing can impact the environment. Water usage can be high. Tailings management requires careful planning. Some chemical reagents need safe handling. Strict environmental regulations apply to tungsten extraction methods.
Solution: Design plants with integrated environmental controls. This includes water recycling systems. It also features efficient tailings management in tungsten mining. Minimizing chemical consumption is a goal. ZONEDING designs and supplies eco-friendly solutions. These solutions ensure regulatory compliance. They reduce environmental footprint.
Processing tungsten ore involves a sequence of stages. Each stage refines the material. It progressively increases the tungsten concentration. Operators follow a structured flowsheet. This ensures efficient tungsten beneficiation. The goal is to produce high-grade tungsten concentrate.
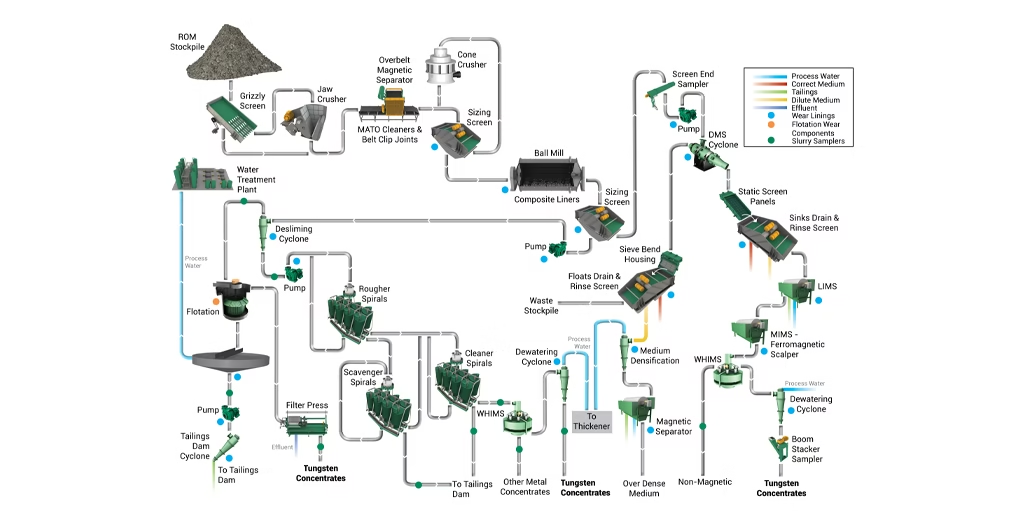
These steps remove gangue. They recover the valuable tungsten minerals. The main steps proceed from physical separation to chemical refining. This systematic approach maximizes recovery. It also ensures final product quality.
This comprehensive strategy addresses diverse ore characteristics. It aims for effective tungsten recovery.
Each stage of tungsten ore processing requires specialized equipment. Proper selection ensures optimal performance. It also maximizes tungsten mineral recovery. ZONEDING provides a full range of robust mineral processing equipment. These solutions cater to every step. They deliver cost-effective tungsten extraction.
Choosing the right equipment impacts efficiency. It affects concentrate quality. It influences the entire operation’s profitability. ZONEDING leverages its expertise. It offers tailored equipment solutions.
Comminution begins with large rocks. Jaw crushers handle primary reduction. They process raw ore from the mine. Their robust frames withstand tough conditions. Cone crushers or impact crushers perform secondary and tertiary crushing. These machines prepare the material for grinding.
