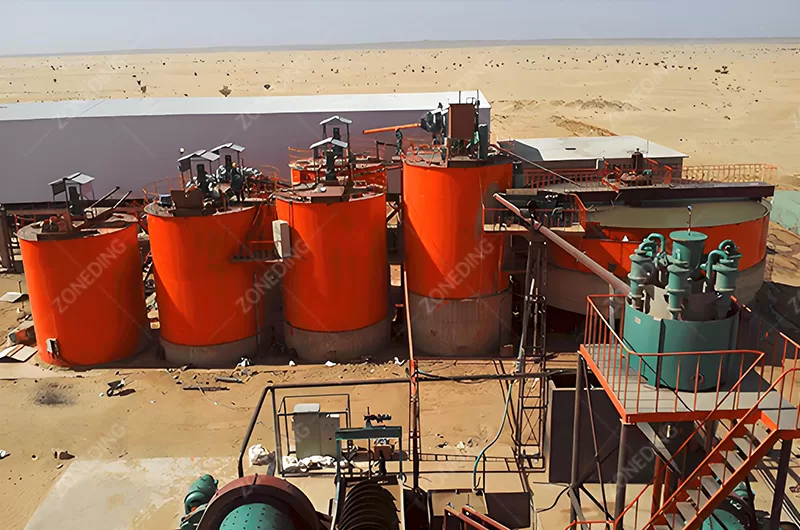
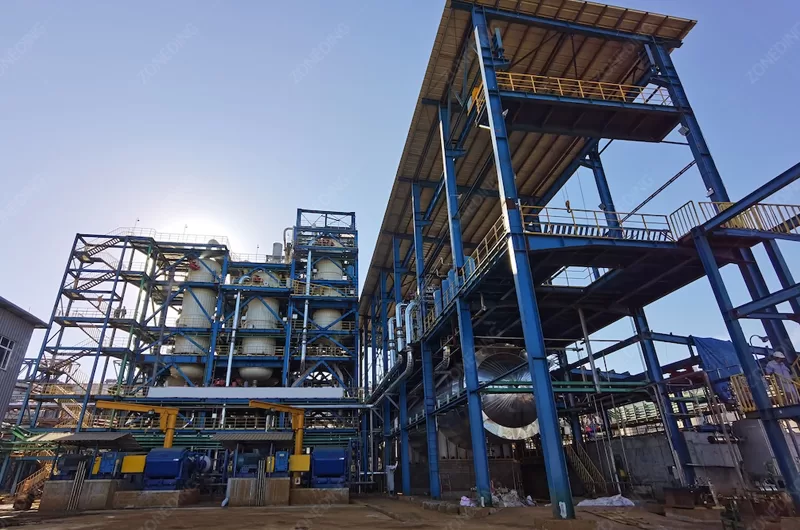
Cyanide leaching stands as the most widespread method for gold extraction globally. This chemical process efficiently dissolves gold from its ore, enabling miners to recover even minute quantities of the precious metal. While incredibly effective, it also presents significant environmental and safety challenges. Understanding both the benefits and concerns surrounding cyanide leaching is crucial for responsible and successful gold mining operations.
This guide explores the fundamentals of the cyanide leaching process. We will discuss its key advantages, highlight the associated risks, and examine modern solutions to mitigate these concerns. I aim to provide a balanced analysis for anyone involved in or interested in gold recovery.
Table of Contents
What is Cyanide Leaching and How Does it Work?
