You interact with copper every single day, often without realizing it. It is in the electrical wiring in your walls, the plumbing pipes that bring you water, and the smartphone in your pocket. My company, ZONEDING, has built the heavy machinery for copper mining and processing since 1990. We have a deep understanding of this essential metal. So, why is copper important? The answer lies in its unique set of properties that make it one of the most versatile and valuable materials for civilization. This guide explores the core uses of copper, its amazing properties, and how we get it from the ground into your home.
Table of Contents
What is Copper?
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with a distinct reddish-orange color. It is one of the very few metals that is in nature in a directly usable metallic form, which is why it was the first metal that humans used over 10,000 years ago. Its discovery marked the end of the Stone Age and the beginning of a new era of technology. Today, it stands alongside iron and aluminum as one of the most important industrial metals in the world, forming the backbone of our electrical infrastructure.
Where Can We Find It?
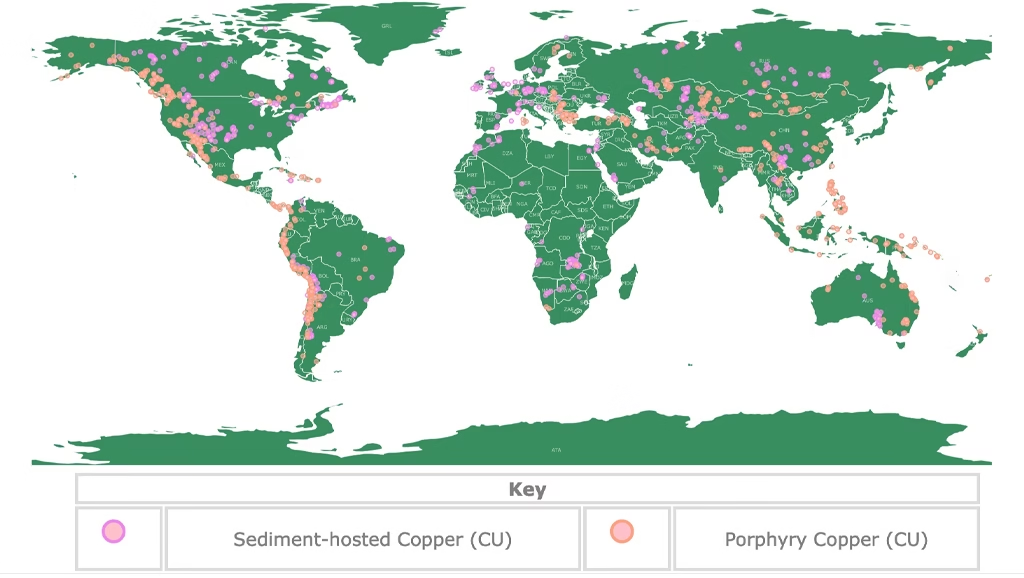
Copper is found in the Earth’s crust all over the world, but it is not distributed evenly. Most copper is from large open-pit or underground mines as copper ore. These are rocks that contain copper-bearing minerals. The largest and most productive copper mines are located in countries along the Pacific Ring of Fire, with Chile and Peru being the world’s top two producers by a large margin. Other major copper-producing nations include China, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the United States. Finding and developing a profitable copper mine is a massive undertaking, requiring billions of dollars in investment and highly specialized equipment to be successful.
What is the Properties of Copper?
Copper is not just one thing; its value comes from a combination of several amazing physical and chemical traits. Many materials have one of these properties, but very few have them all.
- Exceptional Conductivity: This is the most famous of all copper properties. It is a fantastic conductor of both electricity and heat. Its high copper conductivity means energy can pass through it with very little loss, making it incredibly efficient for electrical wiring and heat exchangers.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper does not rust like iron. When exposed to air and moisture, it forms a tough, green outer layer called a patina. This patina actually protects the metal underneath from further corrosion, allowing copper pipes and roofs to last for hundreds of years.
- Malleability and Ductility: These terms mean that copper is very easy to shape. It can be hammered into thin sheets (malleability) or pulled into extremely thin wires (ductility) without breaking. This makes it perfect for manufacturing everything from tiny electronic circuits to large architectural panels.
- Antimicrobial Properties: Copper naturally kills germs. The antimicrobial properties of copper mean that bacteria, viruses, and fungi cannot survive for long on its surface. This makes it a valuable material for high-touch surfaces in hospitals and public spaces.
What is the Benefits of Using Copper?
The unique properties of copper translate directly into real-world benefits that improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
- Energy Efficiency: Because it’s such a good conductor, using copper in wiring and motors reduces energy waste. This saves money on electricity bills and lowers the carbon footprint of electrical systems.
