Mineral Processing Explained: An Easy Guide for Beginners
This guide explains Mineral Processing. It covers how valuable materials are obtained from the Earth. If ever wondered where the metal in a car originates, this guide provides the answer. It aims to make Ore Processing easy to understand. Readers will learn the basics of Mineral Extraction. This guide is for beginners.
Table of Contents
What Exactly is Mineral Processing?
Mineral processing is the first big step after digging up ore from the Earth. It is simply defined as separating the valuable parts from the waste material. For example, when mining for gold, pure gold nuggets are not typically found everywhere. Instead, rock may contain a small amount of gold. Mineral processing takes that rock and extracts the gold. This is a physical process. It primarily uses mechanical methods to achieve separation.
- Initial Step: It follows the extraction of ore from the mine.
- Separation Focus: The core activity is separating valuable minerals from gangue (waste rock).
- Physical Process: It primarily involves mechanical and physical methods, not chemical transformations of the mineral itself.
- Concentration: The goal is to produce a concentrated product, making further refinement economical.
- Preparation: It prepares minerals for subsequent metallurgical or industrial applications.
Why Does Mineral Processing Matter To Us?
Mineral processing is important because it provides the base materials for nearly everything used today. It directly impacts daily lives. Consider a smartphone. It contains copper wires, gold circuits, and many other minerals. All these components began as raw ore. All went through some form of mineral processing. This industry acts as a silent backbone. It supports countless jobs. It also contributes to economic growth worldwide.
- Electronics: Smartphones, computers, televisions use copper, gold, rare earth elements.
- Construction: Buildings, roads, bridges require iron (for steel), cement (from limestone), sand, and gravel.
- Transportation: Cars, planes, trains depend on aluminum, iron (for steel), and other alloys.
- Energy: Power generation and transmission often use copper for wiring and various minerals for fuel or components.
- Healthcare: Medical devices and instruments incorporate specialized metals and materials.
- Consumer Goods: Appliances, packaging, and tools all utilize various processed minerals.
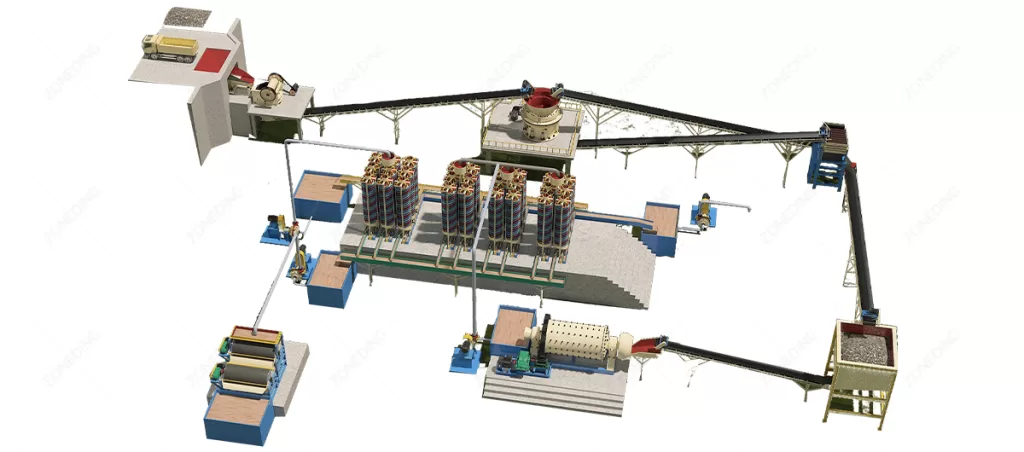
What Are Main Stages of Mineral Processing?
Mineral processing typically occurs in several main steps. These stages ensure maximum value extraction from the ore. They generally include comminution, beneficiation, and sometimes dewatering. Each step has a specific function. They work together. These steps prepare the material for the subsequent stage. This ensures effective mineral recovery.
- Comminution (Size Reduction):
- Crushing: Reduces large ore pieces into smaller, manageable sizes using machinery like jaw and cone crushers.
- Grinding: Further reduces crushed ore into a fine powder or slurry, often using ball or rod mills, to liberate individual mineral particles.