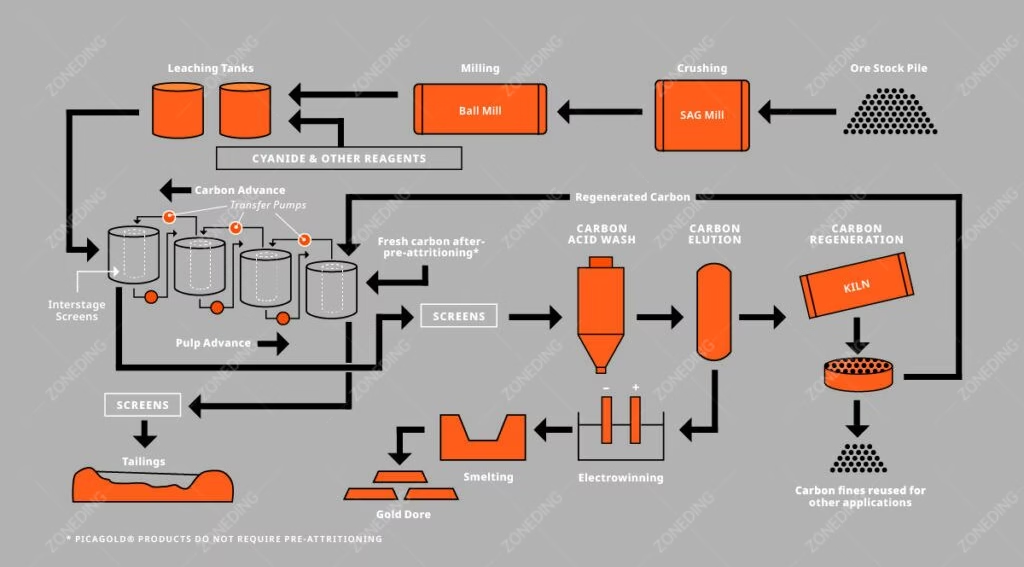
Cyanide leaching is a hydrometallurgical process. It uses a dilute cyanide solution to dissolve gold from gold-bearing ore. This process forms soluble gold cyanide complexes. Miners have used this method for over a century due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The fundamental reaction involves gold, cyanide ions, water, and oxygen.
The primary chemical reaction for gold extraction with cyanide is:
4Au + 8NaCN + O₂ + 2H₂O → 4Na[Au(CN)₂] + 4NaOH
This equation shows that gold reacts with sodium cyanide (NaCN) in the presence of oxygen and water. It forms a soluble gold cyanide complex (Na[Au(CN)₂]). This soluble complex then allows for the separation of gold from the solid ore material. After dissolution, the gold complex is typically adsorbed onto activated carbon. This recovers the gold from the solution. ZONEDING provides essential equipment such as thickener concentrators to prepare the ore pulp for optimal leaching. This ensures the correct pulp density and efficient contact between gold particles and the cyanide solution.
Miners widely adopt cyanide leaching because it offers several compelling advantages for gold extraction. These benefits contribute to its status as the industry’s preferred method for many types of gold ore.
Here are the key advantages of using cyanide leaching:
- High Gold Recovery: The primary benefit is its exceptional ability to dissolve fine gold particles. It achieves high gold recovery rates even from low-grade ores. This makes economically viable operations possible.
- Versatility: Cyanide leaching adapts to various ore types. It effectively processes both free-milling and some refractory ores. This versatility makes it suitable for diverse geological settings.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Despite the need for careful management, the overall operating costs for cyanide leaching can be lower compared to other gold extraction methods. This is particularly true for large-scale operations.
- Simplicity and Reliability: The underlying chemistry is well-understood. The process is relatively simple to operate and control. This ensures consistent gold recovery.
- Scalability: The method scales easily from small heap leaching operations to large, continuous tank leaching plants. This flexibility meets different project requirements.
- Established Technology: Decades of research and operational experience have refined cyanide leaching technology. This has led to robust engineering and safety protocols.
ZONEDING provides durable and efficient mineral processing equipment designed to enhance the effectiveness of your cyanide leaching operations. Our equipment contributes to maximizing your gold recovery rate while maintaining operational stability.
What Are the Main Environmental and Safety Concerns of Cyanide Leaching? (Cons)
Despite its efficiency, cyanide leaching for gold extraction carries significant environmental and safety concerns. These concerns necessitate strict regulations, careful management, and robust mitigation strategies in any mining operation.
Here are the primary disadvantages and risks associated with cyanide leaching:
- Toxicity to Wildlife: Cyanide is extremely toxic to aquatic life and land animals. Even low concentrations in water can be lethal. Spills or uncontrolled discharges can devastate local ecosystems.
- Human Health Risks: Exposure to cyanide, through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, poses serious health risks to workers. Inhalation of hydrogen cyanide gas (HCN), which can form under acidic conditions, is particularly dangerous and potentially fatal.
- Environmental Contamination: Without proper containment, cyanide can leach into groundwater or surface water. This contaminates water sources and soil, posing long-term environmental threats.
