Potash is a vital mineral. It supports global agriculture. Understanding potash production involves much more than just digging. It is a journey. This journey starts deep underground. It moves through advanced processes. This article will outline the entire cycle. It will explain where potash comes from. It will explain why it is so important. And It will explain how it is mined and processed. This includes technologies for Potassium Chloride extraction. Readers will see the complex work involved.
Table of Contents
What Exactly is Potash?
Potash is a common term. It refers to various mined and manufactured salts. These salts contain potassium. It is water-soluble. The most common type is Potassium Chloride. This is also as Muriate of Potash, or MOP. Potash is not just one thing. It includes a group of minerals. These minerals contain potassium in a soluble form. It is essential.
It is underground. And It is in evaporite deposits. The deposits formed millions of years ago. Ancient seas evaporated. They left behind mineral salts. These salts contain potassium. Potash is an alkaline-reacting substance. This means it affects the pH. It is a naturally occurring mineral. It is often found with sodium chloride. Sodium chloride is table salt. The chemical symbol for potassium is K. This is why potash is often called “K” in fertilizer circles. Pure potash is a white or colorless solid. It looks like salt. But it has different properties. Its unique properties make it very valuable.
What are Applications of Potash?
Potash plays a crucial role in many areas. Its primary use is in agriculture. It also helps in various industrial processes.
- Agriculture: It is a key ingredient in fertilizers. It helps crops grow strong. It improves crop yield and quality. And It supports global food security.
- Industrial Uses: It helps make soap and glass. It is in ceramics. It is a part of drilling fluids. and It is in water softeners and some fire extinguishers.
Why is Potash So Essential for Global Agriculture?
Potash is one of the three primary plant nutrients. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are these three. Potassium plays a crucial role. It helps plants in many ways. It improves water retention. and it activates enzymes. Enzymes help with growth processes. It helps strengthen plant stems. This makes plants more resistant to lodging. Lodging means plants falling over. It helps plants withstand drought. And It helps plants resist diseases. These benefits greatly increase crop quality. They also increase crop yield.
Potash is vital for healthy plants. It is one of the three primary nutrients for crops.
- Nutrient Support: It provides essential potassium (K) to plants.
- Plant Health: It improves water retention in plants. It activates enzymes for growth.
- Strength and Resistance: It strengthens plant stems. It helps plants resist drought and diseases.
- Yield Increase: It greatly enhances crop quality and overall yield.
- Food Security: It ensures productive harvests. This helps feed the growing global population.
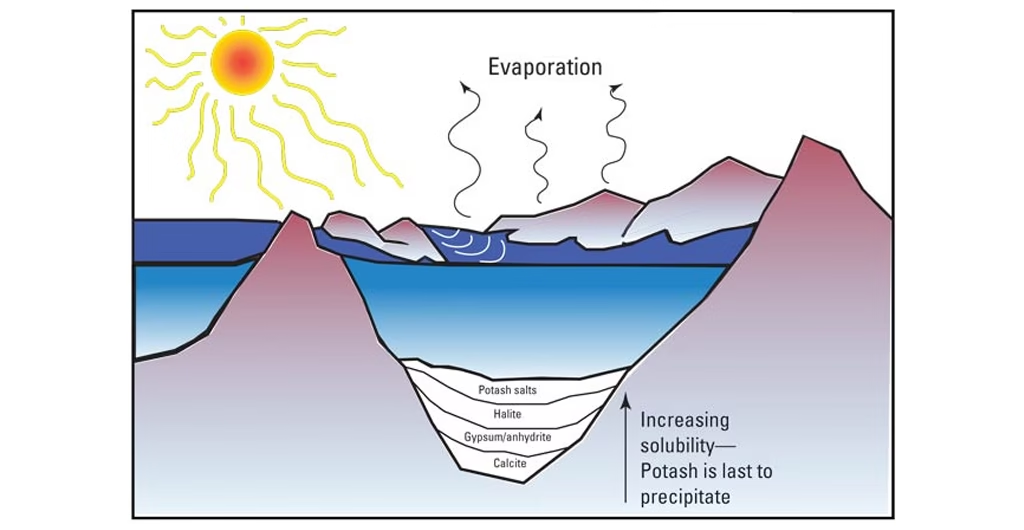
Potash forms over millions of years. It begins with ancient oceans. These oceans covered vast areas. Water entered shallow basins. The sun evaporated the water. This left behind dissolved minerals. These minerals included potassium salts. This process happened many times. It built up thick layers of these salts. These layers are evaporite deposits. Over time, sediments covered these layers. Sediments like mud and sand covered them.
