全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
Feldspar is a critical industrial mineral. It is abundant in the Earth’s crust. Its unique properties prove indispensable. Many modern industries rely on feldspar. These include ceramics, glass, and fillers. Understanding feldspar nature and processing is vital. This guide details every stage. It covers raw ore to high-grade concentrate.
Feldspar beneficiation separates feldspar minerals. It removes quartz, mica, and other impurities. Efficient processing maximizes feldspar recovery. It ensures purity for specific industrial uses. This guide covers feldspar types and properties. It explains processing methods. It concludes with quality control and ZONEDING’s role.
Feldspar minerals form a group. They are rock-forming tectosilicates. They constitute over 50% of Earth’s crust. It is the most abundant mineral group. “Feldspar” comes from German. It means “field crystal.” These minerals form fundamental components. They appear in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Their complex crystal structures offer unique industrial value. Understanding feldspar nature begins with its prevalence.


Feldspar minerals form under diverse conditions. They are found in many geological settings. Their ubiquity explains widespread industrial use. They provide a primary source of alumina and alkalis. These support manufacturing processes. This mineral group appears chemically stable. It is also physically durable. These characteristics make it a preferred material.
Feldspars classify by their chemical composition. They typically contain potassium, sodium, and calcium. These elements combine with aluminum and silica. The general feldspar formula is XAl(Si,Al)SiO₈. “X” denotes potassium (K), sodium (Na), or calcium (Ca).
Two main feldspar series exist:
The specific element ratio defines the feldspar type. This composition impacts its properties. It also dictates industrial applications. Feldspar processing often separates these types. This ensures optimal use for various products.
Feldspar is vital for modern industries. Its unique chemical and physical properties drive demand. It serves as a fluxing agent. It adds alumina and alkalis. Feldspar industrial applications are extensive. They contribute significantly to manufacturing. The high-grade feldspar concentrate forms a cornerstone.
Its prevalence and properties make it invaluable. Feldspar’s role in products often goes unnoticed. Yet, it underpins many everyday materials. This mineral group supports construction and consumer goods. Its applications continuously expand. Technology makes these advancements possible.

Feldspar’s primary uses center on its melting properties. Its alumina content also plays a key role.
These diverse applications highlight efficient feldspar processing. ZONEDING’s equipment helps produce high-quality feldspar. This quality serves these industries. Producing high-grade feldspar concentrate ensures optimal product performance.
Feldspar ore indicates rock. It contains economically viable feldspar minerals. These ores come in several key types. Classification depends on the dominant feldspar mineral. Understanding these types is crucial for effective feldspar beneficiation. Each ore type requires a specific processing approach.
Geological origin and associated minerals characterize feldspar ore types. Some deposits are primary. They form in igneous or metamorphic rocks. Other deposits are secondary. They occur in weathered or sedimentary formations. The ore’s mineralogy dictates processing complexity.



Potassium feldspar, or K-feldspar, possesses high potassium. Orthoclase and microcline are common minerals. They have KAlSi₃O₈ as a chemical formula. K-feldspar is valuable in ceramics. It lowers the vitrification temperature. It contributes to product strength.
Potassium feldspar processing separates it from quartz and mica. Iron removal is crucial. Iron impurities cause discoloration. This affects ceramic and glass products.
Sodium feldspar, or Na-feldspar, contains much sodium. Albite is the primary mineral. Its chemical formula is NaAlSi₃O₈. Na-feldspar is a vital glass manufacturing component. It acts as a flux. It introduces alumina. And It improves glass workability and durability.
Sodium feldspar purification focuses on iron removal. It also separates other color-causing impurities. The beneficiation plant must achieve specific sodium-to-potassium ratios. These ratios are important for certain uses.
Plagioclase feldspar forms a series. It ranges from sodium-rich albite to calcium-rich anorthite (CaAl₂Si₂O₈). Intermediate compositions include oligoclase, andesine, labradorite, and bytownite. Its industrial use is not as widespread as alkali feldspars. Plagioclase feldspar finds niche applications. It is used as filler or aggregate.
Feldspar beneficiation plants customize their flowsheets. They adjust for the precise feldspar ore type. This ensures efficient separation. It maximizes high-grade feldspar concentrate yield.
Feldspar ore properties dictate its suitability. They also influence feldspar processing methods. Understanding these characteristics is fundamental. It allows for optimized feldspar beneficiation strategies. Mineral properties guide extraction technique selection.
