Different Types of Vibrating Screens: Which is Best for You?
The mining screen is what actually makes you money. A screen is the cash register of your entire operation. Its job is to accurately separate your valuable product into sellable sizes. If your screen is inefficient, you are either losing good product to a waste pile or contaminating your final product with the wrong sizes. Choosing the right vibrating screen is just as critical as choosing the right crusher for your plant’s success.
Table of Contents
Vibrating Screen Brief Introduction
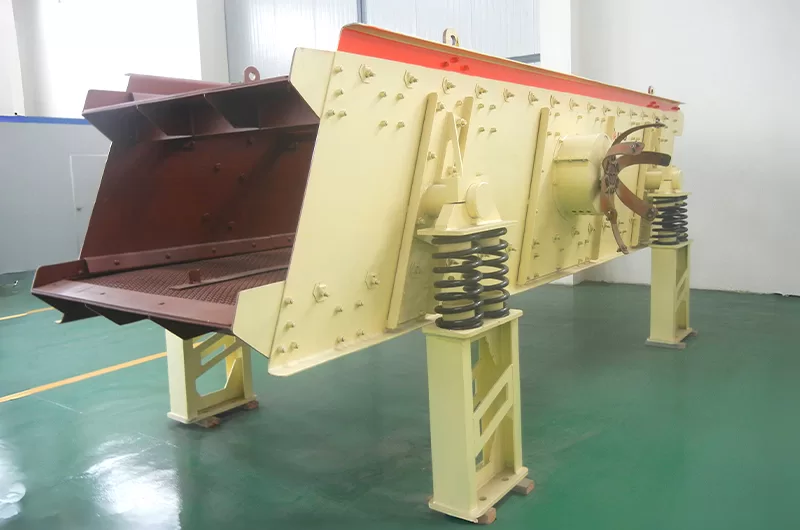
A vibrating screen is a machine used to separate materials by size. Think of it as a large, strong, and very fast sieve. It uses a motor to create a vibration, which makes the material on its surface dance and move. As the material travels across the screen’s surface (called the screen media or mesh), smaller particles fall through the openings. Larger particles continue to travel across the surface and exit at the end. This is the fundamental process for creating specific, graded products in mining, quarrying, and recycling.
Different Types of Vibrating Screen
There are many types of screens, each designed for a specific job. At ZONEDING, we help our clients choose the perfect type for their material and production goals. Here are the most common ones you’ll see.
Inclined Screen
- what are inclined screens?: This is the most common and versatile type of vibrating screen. It is set at an angle, usually between 15 and 30 degrees.
- where are inclined screens used?: General-purpose sizing and scalping in quarries, mining, and recycling. It can handle wet or dry materials.
- how does the inclined screen work?: It uses a circular vibrating motion. Gravity helps move the material down the angled screen deck, making it very energy-efficient.
- what are Advantages of the inclined screen?: High capacity, lower energy use, and a simpler, cost-effective design.
Horizontal Screen
- what are horizontal screens?: As the name suggests, this screen is installed flat, with little to no angle.
- where are horizontal screens used?: It is used where there is limited headroom, such as inside buildings or on mobile crushing plants. and It is also excellent for dewatering.
- how does the horizontal screen work?: Because there is no gravity assist, so it requires a more aggressive, linear (straight-line) motion to move the material forward. This is created by two or three shafts.
- what are the advantages of the horizontal screen?: Excellent for tight spaces and provides very accurate sizing because material stays on the screen deck longer.
Banana Screen
- what are Banana screens?: A high-capacity screen with a distinctive curved profile, like a banana. It has steep sections at the feed end that become progressively flatter.
- where are Banana screens used?: High-volume operations, especially in coal and mineral processing, where maximum throughput is essential.
- how does the Banana screens work?: The steep angle at the start allows material to travel very fast, quickly removing the fine particles. As the material moves to the flatter sections, it slows down, allowing for more accurate sizing of the near-size particles.
- what are advantages of Banana screens ?: Extremely high capacity for its footprint. It can often replace two smaller conventional screens.
Dewatering Screen
- what are the dewatering screens?: A specialized screen designed to remove water from a slurry of material, typically sand or fine minerals.
- where are dewatering screens used?: Used in sand washing plants, mineral processing, and coal preparation to produce a drip-free, easy-to-handle product.
- how does the dewatering screen work?: It uses a high-frequency linear motion and is installed at a slight uphill angle. And The vibration forces the water to drain through the polyurethane screen panels while the solids are conveyed uphill.
- what are advantages of the dewatering screen?: Produces a final product with very low moisture content (often less than 15%), making it ready for sale or further processing.