- Accidental Release Potential: Despite stringent safety measures, accidental spills during transportation, storage, or processing remain a risk. Such incidents can have severe and widespread consequences.
- Public Perception and Social License: The inherent toxicity of cyanide often leads to strong public opposition and negative perceptions of mining projects. This can hinder a company’s “social license to operate.”
- Regulatory Challenges: Strict regulations govern the use, storage, and disposal of cyanide. Compliance requires substantial investment in infrastructure, monitoring, and personnel training.
ZONEDING emphasizes integrated solutions for gold recovery that prioritize safety and environmental responsibility. Our equipment and process designs aim to support the safest possible operation of the cyanide leaching process when it is the optimal extraction method.
How Can Risks Associated with Cyanide Leaching Be Minimized? (Solutions)
Minimizing the risks associated with cyanide leaching is paramount for sustainable gold extraction. Industry best practices and technological advancements offer robust solutions to manage environmental and safety concerns. A multi-faceted approach combines detoxification, secure containment, and continuous monitoring.
Here are key solutions and mitigation strategies:
- Cyanide Detoxification: Before discharge, process solutions and tailings must undergo detoxification. Common methods include:
- INCO Process (SO₂/Air): Uses sulfur dioxide and air to convert cyanide into less toxic compounds.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Oxidizes cyanide, converting it into cyanate and other less harmful substances.
- Biological Detoxification: Utilizes microorganisms to break down cyanide.
- Closed-Loop Systems: Designing gold processing plants as closed-loop systems effectively recycles process water and prevents uncontrolled discharges. This significantly reduces fresh water consumption and minimizes contamination risks.
- Robust Tailings Management: Tailings storage facilities (TSFs) are engineered for zero discharge. They feature impermeable liners, leakage detection systems, and dedicated water treatment plants.
- Strict Monitoring and Emergency Response: Continuous, real-time monitoring of cyanide levels in process streams and surrounding environments is essential. Comprehensive emergency response plans, including spill containment and rapid remediation procedures, must be in place.
- Safe Handling and Storage: Secure, controlled facilities are critical for cyanide storage. Strict protocols for transportation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and worker training are mandatory to prevent human exposure.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to international best practices and local regulations, such as the International Cyanide Management Code, provides a framework for responsible cyanide use.
ZONEDING actively contributes to safer gold recovery solutions through its integrated plant designs and cutting-edge mineral processing equipment. We help implement efficient dewatering solutions, like our thickener concentrators, which are crucial for minimizing water and chemical usage within closed-loop systems.
Different Ways to Apply the Cyanide Leaching Process
The cyanide leaching process is applied through several distinct methods for gold extraction, each suited to different ore characteristics and operational scales. Understanding these variations helps select the most efficient gold recovery approach for a specific project.
The main applications of cyanide leaching include:
- Tank Leaching (CIP/CIL):
- Carbon-in-Pulp (CIP): In this method, gold ore is ground into a fine pulp. This pulp then undergoes agitation in a series of tanks. Cyanide solution dissolves the gold. Activated carbon is then added directly to the pulp. The carbon adsorbs the dissolved gold.
- Carbon-in-Leach (CIL): Similar to CIP, but the leaching and carbon adsorption steps occur concurrently in the same tanks. This allows for faster processing and can reduce capital costs. ZONEDING’s flotation machines can also be integrated into the processing flow, especially for pre-concentration or to recover gold associated with sulfides before CIL.
- Heap Leaching:
- This method is suitable for low-grade ores. It avoids the need for fine grinding. Crushed ore is stacked on an impermeable pad. Cyanide solution is then sprayed over the top of the heap. As the solution trickles down through the ore, it dissolves the gold. The gold-rich solution (pregnant solution) then collects at the base.
- Heap leaching is cost-effective for large volumes of low-grade ore. It requires a larger land footprint and longer leaching times.
- Agitation Leaching:
- This method involves grinding the ore to a very fine particle size. The finely ground pulp is then mixed with cyanide solution in large, agitated tanks. This ensures intimate contact between the gold particles and the leaching agent. It is ideal for ores requiring fine liberation for efficient gold dissolution. This method is often part of a complete gold processing plant.
- Vat Leaching:
- An older method but still used for some higher-grade, permeable ores. The ore is loaded into large vats or tanks. Cyanide solution is then passed through the ore, typically by percolation.