Feldspathic minerals show distinct attributes. They use physical and chemical properties during processing. Hardness, specific gravity, color, and melting points are key. They all contribute to feldspar nature.
| Property | Potassium Feldspar (Orthoclase/Microcline) | Sodium Feldspar (Albite) | Impact on Processing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Gravity | 2.55-2.63 g/cm³ | 2.60-2.65 g/cm³ | Useful for gravity separation. It works if density differences occur. |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6-6.5 | 6-6.5 | Robust crushing and grinding equipment is necessary. |
| Color | White, pink, grey, colorless | White, grey, reddish | Iron impurities must be removed. This serves glass/ceramics. |
| Melting Point | approx. 1,150-1,200 °C | approx. 1,100-1,120 °C | Crucial for fluxing properties in glass and ceramics. |
| Cleavage | Good cleavage in two directions at 90° | Good cleavage in two directions at 90° | This impacts grinding behavior and particle shape. |
Potassium feldspar (K-feldspar) and sodium feldspar (Na-feldspar) possess similar hardness. This means feldspar crushing and feldspar grinding equipment must perform efficiently. Different melting points and alkali content suit distinct uses. Iron-bearing minerals seriously impact the final product.
Feldspar minerals are relatively inert. This helps make them stable. They do not readily react with environmental factors. Their stability makes them excellent fillers. The main chemical characteristic for processing is composition. Specifically, it involves K₂O, Na₂O, Al₂O₃, and SiO₂ ratios.
Primary chemical impurity concern involves feldspar iron removal. Iron oxides (Fe₂O₃) create unwanted color. Other impurities include mica, quartz, and heavy minerals. These affect high-grade feldspar concentrate purity. Efficient feldspar beneficiation targets these impurities. ZONEDING provides equipment solutions. These improve feldspar quality control.
Feldspar deposits are globally abundant. They occur in many geological environments. The deposit type and quality influence feldspar processing strategies. Understanding location aids resource planning. It also impacts logistics. This affects feldspar beneficiation plant construction.
Feldspar minerals form under various conditions. They are found in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Their widespread distribution makes feldspar accessible. Large-scale deposits often become major mining sites.
Granites, pegmatites, and syenites are primary sources. They form through magma cooling and solidification.
Gneisses and schists are metamorphic rocks. They form under intense heat and pressure. These rocks often contain a significant amount of feldspar. The feldspar minerals in these deposits commonly associate with other silicates. Their processing often uses methods similar to igneous rocks.
Less common for economic mining, arkosic sandstones contain feldspar. These sandstones form from eroded feldspar-rich igneous rocks. They also form from metamorphic rocks. These deposits often require simpler beneficiation. They may have already undergone natural separation. The quality might appear lower.
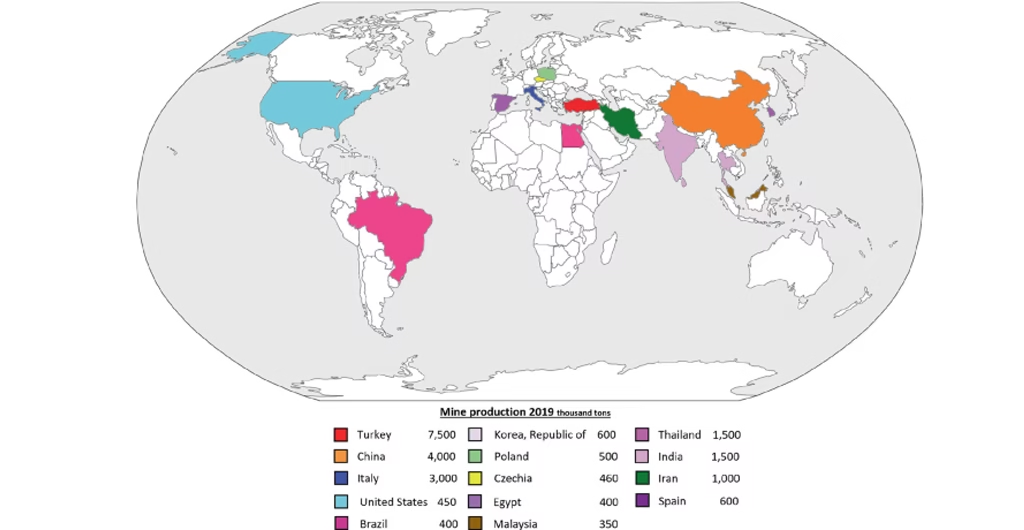
Major feldspar-producing countries include Turkey, Italy, China, India, and the United States. Each region uses specific feldspar equipment solutions. These solutions adapt to unique deposit characteristics. This ensures efficient feldspar industrial applications.