- Beneficiation (Concentration/Separation):
- Physical Separation: Uses mineral properties (e.g., density, magnetism) to separate valuable minerals from waste.
- Chemical Separation: May involve processes like flotation, which uses reagents and air bubbles to separate minerals.
- Dewatering:
- Removes excess water from the concentrated mineral product. This typically involves thickening, filtration, and drying.
How Does Mineral Processing Work?
Mineral processing functions by exploiting the physical and chemical differences between valuable minerals and unwanted rock. The minerals themselves are not changed. They are simply separated from the waste. This is a very specific branch of science. It utilizes properties such as density. It also relies on magnetic attraction. And it depends on how surfaces react (surface chemistry).
- Density Differences: Heavier mineral particles can be separated from lighter waste material using gravity.
- Magnetic Properties: Magnetic minerals are attracted by strong magnetic fields, allowing their separation from non-magnetic materials.
- Surface Chemistry (Hydrophobicity/Hydrophilicity): Some minerals naturally repel water (hydrophobic) while others attract it (hydrophilic), a principle crucial for froth flotation.
- Electrical Conductivity/Charge: Differences in how minerals conduct electricity or acquire static charge can be used for separation.
- Particle Shape and Size: Screening and classification processes utilize these differences to sort materials.
What Are Different Separation Methods of Mineral Processing?
Many methods are used to separate minerals. These methods include gravity separation, magnetic separation, and froth flotation. Each method targets a specific characteristic of the mineral. The best method is chosen. This choice depends on the ore type. It also depends on the minerals to be recovered. This ensures the most efficient separation for operations.
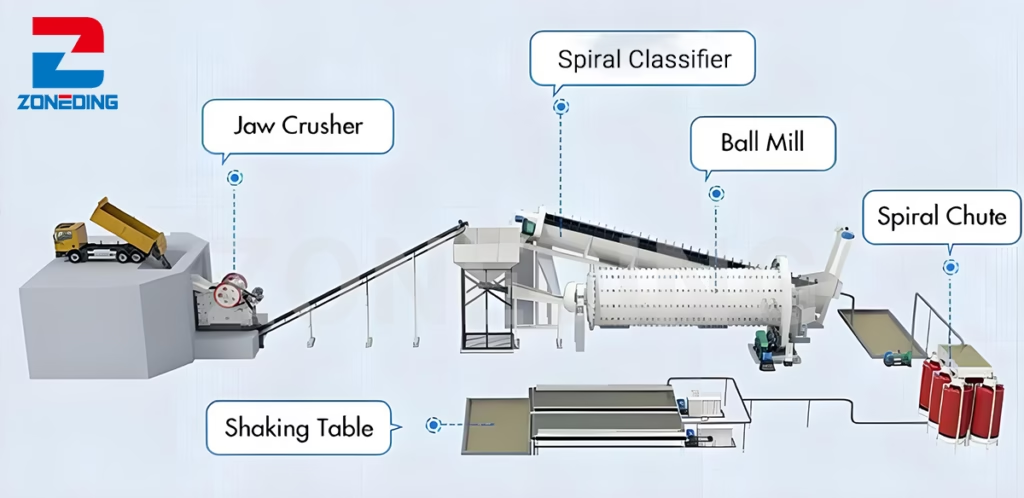
Gravity Separation:
- Principle: Separates minerals based on differences in density in a fluid medium (water or air).
- Equipment: Jigs, spirals, shaking tables, dense medium separators.
- Applications: Effective for heavy minerals like gold, tin, iron ore, and some industrial sands.
- Benefits: Simpler technology, lower operating cost, often environmentally friendly.