- Durability and Low Maintenance: When you install copper pipes or roofing, you can be confident they will last a lifetime. Its corrosion resistance means fewer repairs and replacements, saving resources and money over the long term.
- Sustainability: Is copper a sustainable material? Absolutely. Copper is 100% recyclable and can be recycled over and over again without any loss of its chemical or physical properties. Nearly a third of all copper used today comes from recycled sources.
- Improved Public Health: Using copper for doorknobs, handrails, and hospital bed rails can help reduce the spread of infections, creating a safer environment for everyone.
What are the Main Uses of Copper Applications?
Because of its broad range of benefits, copper applies everywhere. If you look at a breakdown of what is copper application, you can see its importance in every major sector of the economy. These copper applications are the driving force behind global production.
- Building Construction: This is the biggest user of copper, accounting for over 40% of demand. It applied for electrical wiring, plumbing systems, and roofing.
- Electronics & Electrical Equipment: Copper is essential for power generation, transmission, and all kinds of electronic devices. It is in the motors, transformers, and circuit boards that power our world.
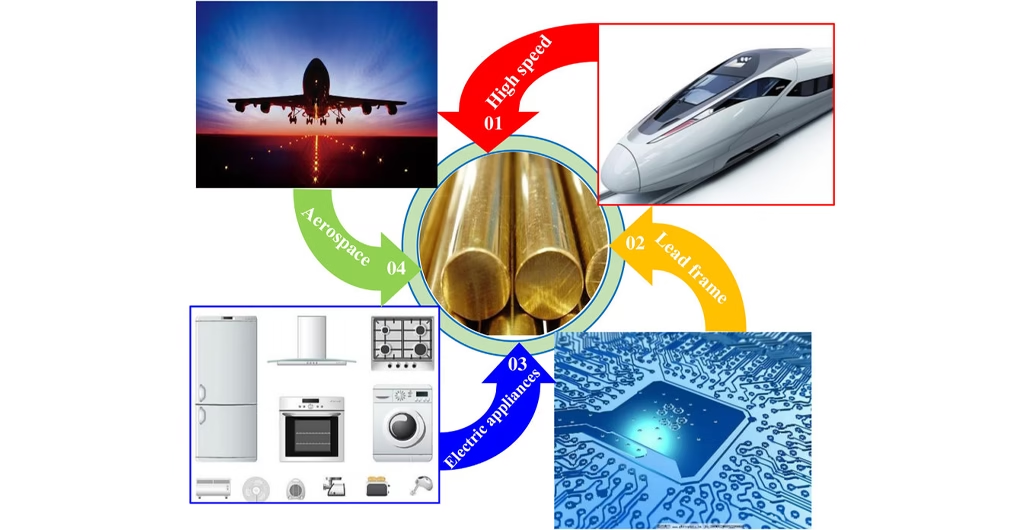
- Transportation: A typical gasoline-powered car contains about 50 lbs of copper. But the real growth is in electric vehicles. The large battery packs and powerful electric motors mean that the amount of copper in electric vehicles can be up to four times higher.
- Industrial Machinery: Copper applies in heat exchangers, industrial motors, and welding equipment due to its excellent thermal conductivity and durability.
How Can We Get Copper from Ore?
Getting pure copper metal from a rock is a complex, multi-step process. As a manufacturer of the necessary machinery, we at ZONEDING are experts in this field. The basic process involves three main stages:
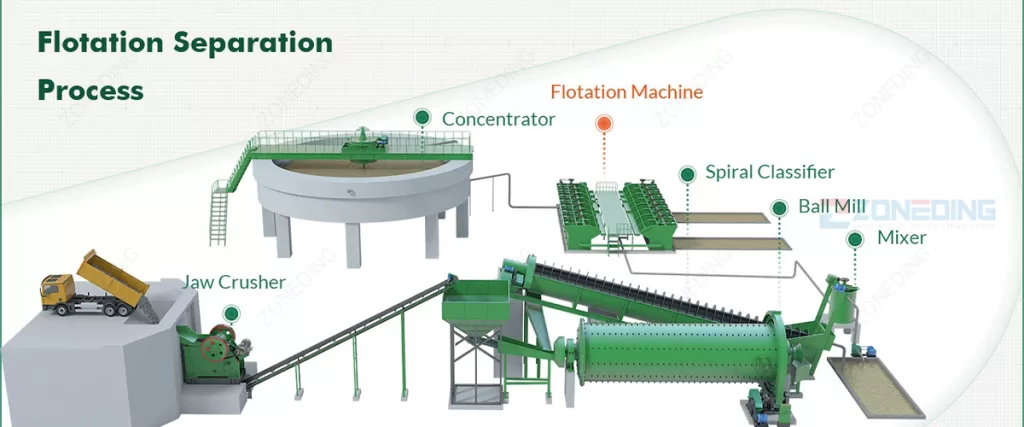
- Mining and Comminution: First, the copper ore is from the mine. This ore, which may contain less than 1% copper, is then crushed into smaller rocks by jaw crushers and the large grinding mills will grind it into powders.