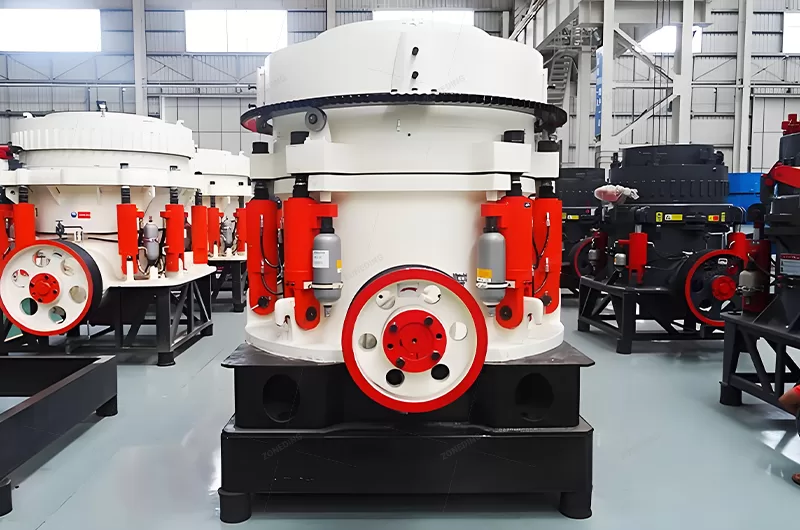
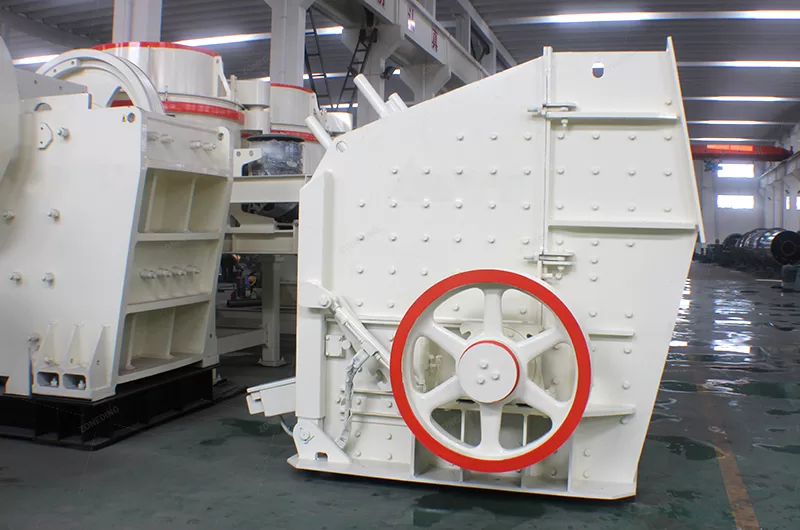
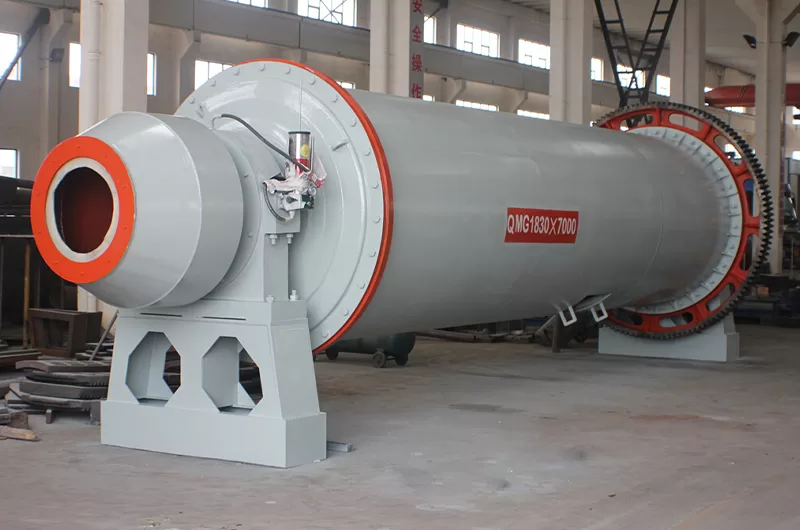



Grinding further reduces particle size. Ball mills and rod mills achieve fine liberation. They create a slurry. This slurry is suitable for downstream beneficiation. ZONEDING’s comminution equipment offers high throughput. They ensure minimal wear.