The weight of these sediments compressed the salt layers. It caused them to solidify. Geological forces then changed these deposits. They caused folding and faulting. This created the deep underground beds that are mined today. The purity of the potash deposits varies. It depends on the local geological conditions. These conditions were present during formation. The formation of these deposits makes them unique. It also dictates how to extracted. This natural process creates a resource vital to life on Earth.
Where Do We Find Potash Deposits?
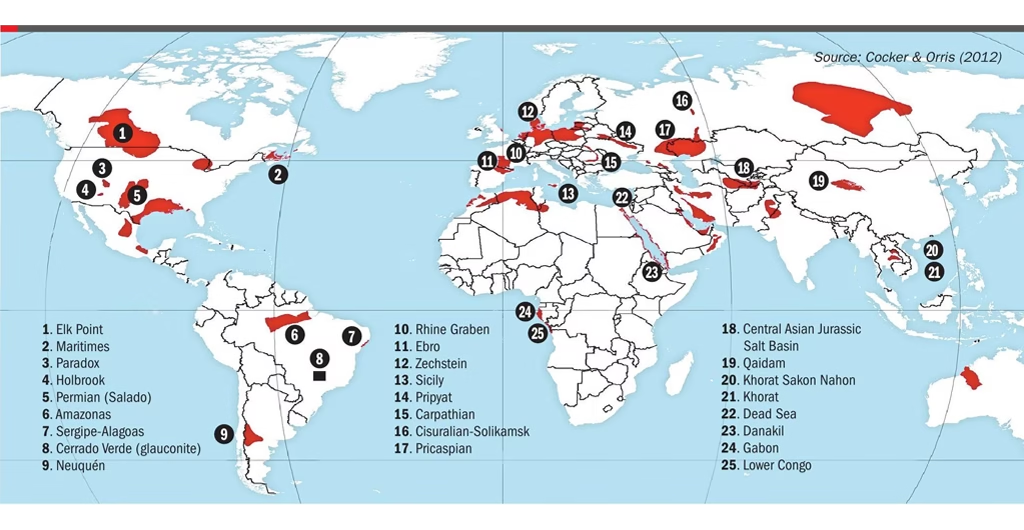
Potash deposits are found globally. But they are not everywhere. They are in specific regions. These regions were once ancient sea beds. Canada is the largest producer. It has vast deposits in Saskatchewan. Russia is another major player. It has large reserves in the Urals region. Belarus also has significant deposits. Its mines are in the Starobin region. Germany has deposits in its central regions. The United States has deposits too. These are in New Mexico and Utah. China and Brazil also have some notable deposits.
These are areas where ancient seas once existed.
- Major Producers: Canada (Saskatchewan), Russia (Urals), Belarus (Starobin), and Germany are key locations.
- Other Deposits: The United States (New Mexico, Utah), China, and Brazil also have reserves.
- Varying Depths: Deposits lie at different depths. This affects mining methods and costs.
- Global Trade Impact: These locations influence potash trade worldwide.
What are the Main Potash Mining Methods, and How Do They Differ in Practice?
There are two primary methods for potash mining. These are conventional Underground Potash Mining and Solution Mining. Each method has unique characteristics. Each suits different types of deposits.
There are two main ways to mine potash. Each method suits different deposit conditions.
- Underground Potash Mining:
- Method: Miners dig tunnels deep underground. Large machines extract solid ore.
- Suitability: Best for shallow, thick, and stable deposits.
- Characteristics: It can be labor-intensive. It requires extensive underground infrastructure.
- Solution Mining:
- Method: Hot water is pumped underground. It dissolves the potash. The dissolved solution is then pumped to the surface.
- Suitability: Good for deeper or less stable deposits.
- Characteristics: It is less labor-intensive underground. It uses more water and energy. It causes less surface disturbance.