Feldspar processing transforms raw ore. It converts it into a usable industrial product. It involves several stages. These stages remove impurities. They also upgrade feldspar content. The entire process ensures a high-grade feldspar concentrate. This goes from feldspar crushing to feldspar purification. The specific flowsheet adapts to ore mineralogy. It also depends on the desired final product.
The primary goal separates feldspar from quartz, mica, and iron. Each stage uses different physical principles. This sequence achieves required purity levels. Feldspar beneficiation plant designs focus on efficiency. They also target cost-effectiveness.
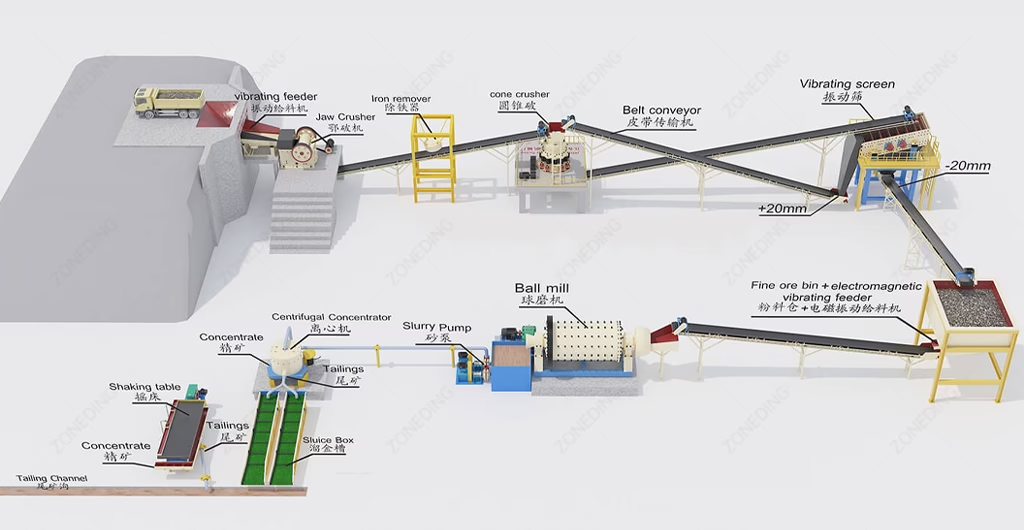
Raw feldspar ore arrives from the mine. Its size is typically large. Feldspar crushing reduces these large lumps.
Feldspar grinding mills the crushed ore. It creates a fine powder or slurry.
After crushing, ore often undergoes screening and washing.
Feldspar flotation is the most common method. It separates feldspar from quartz, mica, and other silicates. This is a complex process. It requires careful reagent control.
The process often involves multiple stages. These include roughing, scavenging, and cleaning cells. This maximizes feldspar recovery. This also enhances concentrate purity. ZONEDING’s flotation machines ensure efficient separation. They accommodate various reagent schemes.
Even after flotation, iron-bearing minerals might remain. Feldspar iron removal is critical for glass/ceramic uses.
The final concentrate undergoes further purification. This often includes de-sliming. It removes very fine particles. These particles cause unwanted effects in final products. Filtration removes excess water. Rotary dryers dry the high-grade feldspar concentrate. It prepares the concentrate for shipment.
The dried concentrate is often dry-milled. It achieves specific particle size distributions. This meets customer requirements. ZONEDING customizes feldspar processing plant designs. This delivers tailored solutions for optimal feldspar quality control.
A modern feldspar beneficiation plant uses a range of specialized equipment. Each machine performs a specific function. It contributes to overall efficiency. Selecting the right feldspar equipment solutions is crucial. This ensures a cost-effective feldspar extraction. ZONEDING offers a comprehensive portfolio. These machines design for reliability and high performance.
Equipment selection depends on the ore body. It also relies on desired final product specifications. An integrated plant design ensures seamless operation.
