全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
Nickel is a vital metal in modern industry. It offers unique properties. These include high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. Demand for nickel grows steadily. It powers electric vehicle batteries. It reinforces stainless steel. Extracting nickel is a complex journey. It starts from raw ore. It moves through mining, refining, and processing. Understanding this entire process is crucial. This guide provides a full overview. It details how nickel reaches the market.
The journey of nickel extraction faces many challenges. Different ore types require specific methods. Advanced technologies ensure efficient recovery. Sustainability is a growing concern in all stages. This includes minimizing environmental impact. ZONEDING equipment plays a key role. It supports operations from mining to purification. The path from earth to finished product is intricate.
Nickel is a silvery-white metal. It appears hard and malleable. It offers excellent corrosion resistance. and It maintains strength at high temperatures. These properties make it highly valuable. It holds a critical place in numerous industries. Its demand continues to surge globally.
This metal forms the backbone of many advanced technologies. It helps to drive innovation. Its unique characteristics are irreplaceable. Understanding its importance highlights why nickel mining and nickel processing are so vital.


Nickel’s versatility leads to diverse applications. Each application benefits from nickel’s specific traits.
Global nickel extraction efforts focus on these key sectors. ZONEDING provides essential equipment. This equipment supports the initial stages. It prepares nickel-bearing ores for these vital applications.
Nickel occurs in two main types of ore deposits. Each type has distinct characteristics. These characteristics influence mining and processing methods.
Understanding ore type is critical. It determines the entire nickel processing flowsheet. This impacts equipment selection. It also influences overall project economics.
Nickel mining is the first step in extraction. It involves removing nickel-bearing ore from the ground. The choice of mining method depends on the ore body. Factors include depth, size, and geological structure. Once mined, the ore undergoes initial preparation. This prepares it for transport and further processing.
This initial stage sets the foundation. Efficient mining delivers ore to the processing plant. It maximizes resource recovery. It also minimizes operational costs. ZONEDING mining equipment supports these critical initial steps.
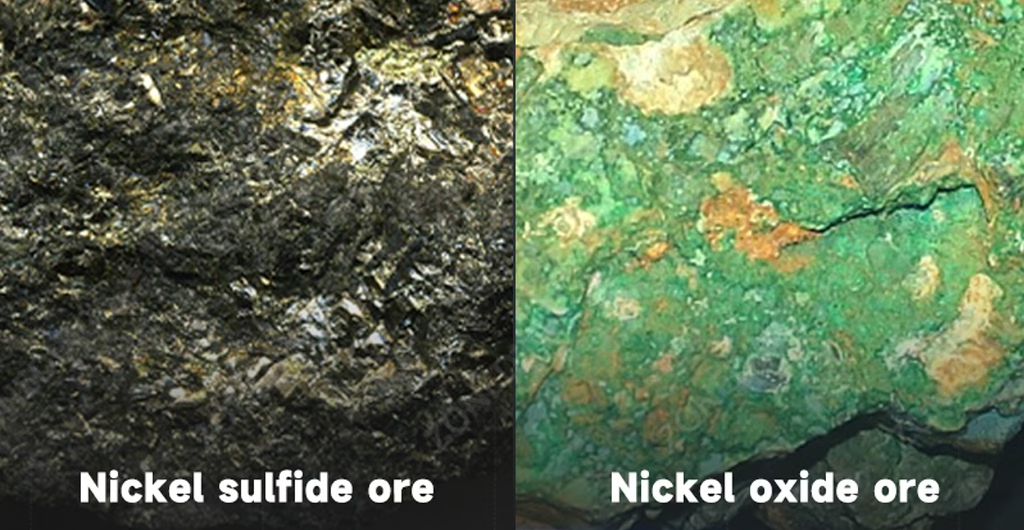
Sulfide nickel deposits often reside deep underground.
Laterite nickel deposits usually occur closer to the surface.