Gravity Separation Tungsten:
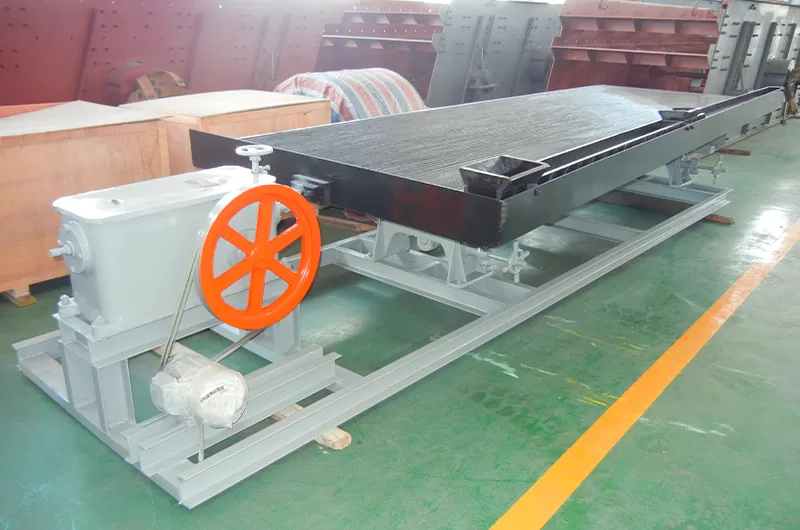
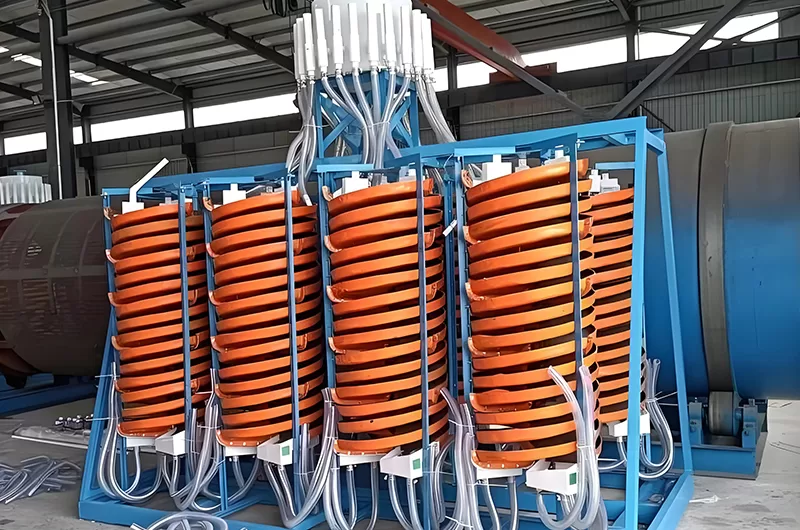
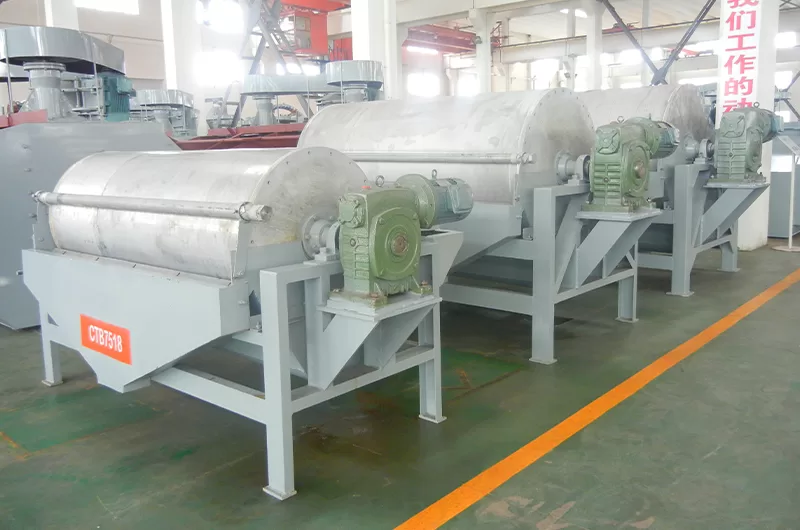



Electrostatic separators further refine concentrates. They can also perform tungsten ore upgrading. These machines separate minerals based on conductivity differences. They help achieve very high purity levels. This is often a final cleaning step.
ZONEDING supports clients in designing chemical refining circuits. While not directly manufacturing chemical reactors, ZONEDING provides overall plant design and integration expertise. This ensures a seamless transition. It moves from physical beneficiation to chemical refining.