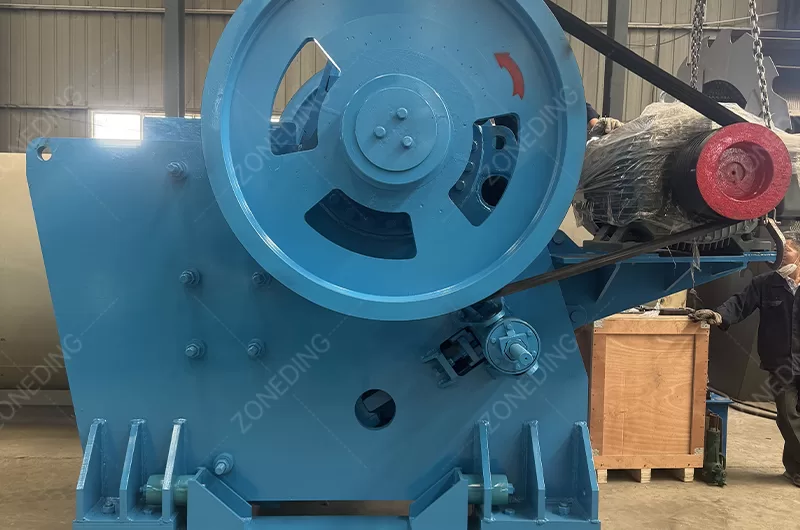
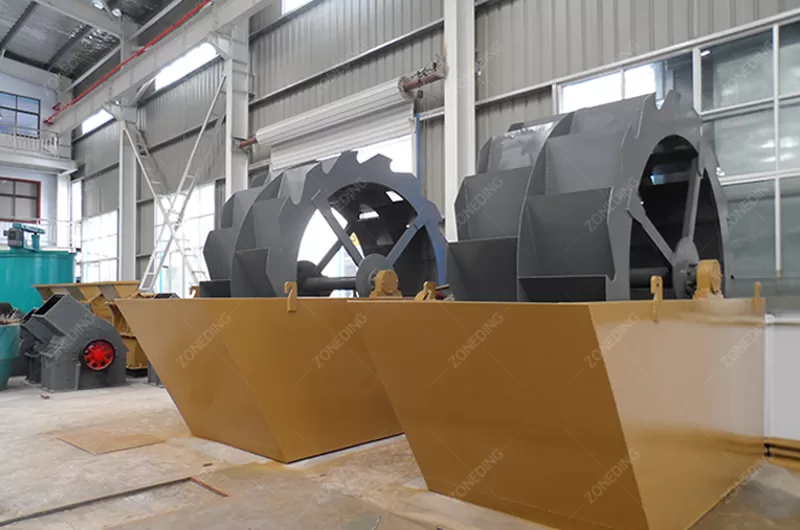
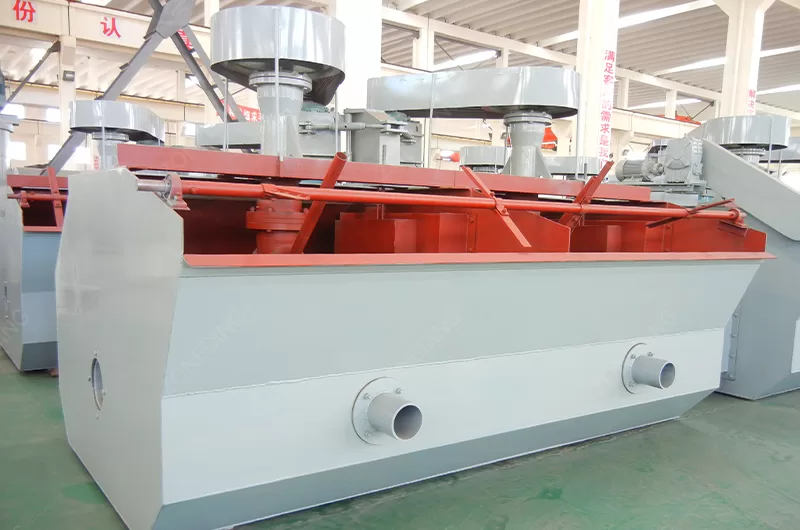



ZONEDING provides integrated solutions. These solutions support every stage of feldspar processing. Their expertise ensures optimal equipment combination. It meets specific project needs.
Ensuring consistently high-quality feldspar is crucial. Different industrial applications have strict requirements. Meeting specifications involves stringent feldspar quality control. It relies on precise process management. It requires constant monitoring throughout feldspar processing. This guarantees high-grade feldspar concentrate production.
Quality control minimizes impurities. It maintains specific chemical compositions. It ensures consistent physical properties. These factors are vital for end-product performance. ZONEDING designs processes that deliver reliable quality.