ZONEDING specializes in designing and supplying complete mineral processing plants that integrate these leaching methods with optimal comminution and separation stages. This ensures maximum gold recovery for each specific ore type.
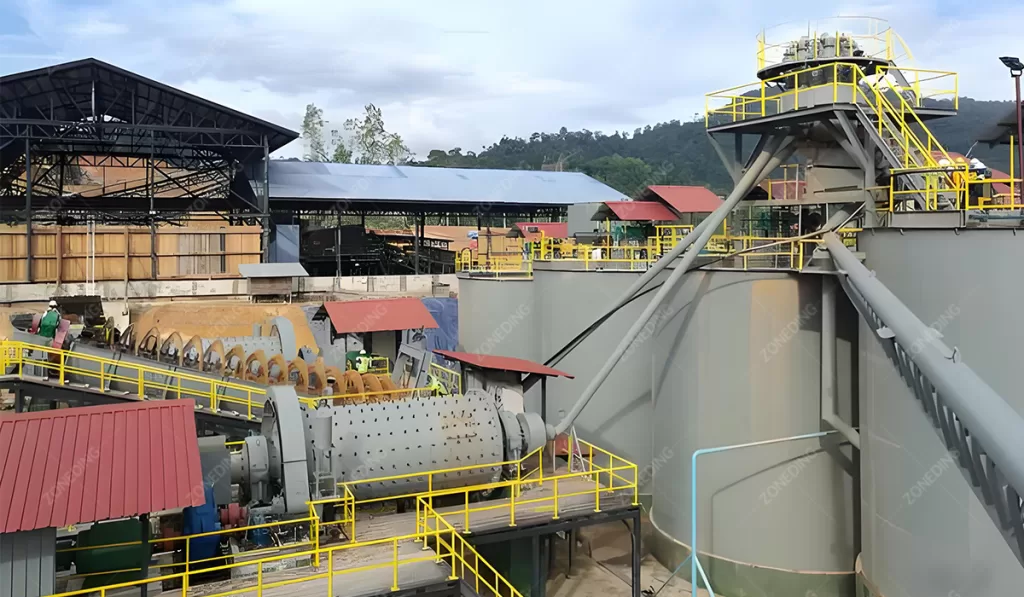
What Equipment is Essential for an Efficient Cyanide Leaching Plant?
An efficient cyanide leaching plant for gold extraction requires a suite of specialized equipment. Each piece plays a critical role in preparing the ore, dissolving the gold, and recovering the precious metal safely. Investing in high-quality, reliable equipment is paramount for maximizing gold recovery and minimizing operational risks.
Key equipment components typically include:
- Crushing and Grinding Equipment: Before leaching, ore must be reduced to a suitable size.
- Thickeners and Classifiers:
- Thickener Concentrators are vital for dewatering and controlling pulp density before and after leaching.
- Spiral Classifiers separate fine particles from coarse ones, ensuring uniform feed for grinding.
- Leaching Tanks: These large, agitated tanks provide the environment for gold dissolution. They feature robust stirring mechanisms to ensure uniform mixing of ore pulp and cyanide solution.
- Carbon Adsorption Columns (CIP/CIL Plants): Series of tanks or columns filled with activated carbon. These are where dissolved gold is adsorbed from the cyanide solution.
- Desorption and Electrowinning Systems: Equipment for stripping gold from the carbon (desorption) and then plating it out of solution onto cathodes (electrowinning).
- Cyanide Detoxification Plant: Essential equipment for treating barren solution and tailings before discharge, as discussed previously.
- Pumps, Pipes, and Valves: Specialized, corrosion-resistant equipment for safely handling and transporting corrosive and toxic process solutions.
- Safety and Monitoring Systems: Comprehensive sensors, alarms, and emergency shutdown systems to detect leaks, monitor cyanide levels, and ensure worker safety.
2025 Latest Trends in Cyanide Leaching and Gold Extraction
The landscape of gold extraction via cyanide leaching is continuously evolving. New trends focus on enhancing efficiency, improving safety, and reducing the environmental footprint. For 2025, the industry is seeing significant advancements driven by technological innovation and a commitment to more sustainable practices. These developments aim to boost the gold recovery rate while also addressing public and regulatory concerns.