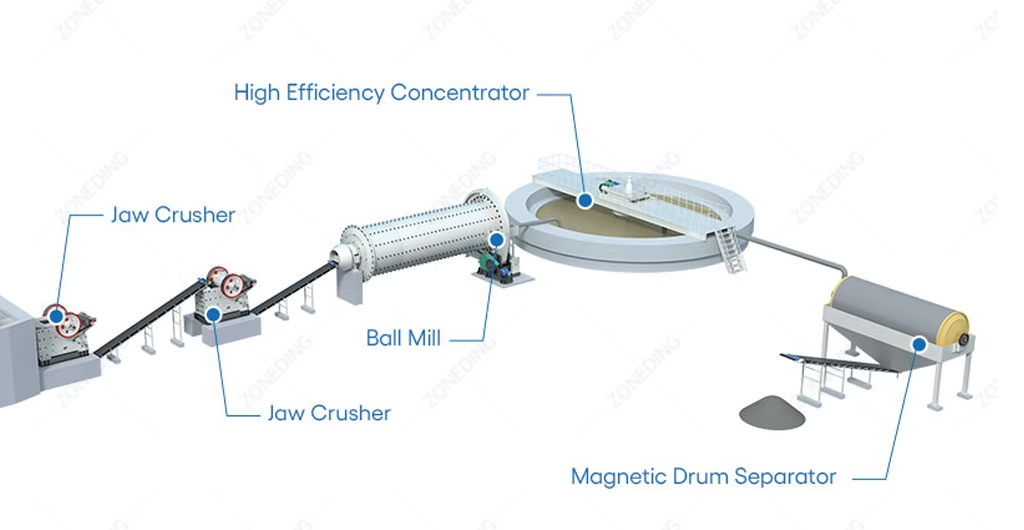
Magnetic Separation:
- Principle: Separates minerals based on their magnetic susceptibility.
- Equipment: Magnetic separators (dry or wet), drum separators, high-intensity magnetic separators.
- Applications: Primarily used for iron ores (magnetite, hematite), tantalite, and some manganese ores.
- Benefits: Efficient for magnetic minerals, can achieve high purity.
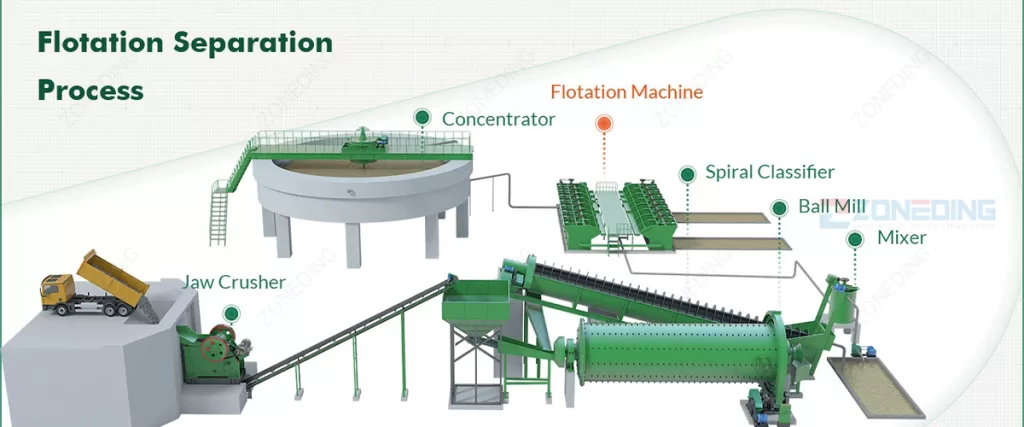
Froth Flotation:
- Principle: Uses differences in surface properties (hydrophobicity) of minerals to attach them to air bubbles, which then float to the surface.
- Equipment: Flotation cells (mechanical or pneumatic), flotation columns.
- Applications: Widely used for sulfides (copper, lead, zinc), phosphates, and some industrial minerals.
- Benefits: Can effectively separate very fine particles and complex ores, producing high-grade concentrates.
Electrostatic Separation:
- Principle: Separates minerals based on differences in electrical conductivity or surface charge when exposed to an electric field.
- Equipment: Electrostatic plate separators, roll separators.
- Applications: Common for beach sands minerals like zircon and rutile, sometimes coal cleaning.
- Benefits: Dry process, good for fine particles, effective for conducting vs. non-conducting materials.
What Are Main Equipment in A Mineral Processing Plant?
Many types of machines operate together in a mineral processing plant. Key machines include crushers, grinding mills, screens, conveyors, and various separators. Each piece plays a critical role. They ensure the ore moves smoothly through all stages. This creates a continuous and efficient process for clients.
- Crushers:
- Purpose: Reduce large ore pieces to smaller sizes suitable for grinding.