The extraction of potash is a multi-step process. It transforms raw ore into a usable product. The process after the ore leaves the mine is as follows:
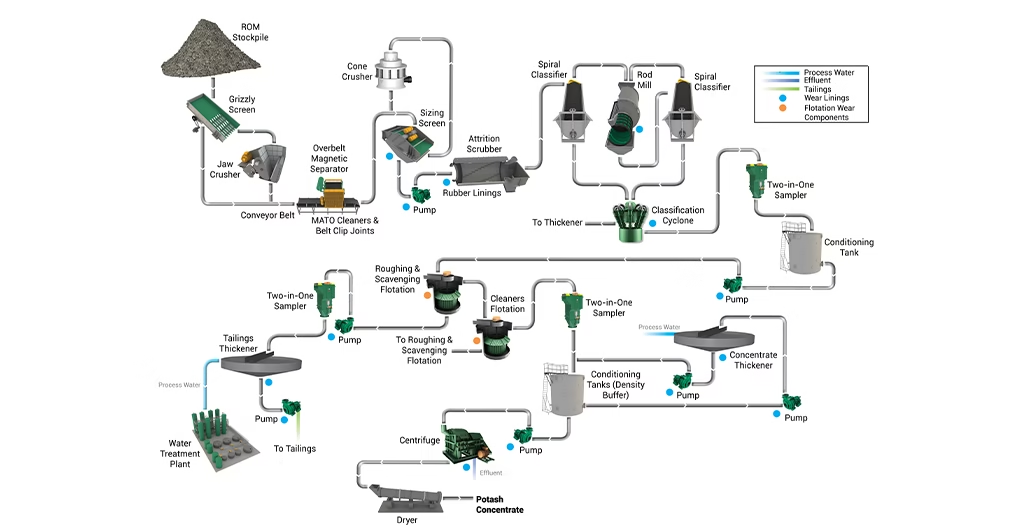
- Crushing and Grinding: First, the raw potash ore is transported. It goes to a processing plant. Here, large crushers break down the ore. They reduce it to smaller pieces. Then, grinders further reduce the particle size. This makes the minerals easier to separate. The goal is to liberate the valuable potash from other minerals.
- Beneficiation (Separation): After crushing, the smaller particles are separated. This step is where Mineral Processing Potash takes place.
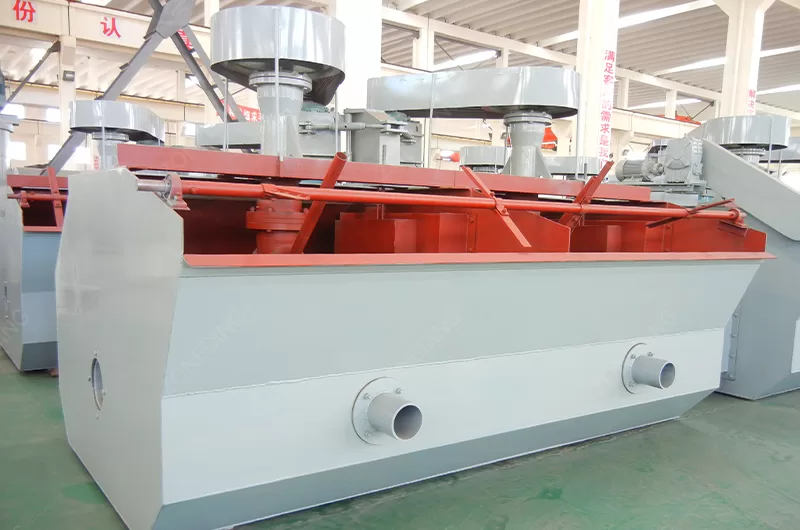
- Flotation Potash: This is a common method. The ore slurry is mixed with water and chemicals. These chemicals make potash particles hydrophobic. Air bubbles are introduced. Potash particles attach to the bubbles. They float to the surface. A froth is formed. This froth, rich in potash, is skimmed off. This separates it from other minerals.
- Heavy Medium Separation: It uses a liquid with a specific density. This liquid is between potash and gangue minerals. Potash floats, and gangue sinks.
- Washing and Leaching: The concentrated potash, often in a brine solution, needs further purification. Unwanted salts, like sodium chloride, are sometimes leached out. This step involves dissolving and re-crystallizing the potash. This process leads to high purity.
- Crystallization Potash: The purified potash solution is then heated. Then, it begins to cool. This controlled cooling makes potash crystals form. This is called Crystallization Potash. These crystals are pure. They are separated from the remaining brine. The size of the crystals can be controlled.