Key trends shaping cyanide leaching and gold extraction include:
- Smart Plant Automation and AI: Integration of artificial intelligence with real-time process control systems is optimizing leach parameters, reagent dosing, and overall plant efficiency. This predictive analytics reduces human error and maximizes gold recovery.
- Enhanced Detoxification Technologies: Research and implementation of more rapid and effective cyanide detoxification methods are ongoing. These include advanced oxidation processes and novel biological treatments. They ensure lower residual cyanide levels in tailing discharges.
- Closed-Loop System Optimization: Further refinement of closed-loop systems is minimizing fresh water usage. It is also reducing effluent discharge by maximizing water recycling. This includes advanced membrane filtration and reverse osmosis in some applications.
- Robotics and Remote Operations: Increased use of robotics for sampling and maintenance tasks in hazardous areas enhances worker safety. Remote monitoring and control capabilities improve operational flexibility and reduce on-site personnel exposure.
- Tailings Re-processing Technologies: Innovations in re-processing historical tailings, often with lower cyanide concentrations and more benign reagents for residual gold, are becoming economically viable. This turns waste into a valuable resource and improves the overall gold recovery rate.
- Advanced Carbon Management: New methods for reactivating and handling activated carbon more efficiently improve the overall robustness of CIP/CIL circuits.
These advancements demonstrate the industry’s commitment to continuously improving the cyanide leaching process. They ensure its continued viability for gold extraction in a more responsible and sustainable manner.
Choosing a Supplier for Your Cyanide Leaching Plant
Selecting the right supplier for your cyanide leaching plant is a critical decision. It directly impacts your gold extraction efficiency, safety, and long-term financial success. A strong partner offers not just equipment but also comprehensive expertise. This includes process design, engineering, and commitment to safe and sustainable operations.
Here are key factors to consider when choosing a supplier:
- Technical Expertise: Look for a supplier with deep knowledge of gold recovery principles and the cyanide leaching process. They should understand your ore’s specific characteristics.
- Integrated Solutions: A supplier offering a complete range of mineral processing equipment can ensure seamless integration and optimal plant performance. This includes everything from crushers to thickeners.
- Customization Capabilities: Every gold ore is unique. The supplier should be able to tailor equipment and process flow designs to your specific needs.
- Safety and Environmental Focus: Choose a partner committed to designing plants with robust safety features and environmental protection measures, including effective detoxification systems.
- After-Sales Support: Reliable installation, commissioning, operator training, and readily available spare parts are crucial for continuous operation and maximizing uptime.
- Global Experience: A supplier with international experience understands diverse regulatory environments and operational challenges.
ZONEDING provides full-process solutions for gold recovery, including expert metallurgical testing, plant design, equipment manufacturing, and robust after-sales service. Our commitment to quality and safety ensures your cyanide leaching project is efficient, reliable, and compliant.
Common Questions About Cyanide Leaching
- Question 1: Is cyanide leaching the only method for gold extraction?
- No, it is not the only method. Gravity separation, flotation, and other chemical processes exist. However, cyanide leaching remains the most dominant method due to its high efficiency and versatility for gold recovery.
- Question 2: How does a “closed-loop” cyanide plant benefit the environment?
- A closed-loop system recycles process water and limits discharge. This minimizes the risk of cyanide release into the environment. This practice significantly reduces water consumption and environmental impact during gold extraction.
- Question 3: What is the International Cyanide Management Code?
- The International Cyanide Management Code is a voluntary program designed to help gold mining companies manage cyanide responsibly. It covers manufacturing, transport, and use to protect human health and the environment during gold recovery.
- Question 4: Can arsenic or other impurities affect cyanide leaching efficiency?
- Yes, certain impurities like arsenic, copper, or sulfide minerals can interfere with the cyanide leaching process. They can consume cyanide, inhibit gold dissolution, or reduce carbon adsorption efficiency. Pre-treatment methods often address these challenges.
- Question 5: What is the estimated cost range for setting up a cyanide leaching plant?
- The cost varies significantly. It depends on plant capacity, ore type, required equipment, and environmental controls. A small heap leach might cost a few million dollars. A large, complex CIL plant can cost hundreds of millions for gold extraction.