- Concentration: Next, the valuable copper minerals are separated from the waste rock. The most common method is froth flotation, where the powdered ore is mixed with water and reagents in flotation cells. The copper minerals attach to air bubbles and float to the top, forming a “concentrate” that can be over 30% copper.
- Extraction (Smelting and Refining): The copper concentrate is then heated to very high temperatures in a smelter to remove impurities like sulfur. The final step is electrolytic refining, which uses an electrical current to produce copper cathodes that are 99.99% pure.
What are the Main Types of Copper Ore You Can Process?
Copper rarely exists alone; it often come with other elements. The two main categories of copper ore each require a different processing approach:
- Sulfide Ores: This is the most common type, accounting for over 70% of the world’s copper resources. In these ores, copper is with sulfur. The main minerals are chalcopyrite, bornite, and chalcocite. Sulfide ores are almost always processed using the grinding and flotation method described above.
- Oxide Ores: In these ores, copper has bonded with oxygen. They are typically closer to the Earth’s surface. The main minerals are malachite, azurite, and chrysocolla. Oxide ores cannot use flotation method. Instead, they are treated with a chemical process called heap leaching, where a weak acid solution is used to dissolve the copper.
What are the Key Equipment for Copper Processing?
A successful copper processing plant is a carefully complexe system of massive and powerful machines.
- Jaw Crushers & Cone Crushers: These are the primary and secondary workhorses that do the initial job of breaking large ore rocks down to a manageable size.
- Ball Mills: These large rotating cylinders are full of steel balls. They take the crushed rock and grind it into a fine powder, which is necessary to liberate the tiny copper mineral particles from the waste rock.
- Flotation Machines: These are the heart of a sulfide ore processing plant. They create the environment of water, air, and chemicals needed to separate the valuable copper minerals.
- Thickeners and Filters: After flotation, these machines are used to remove water from the copper concentrate before it is sent to the smelter.
What are the Problems When We Using Copper?
While copper is an amazing material, it is not without its challenges.
- Cost and Price Volatility: Copper is a global commodity, and its price can swing dramatically based on supply, demand, and economic conditions. This price volatility can be challenging for manufacturers.
- Weight: Copper is a dense, heavy metal. In some applications, like aerospace and automotive, lighter alternatives like aluminum are sometimes preferred, even though they are less conductive.
- Environmental Impact of Mining: Extracting copper requires large mines and significant amounts of energy and water. Modern mining companies and equipment manufacturers like ZONEDING pay attention to developing more sustainable and efficient technologies to minimize this impact.
Why is Global Demand for Copper Expected to Skyrocket?
The future looks very bright for copper. The copper demand forecast shows a massive increase in the coming years, driven by three major global trends:
- The Green Energy Transition: Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are far more copper-intensive than traditional power plants. A single wind turbine can contain over a ton of copper.
- Electrification of Transportation: The global shift to electric vehicles is a huge driver of copper demand. EVs use much more copper in their batteries, motors, and charging infrastructure.
- Global Electrification and Data: As more of the world gains access to electricity and the internet, the demand for copper wiring, data centers, and communication cables will continue to grow.
FAQ
- Can you get copper poisoning from pipes?
- It is extremely rare. Copper is an essential nutrient for the human body in small amounts. While very high levels of copper in drinking water can cause health issues, modern plumbing codes and water treatment standards are to keep copper levels well within safe limits.
- Is copper better than gold for wiring?
- Electrically, silver is the best conductor, followed by copper, and then gold. While gold is an excellent conductor and does not corrode, it is far too expensive for general wiring. Copper provides the best balance of high conductivity, corrosion resistance, and affordable cost.
- What is the difference between copper and brass?
- Copper is a pure element. Brass is an alloy, which means it is a mixture of metals. Brass is by combining copper with zinc. Adding zinc makes the metal harder and gives it a more yellowish, gold-like color.
Conclusion and Final Advice
So, why is copper so important? It is the engine of our electrical world and a key building block for a sustainable future. Its unique combination of conductivity, durability, and recyclability makes it an irreplaceable material for the global transition to green energy and electric transportation. Copper is important in mordern life, and our modern way of life depends on it.
For anyone involved in the resource sector, understanding the entire copper value chain is critical. The massive expected increase in demand represents a significant opportunity, but it can only be met with efficient, reliable, and technologically advanced mining and processing solutions.