Impurity control stands as the most critical aspect. Iron oxides (Fe₂O₃) are primary concerns. They cause discoloration. They reduce glass transparency. And They create specks in ceramics.
Tailings are the waste materials from mineral processing. Their proper management is vital. Dry stacking tailings reduces water use. It also minimizes land footprint. It lowers the risk of dam failures. Coder co-disposal with waste rock is another option. ZONEDING helps design effective tailings storage facilities. These facilities are stable and environmentally secure.
Different applications demand specific alkali ratios. For instance, potassium feldspar processing and sodium feldspar purification target distinct K₂O and Na₂O levels.
Particle size impacts feldspar performance. It affects melting behavior in ceramics. It influences dispersibility as a filler.
Modern feldspar beneficiation plants use automation. This ensures consistent operating conditions. Automated systems monitor critical parameters. These parameters include reagent dosages, slurry densities, and pH levels. Real-time adjustments maintain optimal performance. This reduces human error. It enhances feldspar quality control. ZONEDING integrates these technologies into plant designs.
Feldspar processing presents unique challenges. Operators must address them for success. These challenges stem from ore variability. They also arise from stringent product specifications. Overcoming them ensures efficient and profitable feldspar beneficiation. ZONEDING develops solutions to mitigate these difficulties.
These challenges include fine particle impurities. They also involve variable mineralogy. Water management and iron contamination are key issues. Environmental regulations add complexity. Addressing these proactively secures sustainable feldspar mining.
Feldspar often occurs with fine-grained quartz. It also appears with mica and iron-bearing minerals. These are difficult to separate. The complex mineralogy of some ores makes selective separation hard. Especially, achieving high purity presents challenges.
Solution: Advanced feldspar flotation techniques are needed. This includes multi-stage flotation circuits. They use specialized reagents. Fine grinding is also essential. However, avoid over-grinding. It creates excessive fines. High-intensity magnetic separators effectively remove fine iron impurities. ZONEDING’s flotation machines are designed for precise control.
Many feldspar industrial applications (e.g., optical glass) need very low iron. This means very small iron oxide amounts must be removed. This is often below 0.05% Fe₂O₃. This presents a significant challenge. It arises when ore contains iron.
Solution: Ultra-high intensity feldspar iron removal techniques are employed. They include powerful magnetic separators. Optimized grinding also helps. It liberates very fine iron particles. Acid leaching may serve as a final purification step. This is for specific ultra-high-purity products. ZONEDING’s equipment facilitates these stringent requirements.
Feldspar processing uses much water. Discharging untreated process water is unacceptable. Regulations for water discharge and tailings disposal are strict. This demands sustainable practices.
Solution: Implement closed-loop water circuits. Maximize water recycling. Thickeners and filter presses efficiently recover water from slurries. Proper tailings management uses dry stacking. This reduces water use. It also minimizes land footprint. ZONEDING’s plant designs emphasize eco-friendly solutions. They support sustainable feldspar mining.
Feldspar crushing and feldspar grinding are energy-intensive processes. Feldspar’s hardness causes high power consumption. This impacts operational costs significantly.
Solution: Optimize the comminution circuit. Select energy-efficient crushers and mills. Implement advanced control systems. These systems monitor particle size. They adjust feed rates. This prevents over-grinding. ZONEDING’s crushers and mills are designed for optimal energy efficiency. This reduces overall operating costs. It contributes to cost-effective feldspar extraction.
ZONEDING offers comprehensive expertise. This applies to mineral processing. Their solutions specifically target feldspar processing projects. The company’s in-depth knowledge and advanced feldspar equipment solutions ensure project success. ZONEDING provides a holistic approach. It moves from initial design to operational optimization.
Choosing ZONEDING means partnering with a leader. The company prioritizes efficiency, purity, and sustainability. Their commitment to feldspar quality control sets them apart.
This article explains origins and unique properties of perlite, applications, industrial perlite processing chain from mining to final screening & grading.
View detailsLooking for the best rock crusher for gold? Our guide compares Jaw, Cone, and Hammer Mill crushers to maximize your gold recovery from hard rock.
View detailsMaximize yield with Gold Gravity Separation Equipment. From Centrifugal Concentrators to Shaking Tables, we offer a complete solution to recover fine gold.
View detailsChoosing between used & new ball mill? This guide compares pros, cons, costs, performance, and maintenance of them, to help you select right grinding solution.
View details