- Drying: The wet potash crystals are moved to large dryers. These dryers remove all moisture. Rotary dryers are commonly used. They tumbling the crystals. They use hot air. This ensures a dry, free-flowing product.
Which Equipment is Needed During this Process?
A full potash extraction plant uses many specialized machines. The equipment changes slightly with the mining method. But some are common.
For mining, especially Underground Potash Mining, the following are essential:
- Continuous Miners: These are huge machines. They cut and load the ore directly from the face.
- Shuttle Cars and Conveyor Systems: These transport the raw ore. They take it from the mining face. They take it to the main shafts. The ore then travels to the surface.
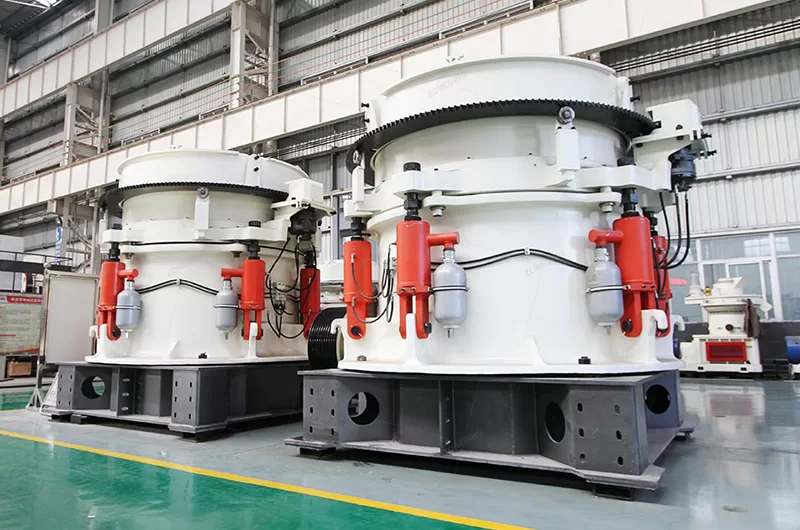
In the processing plant, for crushing and grinding, the following are essential:
- Jaw Crushers: They break large rocks into smaller ones.
- Cone Crushers: They further reduce the ore size.
- Hammer Mills: These are very effective for grinding potash.
- Rod and Ball Mills: These are used for fine grinding, especially before flotation.
For beneficiation, including Flotation Potash:
- Flotation Cells: These are tanks. They have agitators. They create bubbles. Potash sticks to them.
- Thickeners and Filters: These separate solids from liquids. They make sure the potash is concentrated.
- Centrifuges: They dewater the potash concentrate quickly.
For purification and Crystallization Potash:
- Evaporators and Crystallizers: These machines perform the heating and cooling. They form pure potash crystals.
- Classifiers: They sort crystals by size.
For drying and handling:
- Rotary Dryers: They remove moisture from the final product.
- Screening Machines: They sort the dried potash by particle size.
- Conveyors, Stackers, and Reclaimers: These are crucial. They move the product around the plant. They load it for shipping. This complete setup ensures that all materials are handled efficiently. It supports the entire Potash Plant Technology lifecycle.
What Advanced Technologies are Enhancing Efficiency and Sustainability in Potash Production?
Modern potash operations increasingly use advanced technologies. These innovations aim to boost efficiency. They also aim to improve sustainability. Operators see a clear shift towards smarter processes.
- Automation and Robotics: Automated systems now control many tasks. This includes mining machines and conveyor belts. Robots handle repetitive jobs. This reduces human error. It also enhances safety. Remote operation centers monitor entire sites. This improves response times.
- Digitalization and Data Analytics: Sensors collect vast amounts of data. This data covers every stage. From mining depth to dryer temperatures. Advanced software analyzes this information. It helps identify inefficiencies. It predicts maintenance needs. This allows for proactive adjustments. It optimizes throughput.
- Energy Efficiency: New technologies focus on reducing energy use. For example, more efficient motors and pumps are common. Waste heat recovery systems capture energy. They reuse it within the plant. This lowers greenhouse gas emissions. It also cuts operating costs.
- Water Conservation: Potash processing often uses a lot of water. Modern plants aim for closed-loop water systems. This means they recycle and reuse water multiple times. New filtration and desalination technologies also enable using lower quality water or making existing water usable. This minimizes freshwater intake. It reduces wastewater discharge.