- Types: Jaw crushers (for primary breaking), cone crushers (for secondary/tertiary crushing), impact crushers.
- Grinding Mills:
- Purpose: Further reduce crushed ore into a fine powder or slurry to liberate mineral particles. Types: Ball mills (use steel balls), rod mills (use steel rods).
- Screens:
- Purpose: Sort material by particle size, ensuring only appropriately sized material proceeds to the next stage.
- Types: Vibrating screens, grizzly screens, trommel screens.
- Importance: Prevents oversized material from clogging downstream equipment and allows efficient processing.
- Conveyors:
- Purpose: Transport material efficiently between different stages and equipment within the plant.
- Function: Act as the arteries of the plant, ensuring continuous material flow.
- Separation Equipment:
- Purpose: Perform the actual concentration of valuable minerals (e.g., jigs, spirals, froth flotation cells, magnetic separators).
- Diversity: Equipment varies based on the chosen separation method, targeting specific mineral properties.
- Dewatering Equipment:
- Purpose: Remove excess water from mineral concentrates and tailings for handling or disposal.
- Types: Thickeners (for solid-liquid separation), filters (for removing finer water), dryers.
ZONEDING possesses over 30 years of experience. It is a mining machinery manufacturer. It specializes in comprehensive solutions. This includes everything. From initial planning to equipment supply for full mineral processing plant design. The company focuses on building reliable equipment. It is equipment designed for long-term service.
FAQ
- Q1: Is mineral processing only for valuable metals?
- No, that is not entirely correct. Mineral processing helps extract all kinds of useful minerals. This includes industrial minerals like limestone and sand, not just precious metals. It also handles materials for concrete and road construction.
- Q2: Is mineral processing bad for the environment?
- Modern mineral processing strives to minimize environmental impact. Companies adhere to strict environmental regulations. They utilize cleaner technologies. They also employ methods to reuse water and manage waste carefully. ZONEDING focuses on designing efficient systems that reduce resource consumption.
- Q3: How is the right separation method chosen?
- Methods are selected based on the specific qualities of the minerals and the ore. Density, magnetic properties, and how they react to water are considered. The size of the particles is also a factor. Often, a combination of methods is used for optimal recovery.
- Q4: Can ZONEDING assist with setting up a new mineral processing plant?
- Yes, ZONEDING has over 30 years of experience. The company provides full-service support. This includes design, manufacturing, installation, and training. It helps clients set up an entire plant, guiding them from conception to completion. Its engineers offer expert consultation for comprehensive solutions.
ZONEDING’s Competitive Advantages
- Extensive Experience: Over 30 years in mining machinery manufacturing since 1990.
- Comprehensive Product Line: Offers both individual machines and complete plant solutions for mineral processing plant design and brick production.
- Customization Capabilities: Designs equipment and production lines based on specific client needs, raw materials, and output requirements.
- Quality and Durability: Utilizes high-wear-resistant steel and incorporates world-renowned brands for components (e.g., Siemens PLC, Schneider inverters).
- Factory Direct Sales: Provides competitive pricing by eliminating intermediaries.
- Global Reach: Products exported to over 120 countries, with a deep understanding of international market needs.
- Full-Service Support: Offers end-to-end services, including design, manufacturing, installation, commissioning, training, and after-sales maintenance.
- Advanced Manufacturing: Equipped with CNC machine tools, large cutting machines, welding equipment, and lifting equipment in an 8000 sqm facility.
Summary and Recommendations
This guide explained that mineral processing is a crucial first step. It transforms raw ore into usable materials. It covered how this occurs through stages such as crushing, grinding, and various separation methods. These steps prepare minerals for use in daily life. This process is complex. It relies on specific equipment and expert planning. ZONEDING is a significant entity in this field, offering substantial expertise and solutions.
- Mineral processing is essential for converting raw ore into valuable, usable resources.
- The process involves systematic stages: size reduction (comminution), separation (beneficiation), and dewatering.
- Various separation methods (gravity, magnetic, flotation, electrostatic) are chosen based on mineral properties.
- Specialized equipment, from crushers to conveyors, ensures efficient plant operation.
- ZONEDING provides comprehensive solutions and durable machinery for the entire mineral processing workflow.