High Frequency Screen
- what are high frequency screens?: A screen that vibrates at a very high speed (e.g., 3600 RPM) with a very small amplitude (stroke).
- where are high frequency screens used?: Exclusively used for separating fine materials, typically anything smaller than 5mm. It is common in manufactured sand production and industrial minerals.
- how does the high frequency screen work?: The high-speed vibration breaks the surface tension and prevents fine, damp particles from sticking together and blinding the screen mesh.
- what are advantages of the high frequency screen?: The only effective way to screen fine, difficult materials accurately at a high rate.
Grizzly Screen
- what are grizzly screens?: A very heavy-duty type of scalping screen. It does not use mesh but rather a series of thick, parallel steel bars or “fingers.”
- where are grizzly screens used?: Used at the very beginning of a crushing plant to remove dirt and undersized rock from the feed before it enters the primary crusher.
- how does the grizzly screens work?: Large boulders tumble over the bars, while smaller material falls through the gaps. This protects the crusher from unnecessary wear and increases the overall plant capacity.
- what are advantages of grizzly screens?: Extremely robust and can handle massive impact from large rocks.
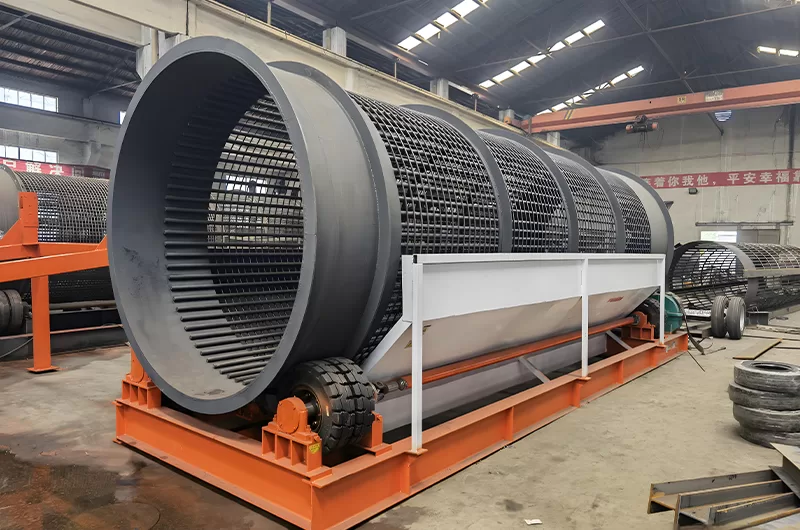
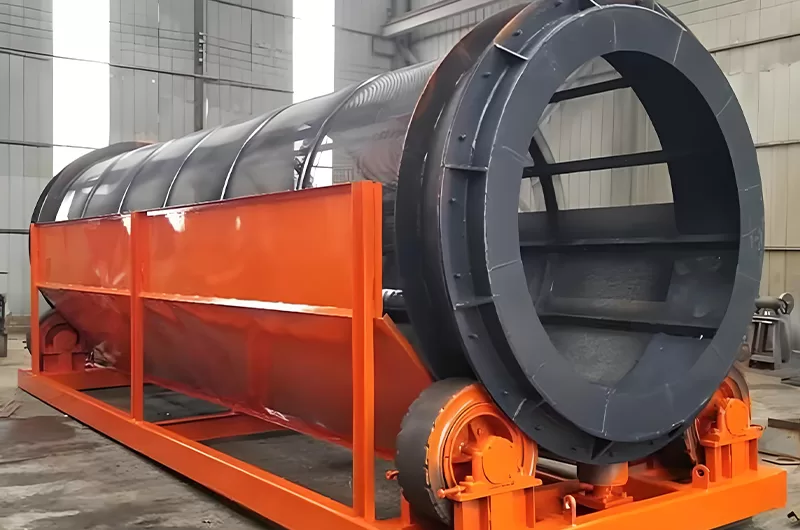
Trommel Screen
- what are trommel screens: Also known as a rotary screen, this machine consists of a large rotating cylindrical drum with screen panels for walls.
- where are trommel screens used?: Excellent for light-duty applications and for materials that are wet, sticky, or contain a lot of organic matter, like topsoil, compost, and municipal waste.
- how does the trommel screen work?: The material is fed into the angled drum. As the drum rotates, the material tumbles. Smaller particles pass through the screen openings, while larger material exits at the end of the drum.
- what are advantages of the trommel screen?: Very effective at preventing blinding with sticky materials.
The surface that does the actual separating is called the screen media. Choosing the right type is a balance between wear life and screening efficiency.