Designing an environmentally friendly tungsten processing plant is paramount. Compliance with regulations is essential. It minimizes environmental impact. It also builds community trust. Sustainable tungsten production integrates best practices. ZONEDING prioritizes these aspects in its plant designs.
An eco-conscious design balances economic viability with environmental stewardship. It focuses on several key areas. These include water management, waste reduction, and energy efficiency. Tailings management in tungsten mining is also critical.
Tungsten beneficiation uses significant amounts of water. Implementing closed-loop water systems is key. Water recycling minimizes fresh water intake. It also reduces process water discharge. Thickening and filtering technologies are crucial here. ZONEDING provides thickening equipment for efficient water recovery.
Installing robust water treatment facilities is also important. These facilities ensure discharged water meets environmental standards. They remove contaminants before release.
Tailings are the waste materials from mineral processing. Their proper management is vital. Dry stacking tailings reduces water use. It also minimizes land footprint. It lowers the risk of dam failures. Coder co-disposal with waste rock is another option. ZONEDING helps design effective tailings storage facilities. These facilities are stable and environmentally secure.
Some tungsten extraction methods involve chemicals. Minimizing their use reduces environmental risk. Optimizing reagent dosages is crucial for flotation. Safe handling and storage of chemicals are mandatory. Emergency response plans are implemented. Using less toxic alternatives is always preferred.
High energy consumption is common in mining. Optimizing crushing and grinding circuits saves energy. ZONEDING’s efficient equipment contributes to this goal. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is another objective. This involves using cleaner energy sources. It also includes optimizing operational processes.
Tungsten ore processing requires significant investment. Many factors influence its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. These factors impact both operational costs and final profitability. Careful consideration of each element leads to a successful tungsten operation. Effective tungsten beneficiation balances recovery with expenditure.
Understanding these influences helps optimize plant design. It also aids in daily operational decisions. ZONEDING focuses on these factors. It develops solutions for maximizing client returns.
The type of ore is primary. Its grade, mineralogy, and physical properties are crucial. High-grade ores are more profitable. Complex mineralogy increases processing difficulty. Hardness impacts comminution costs (Tungsten Crushing & Grinding). Different mineral associations require tailored flowsheets. For example, scheelite processing differs from wolframite processing.
Choosing the right equipment is vital. High-performance machinery ensures efficient material handling. It maximizes recovery rates. Reliable machines reduce downtime and maintenance costs. ZONEDING’s full line of mineral processing equipment offers robust solutions. This includes all necessary Tungsten mining equipment.
The design of the process flowsheet directly impacts efficiency. An optimized flowsheet minimizes processing steps. It maximizes liberation and separation. It also reduces reagent consumption. Continuous optimization improves existing operations. This enhances tungsten mineral recovery.
Energy represents a significant operating cost. Efficient comminution circuits reduce power consumption. Water recycling systems lower water costs. They also decrease the need for discharge treatment. Incorporating smart management practices improves cost-effectiveness.
Labor costs, spare parts, and consumables impact profitability. Modern, automated plants can reduce labor needs. Proactive maintenance extends equipment life. It prevents costly breakdowns. ZONEDING equipment is designed for longevity and easy maintenance. This supports cost-effective tungsten extraction.
ZONEDING brings extensive experience to tungsten ore processing. The company’s expertise covers the entire project lifecycle. It ensures successful outcomes for clients. ZONEDING integrates advanced technology. It combines this with practical field knowledge. This approach leads to optimized tungsten beneficiation solutions.
ZONEDING’s comprehensive services and high-quality equipment guarantee efficiency. They maximize tungsten mining equipment performance. They secure the high-grade tungsten concentrate needed by industries.

Dive into the ultimate comparison of impact and hammer crushers. Understand key differences in design, operation, andscenarios for maximum crushing efficiency.
View detailsLearn steps, permits, machine, cost and market analysis needed to launch a quarry business. Get advice for new starters and successful project initiation.
View detailsThis checklist outlines the essential mineral tests required for any beneficiation project, from mineralogy and comminution to flotation and hydrometallurgy.
View detailsUnlock economic potential of gabbro deposits. Learn what gabbro is and how the crushing plant can turn gabbro into valuable resource for construction projects.
View details