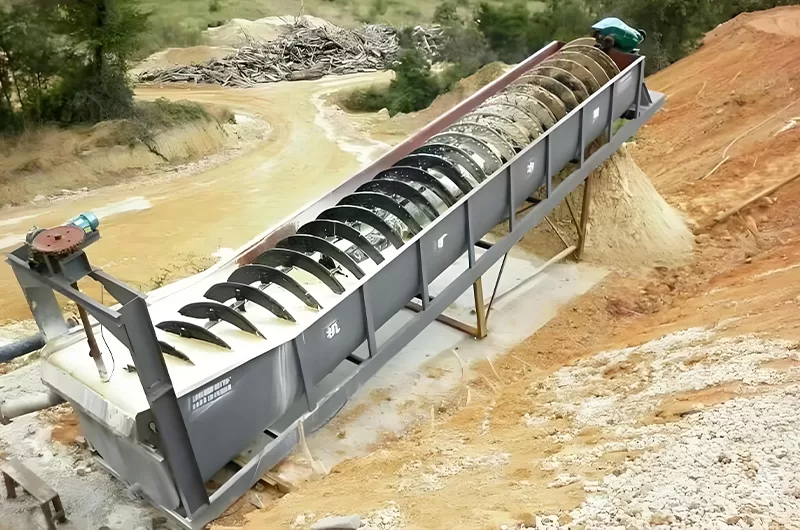
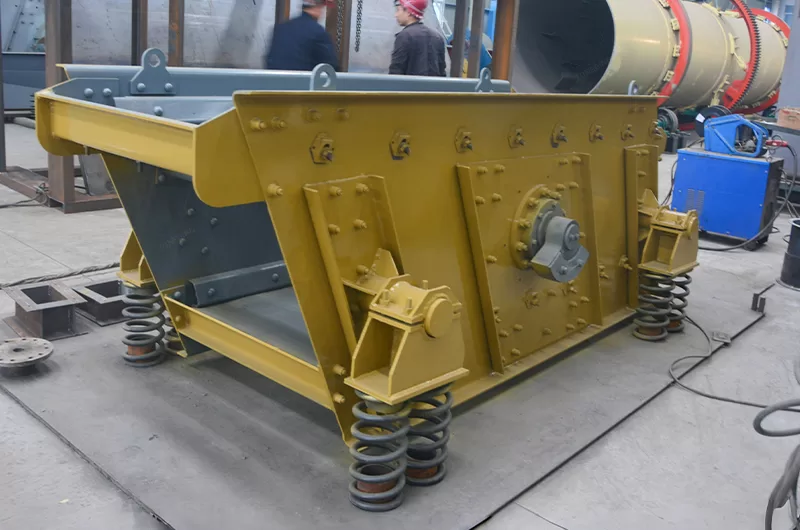
Beneficiation is the stage after mining. Its goal is to increase nickel concentration. It removes unwanted gangue minerals. This reduces the amount of material entering costly refining steps. Different ore types require different beneficiation methods. This stage improves the overall efficiency of nickel processing.
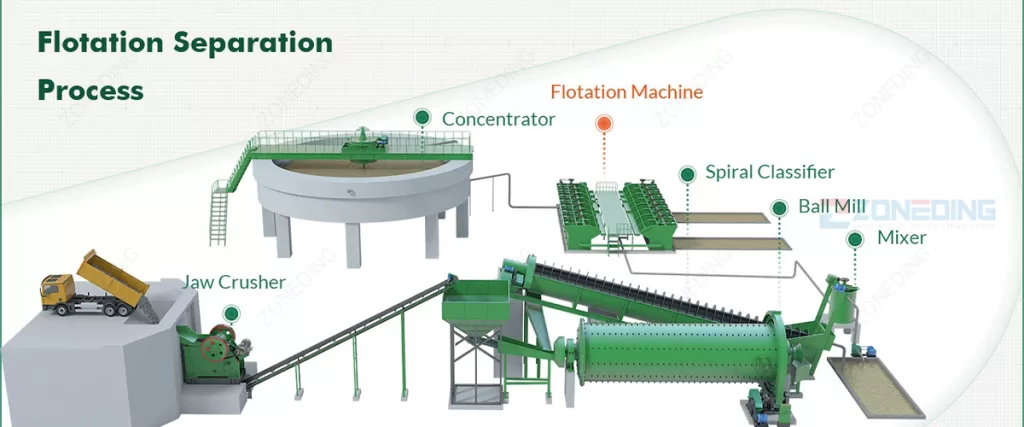
Effective beneficiation significantly lowers refining costs. It maximizes metal recovery. It also minimizes waste. ZONEDING provides key equipment for these critical preparation processes.