- Improved Beneficiation Techniques: Research continues into new separation methods. These methods are more selective. They are more energy-efficient. They maximize potash recovery. And They also reduce waste. This leads to higher yields from the same amount of raw ore. This emphasis on innovation is making potash production smarter. It makes it cleaner and more productive. It ensures a sustainable future for the entire Potash Industry.
What Environmental Considerations and Best Practices are Vital for Modern Potash Operations?
The Potash Industry is aware of its environmental footprint. Modern operations focus heavily on sustainability. There are many important considerations. Compliance with environmental regulations is non-negotiable.
- Waste Management: Potash mining creates significant waste. This waste often consists of salt tailings. These are sodium chloride, or common salt. Proper storage is crucial. Tailings ponds are lined. They prevent salt brine from seeping into groundwater. New methods are exploring ways to reuse these salt by-products. This reduces waste volume.
- Water Usage and Protection: Large amounts of water are used in processing. Companies strive to minimize this. They implement water recycling programs. They treat wastewater. and They release it carefully. This protects local water sources. It avoids contamination.
- Land Reclamation: After mining, the land must be restored. This is especially true for surface mines. Companies commit to reclaiming disturbed land. They return it to its natural state. They replant vegetation. and They restore ecosystems. This ensures long-term ecological balance.
- Air Quality Control: Dust is a concern. It comes from crushing and drying. Modern plants use dust suppression systems. Filters reduce particulate emissions. This improves air quality for workers and nearby communities.
- Energy and Emissions:Reduce energy consumption is important. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Using renewable energy sources is becoming more common. This lowers the overall carbon footprint.
These best practices are vital. They ensure that potash production is responsible. It protects our planet. It secures resources for future generations. This is all part of having a positive Environmental Impact Potash.
How Can ZONEDING’s Robust Material Handling and Industrial Equipment Optimize Potash Facility Logistics?
ZONEDING understands the demands of the potash industry. The company excels at providing robust and efficient equipment. Its equipment is specifically for material handling. It is also for industrial processing. This helps optimize complex logistics within any potash facility.
- Comprehensive Machinery: Provides various crushers, conveyors, stackers, and reclaiming equipment.
- Material Handling: Moves raw ore and finished product efficiently throughout the plant.
- Continuous Flow: Ensures smooth material transport. This avoids bottlenecks in processing.
- High Quality: Equipment uses high-wear-resistant steel. Key components come from top global brands like Siemens and Schneider.
- Durability and Reliability: Built for long life and minimal downtime. This ensures consistent operations.
- Custom Solutions: Designs and provides tailored equipment. This includes full production lines for specific client needs.
- Improved Efficiency: Helps increase throughput. It reduces operating costs and enhances safety.
FAQ
- Q: What is the main difference between Muriate of Potash (MOP) and Sulfate of Potash (SOP)?
- A: MOP (Potassium Chloride) is more common. SOP (Potassium Sulfate) is premium. SOP has lower chloride. It is better for chloride-sensitive crops.
- Q: Is potash mining environmentally friendly?
- A: Modern potash operations work hard to be sustainable. They use best practices. These include waste management and water recycling. This reduces environmental impact.
- Q: Why is potassium important for plants?
- A: Potassium helps plants with water retention. It activates enzymes. It strengthens stems. and It improves disease resistance.
- Q: Can potash be synthesized?
- A: Potash is primarily a mined mineral. It is extracted from natural deposits. It is not generally synthesized in industrial quantities.
- Q: What are tailings in potash mining?
- A: Tailings are the waste materials left after processing. In potash mining, they are mostly sodium chloride (salt).
Summary and Recommendations
This article has detailed how potash is made. It is a critical journey. It starts with deep mining. and It moves through complex processing. Potash production was covered. It was shown how it supports global agriculture. Different mining methods were reviewed. Modern processing was also explored. This includes Flotation Potash and Crystallization Potash. Each step is important.
Effective potash processing uses specialized equipment. It incorporates advanced technologies. These technologies improve efficiency. They promote sustainability. Environmental considerations are vital for every operation. Modern practices focus on waste, water, and land protection. These secure the future of this essential resource. To maximize output and minimize impact, focus on robust equipment. ZONEDING provides solutions for this.
For potash projects, consider these: Carefully choose your mining method. Select the right processing technology. Use efficient equipment. This will optimize operations. Consult ZONEDING for customized equipment solutions. This can help achieve higher efficiency. It can help with sustainable potash production.