- Woven Wire Mesh: The most common and traditional choice. It offers the best open area, meaning maximum throughput. However, it wears out the fastest, especially with abrasive rock.
- Polyurethane: A durable synthetic material. It lasts much longer than wire mesh and is excellent for wet applications. It is also quieter. The downside is that it has less open area and is more expensive upfront.
- Rubber: The toughest and longest-lasting option. It is used for heavy-impact applications, like on scalping screens. It has the lowest open area and is the most expensive.
- Perforated Plate: A sheet of steel with holes punched in it. It is very strong but has a low open area and is prone to material getting stuck (pegging).
How To Select the Right Vibrating Screen for Your Mining Operation?
Choosing the correct screen can seem complex, but you can narrow it down by answering a few key questions. We walk our clients through this process every day.
- What is your material? Is it hard and abrasive like granite, or soft like limestone? Is it wet and sticky?
- What is your feed size? You should confirm What are the largest and smallest particles being fed to the screen.
- What products do you need to make? How many finished sizes do you need, and what are they (e.g., 10mm, 20mm, 40mm)?
- What is your required capacity? How many tons per hour (TPH) do you need to process?
- What is the moisture content? High moisture can cause blinding and requires a specific screen type or media.
- What are your space limitations? Do you have enough height for an inclined screen, or do you need a horizontal screen?
How Does Ore Type and Particle Size Affect Screen Selection?
The material itself is the biggest factor. For example, if you are scalping large, heavy granite boulders before your primary crusher, you need a heavy-duty grizzly screen with robust rubber or steel bar media. Trying to use a wire mesh screen here would destroy it in minutes. Conversely, if you are trying to separate sand at 2mm, a grizzly screen is useless. You would need a high frequency screen with fine polyurethane or wire mesh to do the job effectively. The hardness of the ore dictates the durability of the machine, while the particle size dictates the type of screen and media required.
What are the Key Factors that Determine Screening Capacity (TPH)?
A screen’s capacity is not just about its size. Several factors work together to determine its throughput in tons per hour (TPH).
- Screen Area: A larger screen (length x width) can obviously handle more material.
- Deck Angle: A steeper angle moves material faster, increasing capacity, but it can reduce accuracy.
- Vibration Characteristics: The stroke and speed of the vibration must be matched to the material to achieve optimal bed depth and travel rate.
- Screen Media Open Area: More open area allows more material to pass through, increasing capacity. This is why wire mesh often has higher throughput than polyurethane.
- Material Properties: Wet, sticky, or flaky material is much harder to screen and will reduce the effective capacity of any screen.
What are the Most Common Maintenance Issues with Vibrating Screens?
Vibrating screens work hard, and they need regular attention to stay reliable. Neglecting maintenance is a common cause of unplanned downtime.
- Screen Media Blinding and Pegging: This is when particles get stuck in the openings, reducing efficiency. It requires regular cleaning.
- Cracked Side Plates: The constant vibration can cause fatigue cracks in the steel structure. Regular visual inspections are crucial.
- Worn or Broken Springs: The support springs can wear out or break, causing the screen to vibrate unevenly and potentially damage itself.
- Bearing Failure: The vibrator mechanism bearings are under incredible stress. Proper and regular lubrication is absolutely essential to prevent failure.
- Loose Bolts: Vibration can cause bolts to loosen over time. All bolts should be checked and torqued regularly.
Why Choose ZONEDING’s Vibrating Screen?
At ZONEDING, we build our vibrating screens to be tough, reliable, and efficient. We understand that a screen failure can bring your entire operation to a halt. We use high-quality steel, robust vibrator mechanisms, and precision engineering to ensure our screens can handle the toughest applications. Because we manufacture a complete line of crushing and screening equipment, we can design an integrated solution where every component, from the jaw crusher to the final screen, works together perfectly. Our factory-direct model means you get this high-quality equipment at a more competitive price.
FAQ
- What is the difference between linear and circular motion screens?
- Circular motion (like on an inclined screen) is great for general-purpose, high-capacity screening. Linear motion (like on a horizontal screen) is more aggressive, better for moving material without gravity’s help, and provides higher screening accuracy.
- How do you prevent screen blinding?
- Blinding happens when wet or fine particles block the screen openings. You can prevent this by using the correct screen type (e.g., high frequency), using self-cleaning screen media like polyurethane with flexible apertures, or adding a water spray system.
- What does “scalping” mean in screening?
- Scalping is the process of removing a small amount of oversized material from the feed. A grizzly screen is a perfect example of a scalping screen; its only job is to remove the giant rocks before they go into the crusher.