Sulfide ores require fine comminution. This liberates valuable nickel minerals.
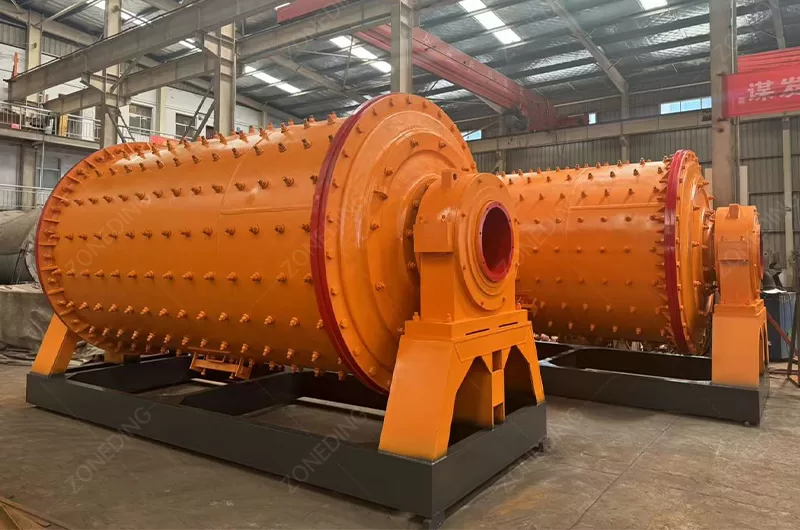

Flotation is the primary method for sulfide ores. It selectively separates nickel minerals.
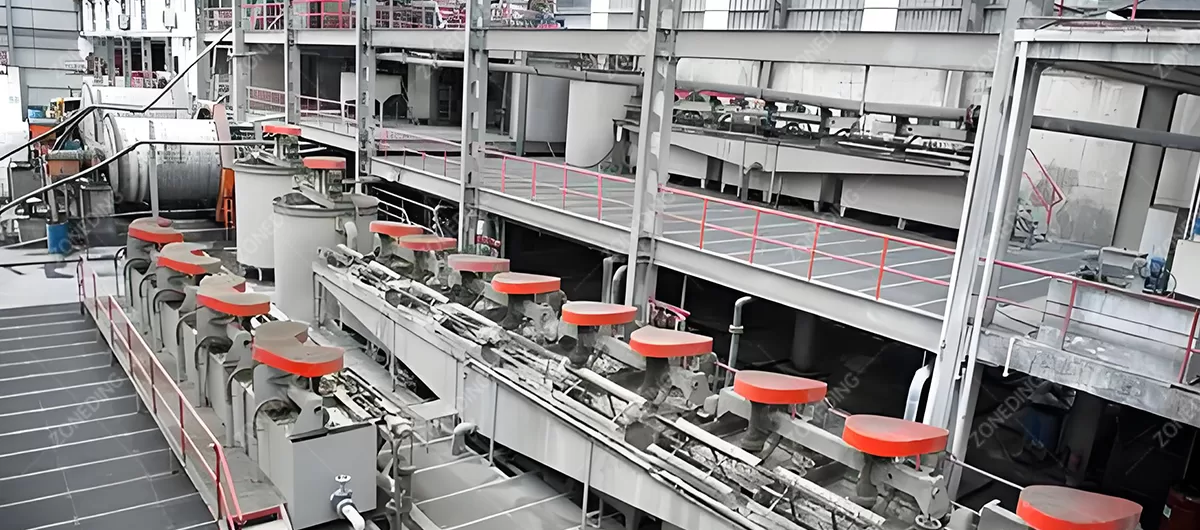

Laterite ores are often low grade. Their beneficiation focuses on removing waste.


Pyrometallurgy uses high temperatures. It extracts metals from their ores. This method is mainly for nickel sulfide concentrates. It purifies nickel. It removes impurities like iron and sulfur. The process involves several stages. Each stage uses intense heat. This method is energy-intensive. It creates a nickel product for further refining.
Pyrometallurgical refining has a long history. It remains a key method for sulfide ores. It produces a semi-refined nickel material. This material then undergoes further purification.

The nickel sulfide concentrate first undergoes roasting.
The molten matte then enters converters.
Hydrometallurgy uses aqueous solutions. It extracts and purifies metals. This method is mainly used for laterite nickel ores. These ores are often low-grade. They are not suitable for pyrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy focuses on dissolving nickel. It then recovers it from the solution. This method is often more environmentally friendly. It has lower energy consumption than pyrometallurgy.
Hydrometallurgical refining has gained traction. It unlocks the vast laterite resources. It produces high-purity nickel products directly.

Leaching is the core of hydrometallurgy. It dissolves nickel from the laterite ore.
After leaching, nickel is recovered from the solution.
Nickel extraction has a significant environmental footprint. Mining, processing, and refining consume resources. They also generate waste. Environmental factors must be carefully managed. Regulations are becoming stricter globally. Sustainable practices are essential. This reduces the impact on ecosystems and communities.
Addressing environmental concerns improves public perception. It ensures long-term viability of nickel mining operations. Companies invest in new technologies. These technologies make extraction cleaner.
Both pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical processes generate waste.
Air emissions are a concern. Smelting releases sulfur dioxide (SO₂). This gas contributes to acid rain. Modern plants capture SO₂. They convert it to sulfuric acid. This significantly reduces emissions. Water usage is also considerable. Mining and processing require much water. Recirculation and water treatment are essential. They minimize fresh water consumption. They prevent water pollution. ZONEDING’s washing and dewatering equipment supports these efforts.
Mining operations disturb land. They change landscapes. Mine closure plans include ecological restoration. This involves revegetation. It restores pre-mining biodiversity. This ensures a responsible end to mining activities. Sustainable practices are integrated throughout. They aim to minimize impacts from exploration to closure.
ZONEDING provides essential equipment. This equipment supports every stage of nickel extraction. From initial mining to advanced beneficiation, our machines perform reliably. We offer comprehensive solutions. These solutions help clients maximize nickel recovery. They also optimize processing efficiency. ZONEDING’s expertise ensures cost-effective and sustainable operations.
Our commitment to quality helps clients succeed. We create customized solutions. These solutions meet specific project requirements. We improve overall nickel processing performance.
Nickel ore often requires extensive comminution. ZONEDING’s crushers and mills prepare the ore perfectly.
ZONEDING offers state-of-the-art beneficiation machines. These machines concentrate nickel minerals.
Effective waste management is vital. ZONEDING’s dewatering solutions help.
ZONEDING provides more than just machines. We offer comprehensive support. Our engineers design tailored solutions. They analyze specific ore characteristics. They consider client requirements. We provide installation guidance and after-sales service. This ensures smooth operation. Our commitment is to long-term success. We help clients achieve efficient nickel processing.
A jaw crusher is a primary stone crusher in mining&aggregate. Learn its types, parts, work principle, maintenance, how to choose. ZONEDING provides good choice!
View detailsA step-by-step guide covers everything from crushing and grinding to advanced magnetic separation and dewatering, ensuring efficient magnetite processing.
View detailsLearn essential machines and solutions for talc beneficiation. Know about crushers, mills, flotation cells & dryers that form an efficient talc processing plant.
View detailsIdeally, the slurry agitator tank is key equipment ensuring full reaction between chemicals and ore. Learn how it prevents sedimentation and boosts recovery.
View details